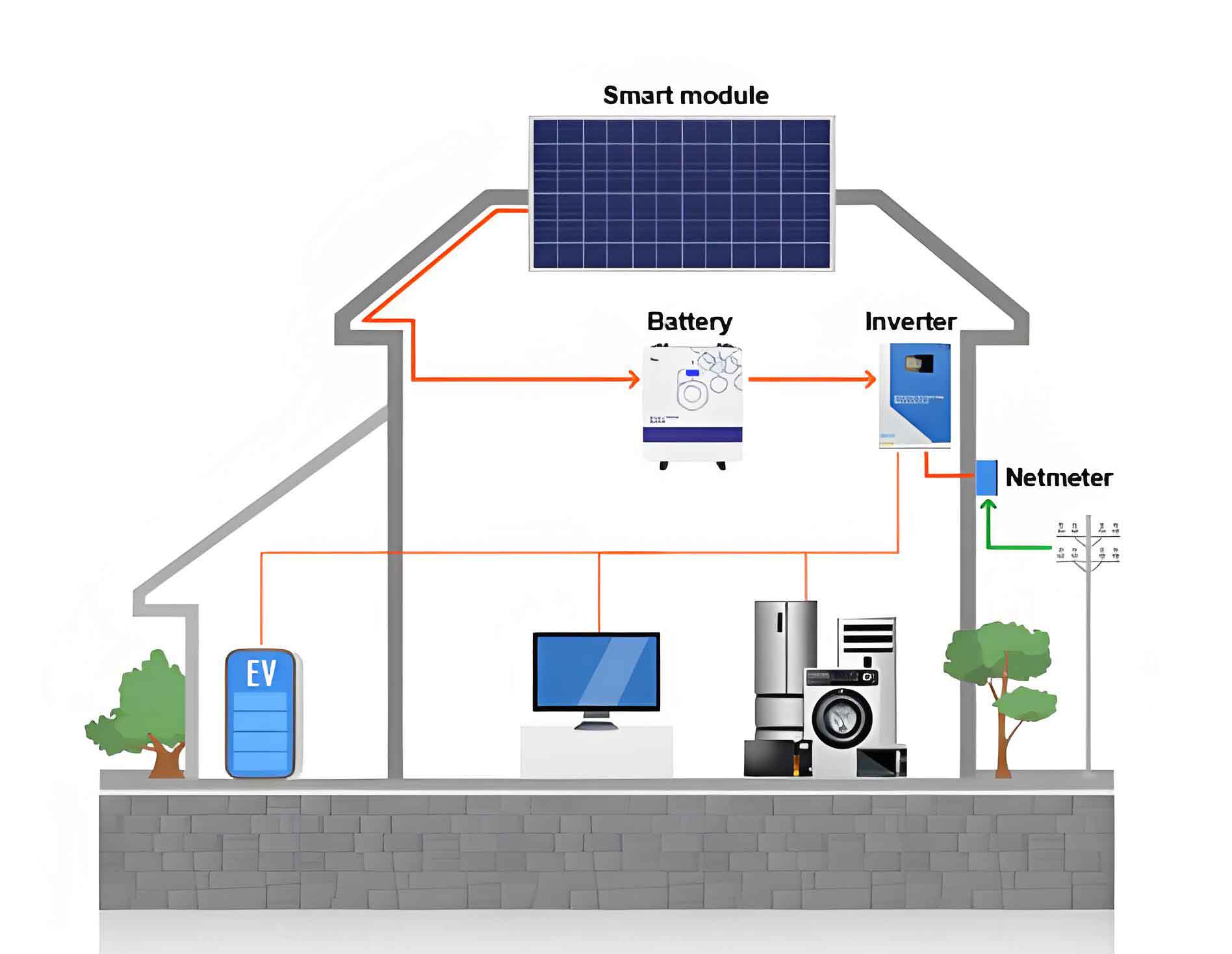
Introduction
As the demand for renewable energy sources continues to grow, solar power systems have become increasingly popular worldwide. At the heart of these systems lies the solar power inverter, a critical component that converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) for use in homes, businesses, and the power grid. However, the global market for solar power inverter faces numerous regulatory and compliance challenges that manufacturers and installers must navigate. This article delves into these challenges, exploring their impact on the industry and how they shape the development and deployment of solar power inverter globally.
Regulatory Frameworks Across Different Regions
The regulatory landscape for solar power inverter varies significantly across different regions, reflecting diverse approaches to energy policy, grid infrastructure, and safety standards. Key regions and their regulatory frameworks include:
- North America: In the United States and Canada, solar power inverter must comply with standards set by organizations such as the Underwriters Laboratories (UL), the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), and the National Electrical Code (NEC). These standards cover aspects such as safety, electromagnetic compatibility, and grid interconnection.
