Chapter 1: How Off Grid Solar System Empowering Remote Living
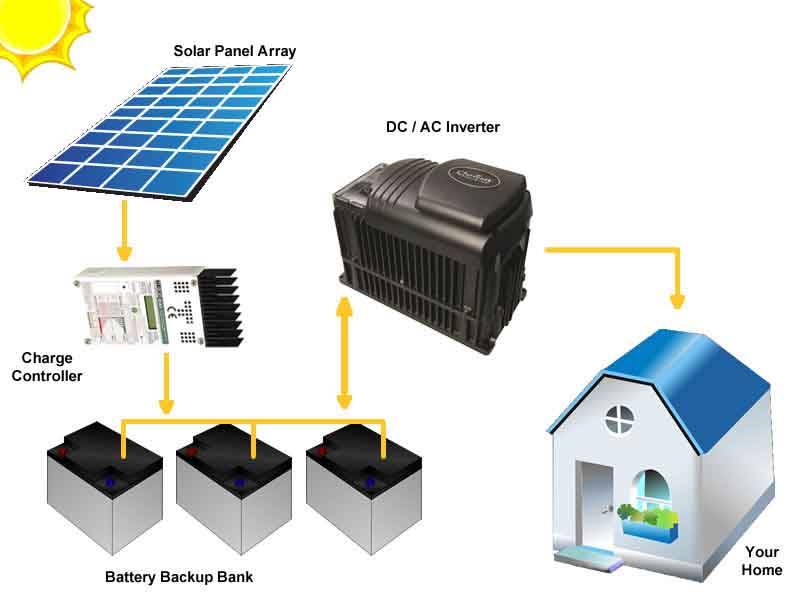
Off grid solar system significantly empowering remote living in various ways:
- Energy Independence: The most direct benefit is energy independence. Remote areas often don’t have access to the main power grid. Off grid solar system provide a reliable and consistent source of electricity, independent of the power grid. This is particularly useful in areas that are either too remote or too expensive to be connected to the national grid.
- Environmental Impact: These systems are environmentally friendly. They use renewable energy from the sun, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and decreasing carbon footprints. This is crucial for maintaining the ecological balance, especially in sensitive remote areas.
- Cost-Effectiveness: In the long run, off grid solar system can be more cost-effective than traditional power sources. Although the initial setup cost can be high, solar panels have a long lifespan and low maintenance costs. Over time, the cost of installing and maintaining off grid solar system can be less than paying for grid electricity, especially in remote areas where extending the grid or using generators can be prohibitively expensive.
- Increased Accessibility and Quality of Life: Off grid solar system can significantly improve the quality of life for residents in remote areas. It allows for basic necessities like lighting, refrigeration, and communication. Access to electricity can lead to better education (through lighting and electronic devices), improved healthcare (refrigeration for medicines, power for medical devices), and enhanced communication (charging mobile phones and running radios or televisions).
- Community Development and Empowerment: Off grid solar system can foster community development. Electrification of remote areas can stimulate local economies by enabling businesses to run more efficiently and for longer hours. It can also lead to the development of new business opportunities that were not feasible without electricity.
- Resilience and Reliability: These systems can be more reliable in certain conditions than grid-connected systems. They are less susceptible to large-scale outages and can be designed to cater specifically to the needs of the individual or community using them.
- Technological Advancement and Integration: Advances in solar technology, battery storage, and energy management systems have made off grid solar system more efficient and user-friendly. The integration of smart technology enables better control and optimization of energy use.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Off grid solar system is scalable and flexible. They can be sized to meet the specific energy needs of a household or community and can be expanded as those needs grow.
Overall, off grid solar system is empowering remote living by providing sustainable, reliable, and cost-effective energy solutions, which enhance the quality of life, economic opportunities, and environmental sustainability.
Chapter 2: The Rise of Off Grid Solar System Installations
The rise of off grid solar system installations can be attributed to several factors and trends:
- Technological Advancements: The technology behind solar panels and batteries has improved significantly. Solar panels are more efficient and cheaper to produce than ever before. Additionally, advancements in battery technology, like lithium-ion batteries, have improved energy storage capabilities, making solar systems more reliable.
- Decreasing Costs: The cost of solar panels and related components has decreased dramatically over the past decade. This reduction in cost makes it more financially feasible for individuals and communities to invest in off grid solar systems. The lower initial investment required has been a significant driver in the adoption of these systems.
