Solar battery systems are revolutionizing residential power solutions, offering a sustainable and efficient way to harness and store solar energy. As the world moves towards cleaner and more renewable energy sources, these systems are becoming an integral part of modern homes. This article explores the role of solar battery systems in enhancing energy independence, improving grid resilience, and contributing to environmental sustainability.
Understanding Solar Battery Systems
Solar battery systems are designed to store excess energy generated by solar panels during the day for use during the night or cloudy days. These systems consist of several key components:
- Solar Panels: Capture sunlight and convert it into electricity.
- Inverter: Converts the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity used by household appliances.
- Battery Storage: Stores excess electricity generated during the day.
- Charge Controller: Regulates the power going into and coming out of the battery.
- Monitoring System: Tracks energy production and consumption, providing real-time data to homeowners.
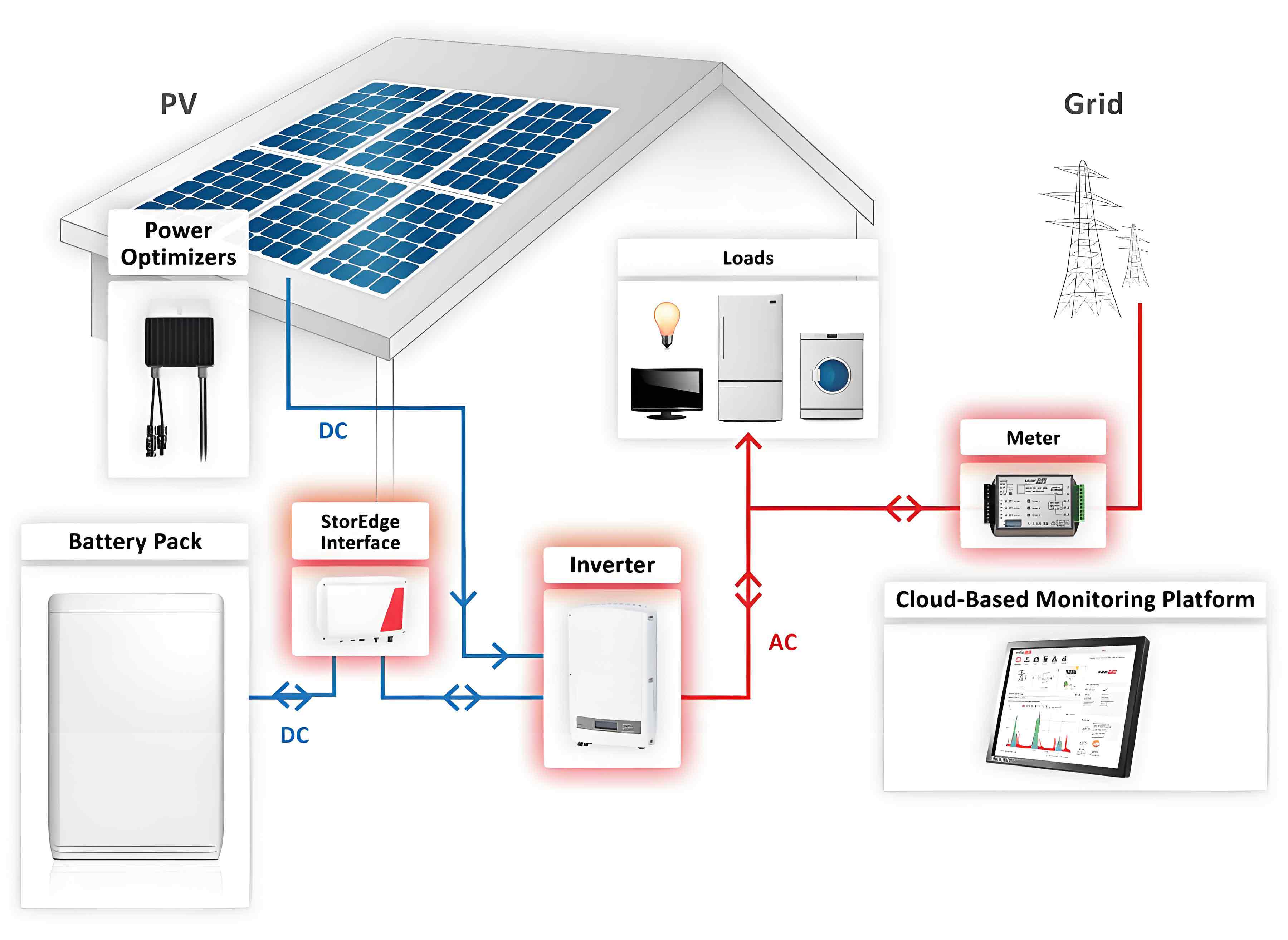
Table 1: Components of a Solar Battery System
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Solar Panels | Capture and convert sunlight into electricity |
| Inverter | Convert DC electricity to AC electricity |
| Battery Storage | Store excess electricity |
| Charge Controller | Regulate power flow to and from the battery |
| Monitoring System | Track and display energy data |
Benefits of Solar Battery Systems
1. Energy Independence
Solar battery systems enable homeowners to achieve greater energy independence. By generating and storing their own electricity, they can reduce reliance on the grid and protect themselves from power outages. This independence is particularly beneficial in remote areas or regions with unstable power supplies.