- Europe: The European Union (EU) has established comprehensive regulations for solar power inverter, including directives on electromagnetic compatibility (EMC), low voltage (LVD), and grid codes defined by the European Network of Transmission System Operators for Electricity (ENTSO-E). The CE marking is mandatory for products sold in the EU, indicating compliance with these directives.
- Asia-Pacific: Countries like China, Japan, and Australia have their own regulatory requirements for solar power inverter. In China, the China Compulsory Certificate (CCC) is required, while Japan follows the Japan Electrical Safety & Environment Technology Laboratories (JET) certification. Australia adheres to standards set by the Clean Energy Council (CEC) and the Australian Standards (AS).
- Middle East and Africa: Regulatory frameworks in this region are still developing, with countries like the United Arab Emirates (UAE) and South Africa establishing guidelines for solar power inverter to ensure safety and grid compatibility.
Compliance Challenges
Manufacturers and installers of solar power inverter face several compliance challenges that can impact their ability to enter and compete in the global market. These challenges include:
- Varying Standards and Certifications: The diversity of standards and certification requirements across regions can be a significant barrier. Manufacturers must invest in understanding and complying with multiple regulatory frameworks, which can be time-consuming and costly.
- Testing and Certification Costs: Obtaining the necessary certifications for solar power inverter involves rigorous testing and evaluation by accredited laboratories. These processes can be expensive, especially for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
- Grid Code Compliance: Grid codes specify the technical requirements for connecting solar power inverter to the power grid. These codes vary by region and can change frequently, requiring manufacturers to continuously update their products to remain compliant.
- Safety and Reliability: Ensuring that solar power inverter meet safety and reliability standards is crucial to prevent failures and hazards. Compliance with safety standards such as UL 1741 in the US and IEC 62109 in Europe is essential for market acceptance.
- Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): Solar power inverter must meet EMC standards to prevent interference with other electronic devices. Compliance with EMC directives is necessary to ensure the safe and reliable operation of solar power systems.
Impact on the Industry
The regulatory and compliance challenges faced by the solar power inverter industry have significant implications for manufacturers, installers, and consumers. These impacts include:
- Increased Costs: Compliance with diverse and stringent regulatory requirements can increase the cost of manufacturing solar power inverter. These costs are often passed on to consumers, affecting the overall affordability of solar energy systems.
- Innovation and Development: Regulatory challenges can either hinder or drive innovation in the industry. On one hand, stringent requirements can slow down the development and deployment of new technologies. On the other hand, they can also encourage innovation by pushing manufacturers to develop more efficient, reliable, and compliant products.
- Market Access: Navigating the complex regulatory landscape can be a barrier to market entry, particularly for SMEs. Companies that successfully comply with global standards gain a competitive advantage and broader market access.
- Quality and Safety: Regulatory compliance ensures that solar power inverter meet high standards of quality and safety, protecting consumers and enhancing the reliability of solar energy systems.
Strategies for Navigating Regulatory Challenges
To successfully navigate the regulatory and compliance challenges in the global market, manufacturers and installers of solar power inverter can adopt several strategies:
- Stay Informed: Keeping abreast of regulatory changes and updates in key markets is essential. Companies should monitor developments in standards and certification requirements to ensure ongoing compliance.
- Invest in Certification: Investing in the necessary testing and certification processes is crucial for market access. Partnering with accredited laboratories and certification bodies can streamline this process.
- Standardization Efforts: Engaging in industry standardization efforts can help harmonize regulations across regions, reducing the burden of compliance. Organizations such as the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) play a key role in developing global standards.
- Product Design and Innovation: Designing products with compliance in mind from the outset can simplify the certification process. Innovation in areas such as thermal management, electromagnetic compatibility, and grid interaction can enhance product compliance and performance.
- Collaboration and Partnerships: Collaborating with local partners, regulatory bodies, and industry associations can provide valuable insights into regional requirements and facilitate smoother market entry.
Key Regulatory Standards for Solar Power Inverter
| Region | Key Regulatory Standards and Certifications |
|---|---|
| North America | UL 1741, IEEE 1547, NEC, CSA, FCC |
| Europe | CE Marking, EN 50549, EN 61000, IEC 62109, ENTSO-E Grid Codes |
| Asia-Pacific | CCC (China), JET (Japan), CEC (Australia), AS 4777 |
| Middle East & Africa | UAE Regulation for Distributed Renewable Resources, SANS (South Africa) |
Conclusion
The regulatory and compliance landscape for solar power inverter in the global market is complex and multifaceted. Manufacturers and installers must navigate varying standards, certification requirements, and grid codes to ensure their products meet the necessary safety, reliability, and performance criteria. While these challenges can increase costs and impact market access, they also drive innovation and ensure the quality and safety of solar energy systems. By staying informed, investing in certification, and adopting strategies to streamline compliance, companies can successfully navigate the regulatory landscape and contribute to the growth of the global solar energy market.