- Increased Environmental Awareness: There’s a growing global awareness of environmental issues and the impacts of climate change. This has led to a surge in interest in renewable energy sources, with solar power being one of the most accessible and sustainable options. Individuals and communities are increasingly seeking to reduce their carbon footprint, and off grid solar systems are a viable solution.
- Energy Independence and Security: For many, the appeal of off grid solar systems is the independence and security they offer. These systems provide a reliable source of energy without the need for connection to a national grid. This is particularly attractive in areas where grid power is unreliable or where individuals seek autonomy from utility companies.
- Government Incentives and Support: In many regions, governments offer incentives for renewable energy installation, including subsidies, tax credits, or feed-in tariffs. These incentives can significantly reduce the net cost of an off grid solar system, making it a more attractive investment.
- Expanding Access in Remote Areas: Off grid solar systems are essential in providing electricity to remote or underserved areas where extending the traditional power grid is impractical or too costly. This not only improves the quality of life for residents in these areas but also promotes economic development.
- Improvements in Off-Grid Technology: Developments in related technologies such as LED lighting, energy-efficient appliances, and smart energy management systems have made off-grid living more feasible and comfortable.
- Rising Electricity Prices: In many areas, the cost of electricity from the grid is increasing, making off grid solar systems a more economically viable option over time.
- Community and Microgrid Developments: There’s a growing trend in creating local microgrids and community-based energy solutions, where off-grid solar plays a pivotal role. These systems can provide a community with shared energy resources, enhancing resilience and sustainability.
The rise in off grid solar system installations is a response to a combination of technological advancements, decreasing costs, environmental awareness, and the need for energy independence. This trend is expected to continue as technology improves and as the global community moves towards more sustainable energy solutions.
Chapter 3: Innovations in Off Grid Solar System Technologies
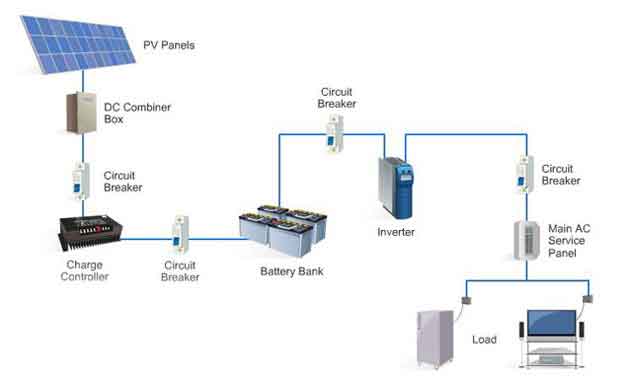
Innovations in off grid solar system technologies have been significant and ongoing, enhancing their efficiency, reliability, and applicability. Some of the key advancements include:
- High-Efficiency Solar Panels: The development of more efficient off grid solar system, such as monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels, has increased energy production. Some newer technologies, like PERC (Passivated Emitter and Rear Cell) and bifacial solar panels, can capture more sunlight and convert it into electricity more efficiently.
- Advanced Battery Storage: The evolution of battery technology has been pivotal in off grid solar systems. Lithium-ion batteries are currently the most popular due to their high energy density, long lifespan, and declining cost. Other technologies like solid-state batteries and flow batteries are also being developed, offering higher safety, energy density, and potentially lower costs.
- Improved Charge Controllers: Charge controllers have become more sophisticated, with Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) technology becoming more common. MPPT controllers optimize the extraction of energy from the off grid solar system by dynamically adjusting the electrical operating point of the modules.
- Energy Management Systems: Smart energy management systems are now integral parts of off grid solar setups. These systems efficiently manage energy usage and distribution, ensuring that power is available when needed and reducing waste.
- Hybrid Systems and Microgrids: There’s an increasing trend in hybrid systems that combine off grid solar system with other forms of renewable energy, like wind or hydroelectric power. These hybrid systems, along with microgrids, can provide more consistent and reliable power supply, especially in areas with variable weather conditions.
- Internet of Things (IoT) Integration: The integration of IoT technology with off-grid systems allows for remote monitoring and control. Users can track energy production, consumption, and system health in real-time from a smartphone or computer, enhancing convenience and maintenance capabilities.
- Portable and Flexible Solar Solutions: Innovations in portable and flexible solar panels have opened up new applications for off grid solar system. These include portable solar chargers, foldable solar panels for camping, and even wearable solar technology.
- Solar Panel Recycling: As the number of solar panels increases globally, so does the need for efficient recycling methods. Innovations in recycling processes ensure that off grid solar system materials like glass, metal, and semiconductor materials can be efficiently reclaimed and reused.