2. Cost Savings
Homeowners with solar battery systems can significantly reduce their electricity bills. They can use stored energy during peak hours when electricity rates are highest, avoiding expensive utility charges. Additionally, many regions offer financial incentives and rebates for installing solar battery systems, further enhancing their cost-effectiveness.
3. Environmental Sustainability
Solar energy is a clean and renewable resource. By using solar battery systems, homeowners can reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to environmental sustainability. This shift away from fossil fuels helps mitigate climate change and promotes a healthier planet.
4. Grid Resilience
Solar battery systems contribute to grid resilience by providing a decentralized source of power. During times of high demand or grid failures, these systems can supply power, reducing the strain on the central grid and minimizing the impact of outages.
5. Enhanced Property Value
Homes equipped with solar battery systems often see an increase in property value. Prospective buyers recognize the long-term benefits of lower energy costs, energy independence, and environmental sustainability, making these homes more attractive in the real estate market.
Challenges of Solar Battery Systems
1. High Initial Costs
The upfront cost of solar battery systems can be substantial, encompassing solar panels, batteries, inverters, and installation. However, the long-term savings and available incentives can offset these initial costs over time.
2. Battery Lifespan and Maintenance
Batteries have a limited lifespan, typically ranging from 5 to 15 years depending on the type and usage. Homeowners will need to replace their batteries periodically, which can add to the long-term costs. Additionally, some batteries require regular maintenance to ensure optimal performance.
3. Efficiency Losses
While solar battery systems have improved significantly, there are still efficiency losses associated with storing and converting energy. Energy is lost during the conversion from DC to AC and during the storage process itself.
4. Space Requirements
Installing a solar battery system requires adequate space for both the solar panels and the battery storage unit. Homes with limited roof space or those located in areas with less sunlight may face challenges in optimizing their solar energy systems.
Table 2: Comparison of Common Solar Battery Types
| Battery Type | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Lead-Acid | Cost-effective, Reliable | Shorter lifespan, Requires maintenance |
| Nickel-Cadmium | Durable, Performs well in extreme temperatures | Toxic, Expensive |
| Lithium-Ion | Long lifespan, High efficiency | Higher cost, Limited availability |
| Flow Batteries | Long lifespan, Scalability | Complex, High initial cost |
Future Prospects of Solar Battery Systems
1. Technological Advancements
The future of solar battery systems is bright, with continuous advancements in battery technology aimed at improving efficiency, reducing costs, and extending lifespan. Solid-state batteries, for example, promise greater energy density, safety, and durability compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries.
2. Smart Home Integration
The integration of solar battery systems with smart home technologies will enhance energy management. Smart inverters, advanced monitoring systems, and automated controls will allow homeowners to optimize their energy usage, monitor performance in real-time, and make adjustments remotely.
3. Virtual Power Plants
The concept of virtual power plants (VPPs) is gaining traction. VPPs aggregate multiple solar battery systems to provide a collective source of energy that can be managed and dispatched to the grid. This not only enhances grid stability but also provides homeowners with an additional revenue stream through energy trading.
4. Electric Vehicle Integration
The integration of solar battery systems with electric vehicles (EVs) represents a significant opportunity for the future. EVs can serve as additional energy storage units, providing flexibility and enhancing the overall efficiency of home energy systems. This integration allows for the use of stored solar energy to charge EVs, reducing reliance on grid electricity.
5. Policy and Incentive Improvements
As the benefits of solar battery systems become more widely recognized, governments and utilities are likely to introduce more favorable policies and incentives. These may include tax credits, rebates, and simplified permitting processes, making it easier and more cost-effective for homeowners to adopt solar battery systems.
Conclusion
Solar battery systems play a crucial role in modern residential power solutions. They offer significant benefits, including energy independence, cost savings, environmental sustainability, and enhanced grid resilience. While there are challenges to overcome, such as high initial costs and battery lifespan, the future prospects are promising. Technological advancements, smart home integration, virtual power plants, and improved policies will drive the continued adoption and improvement of solar battery systems. As we move towards a more sustainable and energy-resilient future, solar battery systems will be at the forefront of this transformation, empowering homes with reliable and clean energy solutions.