- Decentralized Energy Systems: There’s a growing focus on decentralized energy systems, where small-scale generation and storage occur close to the point of use. This approach can reduce transmission losses and increase the resilience of the energy system.
- Integrated Building Materials: The development of solar-integrated building materials, like solar roof tiles and solar glass, allows buildings to generate their own power without the need for traditional panel installations.
These innovations collectively make off grid solar systems more accessible, efficient, and sustainable, further encouraging their adoption in both developed and developing regions worldwide.
Chapter 4: How Off Grid Solar System Changing Energy Consumption
Off grid solar system transforming energy consumption patterns in several key ways:
- Shift to Renewable Energy: By providing a viable alternative to fossil fuels, off grid solar system facilitating a shift towards renewable energy. This is especially significant in remote or underserved areas where traditional grid infrastructure is either unavailable or unreliable.
- Reducing Carbon Footprint: Off grid solar system significantly reduce the carbon footprint of their users. By relying on the sun, a clean and renewable energy source, these systems eliminate the greenhouse gas emissions associated with conventional electricity generation from fossil fuels.
- Energy Independence: Users of off grid solar system gain energy independence, as they are not reliant on the power grid. This not only provides security against power outages and fluctuating energy prices but also encourages a more mindful and efficient use of energy.
- Encouraging Sustainable Practices: The use of off grid solar system often goes hand in hand with adopting more energy-efficient appliances and practices. Since the energy supply is not unlimited, users are typically more conscious of their consumption, leading to a reduction in overall energy use.
- Empowering Rural and Remote Communities: In remote areas, off grid solar system provide access to electricity where it was previously unavailable or too costly. This access can transform lives by improving healthcare, education, and economic opportunities, reducing the use of less efficient and more polluting energy sources like diesel generators and kerosene lamps.
- Decentralization of Energy Production: Off grid solar represents a move away from centralized energy production. It enables localized energy generation, which can be more resilient and less susceptible to large-scale disruptions.
- Innovations in Energy Storage: The need for effective energy storage in off-grid systems has spurred innovations in battery technology. Developments in this area are not only beneficial for off-grid systems but also contribute to the broader energy market by providing more efficient and cost-effective storage solutions.
- Smart Energy Management: With the integration of smart technologies, off grid solar system users can optimize their energy consumption. Smart meters and energy management systems allow for real-time monitoring and adjustments, improving the efficiency and longevity of the system.
- Economic Impacts: Off grid solar system can provide economic benefits by reducing or eliminating electricity bills. They also offer a cost-effective solution for electrification in rural areas, where extending the grid could be prohibitively expensive.
- Encouraging Energy Conservation: Since off-grid systems often have a finite amount of energy available (dependent on the weather and storage capacity), they inherently promote a culture of energy conservation and efficiency among their users.
In summary, off grid solar system changing energy consumption by promoting renewable energy use, reducing carbon emissions, fostering energy independence, and encouraging both technological innovation and sustainable living practices.
Chapter 5: Building Sustainable Homes with Off Grid Solar System
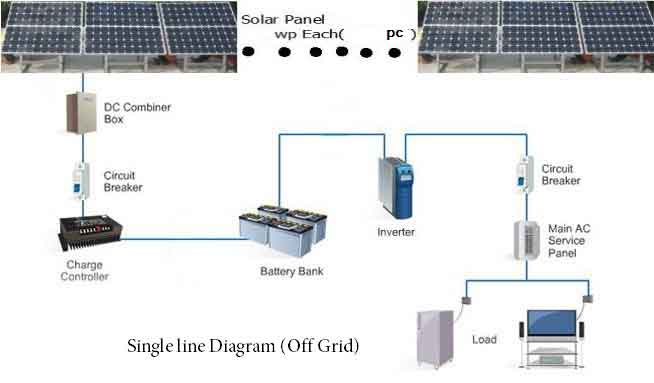
Building sustainable homes with off grid solar system involves a holistic approach to design and construction, focusing on energy efficiency, renewable energy sources, and sustainability. Here are some key aspects to consider:
- Energy Efficient Design: The first step is to design homes that are inherently energy-efficient. This includes proper insulation, energy-efficient windows, and building materials that help maintain consistent indoor temperatures, reducing the need for heating and cooling. The home’s orientation should also be considered to maximize natural lighting and heat from the sun.
- Solar Power System: The heart of an off-grid sustainable home is off grid solar system. This typically includes solar panels, a battery storage system, a charge controller, and an inverter. The system should be sized based on the energy needs of the household, taking into account local climate and solar insolation levels.
- Energy Storage: Since solar energy is intermittent (not available at night or during cloudy days), a robust battery storage system is crucial. This system stores excess energy generated during the day for use when off grid solar system is not available.
- Energy Efficient Appliances and Systems: Utilize energy-efficient appliances and systems within the home, such as LED lighting, energy-efficient refrigerators, and water-efficient fixtures. The use of smart home technologies can further optimize energy usage.
- Water Conservation: Incorporating rainwater harvesting systems and greywater recycling can significantly reduce water consumption. Water conservation is especially important in off-grid homes, where water supply may be limited.
- Use of Sustainable Materials: Building materials should be chosen based on sustainability. This includes using locally sourced, recycled, or renewable materials that have a lower environmental impact. The use of non-toxic materials also improves indoor air quality.
- Heating and Cooling Solutions: For heating, consider passive solar design, well-insulated structures, and possibly solar thermal systems. For cooling, passive strategies like natural ventilation, shading, and reflective roofs can significantly reduce the need for air conditioning.
- Waste Management: Implementing composting and recycling facilities within the home can minimize waste output and contribute to a more sustainable lifestyle.
- Landscaping and Permaculture: Sustainable landscaping, including permaculture principles, can enhance the home’s environment by promoting biodiversity, reducing water usage, and providing organic food sources.
- Integration with Local Ecosystem: The home should be designed to integrate seamlessly with the surrounding environment, minimizing disruption to the local ecosystem and wildlife.
Building a sustainable home with an off grid solar system is not just about energy independence; it’s about creating a living space that respects and harmonizes with the environment, promoting sustainability in every aspect of its design and operation.
Chapter 6: The Comprehensive Benefits of Off Grid Solar System
Off grid solar system offer comprehensive range of benefits, impacting not just individual users, but also communities and the environment at large. Here’s a detailed overview of these benefits:
- Energy Independence: Off grid solar system provide complete independence from the utility grid. This is particularly beneficial in areas with unreliable grid infrastructure, as it ensures a consistent and stable power supply.
- Environmental Benefits: Solar energy is a clean, renewable resource. By using off grid solar system, individuals and communities significantly reduce their carbon footprint, contributing to the fight against climate change and environmental degradation.
- Reduced Energy Costs: After the initial investment in the off grid solar system, the ongoing operational costs are quite low compared to traditional power sources. The sun provides free energy, leading to significant savings on electricity bills over time.
- Accessibility in Remote Locations: For remote or rural locations where grid connectivity is either unavailable or prohibitively expensive, off-grid solar systems are often the most feasible option for electrification.
- Emergency Preparedness: In the event of natural disasters or other emergencies that disrupt power grids, off grid solar system continue to provide electricity, enhancing resilience and safety for their users.
- Advancement of Technology: The growing demand for off grid solar system have spurred advancements in related technologies, including battery storage, solar panel efficiency, and energy management systems.
- Sustainable Development: Off grid solar system support sustainable development by providing clean energy that doesn’t deplete natural resources. This is particularly important for future generations as it helps in creating a more sustainable world.
- Empowerment of Local Communities: By providing energy independence, off grid solar system empower communities, especially in rural or underserved areas. They facilitate better educational and healthcare facilities, improve communication, and support local economic development.
- Improved Public Health: Replacing generators, kerosene lamps, and other polluting sources of energy with solar power reduces air pollution and associated health risks, particularly in indoor environments.
- Job Creation: The installation, maintenance, and servicing of off grid solar system create jobs, contributing to local economies.
- Promotion of Energy Conservation: Users of off-grid systems are often more conscious of their energy consumption, as they are directly responsible for managing their power supply. This promotes a culture of energy conservation and efficiency.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Off grid solar system can be designed to fit specific needs and scaled up as those needs grow. This flexibility allows for a wide range of applications, from small household setups to larger community-based systems.
- Reduced Infrastructure Costs: For governments and local authorities, promoting off grid solar system can reduce the need for expensive grid expansion and maintenance in remote areas.
- Innovation in Energy Storage: The need for efficient storage in off grid solar system drives innovation in battery technology, which can benefit broader renewable energy applications.
The benefits of off grid solar system extend beyond mere energy supply; they encompass environmental conservation, economic savings, community empowerment, sustainable development, and technological innovation. These systems represent not just an alternative to traditional grid electricity, but a holistic approach to a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
