Energy is the cornerstone and driving force of human social development. The development of human society cannot be separated from the development of high-quality energy and the use of advanced energy technologies. In today’s world, the development of energy, the contradiction between energy and environment, is a common concern of the world and an important issue for China’s socio-economic development. With the gradual depletion of energy sources such as oil, natural gas, and coal, solar energy, wind energy, geothermal energy, and other energy sources are bound to attract more attention. However, based on the current state of energy development, the utilization rate of resources such as solar energy is relatively low. Therefore, this article conducts research on photovoltaic power generation systems, including optimizing the maximum power point algorithm, selecting efficient inverter structures, and optimizing the design of key equipment in photovoltaic power generation systems. The aim is to improve the conversion efficiency of photovoltaic inverters and thus enhance the utilization rate of solar energy.
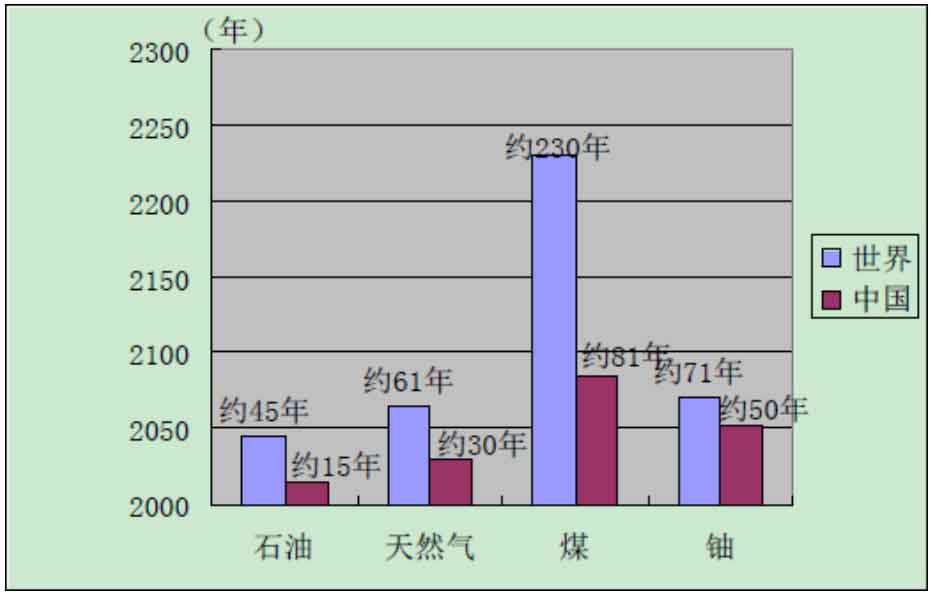
Our common energy sources can be roughly divided into renewable energy and non renewable energy. Renewable energy includes wind energy, hydro energy, ocean energy, tidal energy, solar energy, etc; Non renewable energy mainly includes coal, oil, and natural gas. According to authoritative institutions, non renewable energy in the global energy consumption structure will reach its peak around 2030 in the future, and the proportion of renewable energy will continue to increase, and its proportion in the total energy consumption by 2100 may exceed 60%. Due to the fact that non renewable energy remains the main source of energy in the world today, with continuous depletion, humanity will face an increasingly serious energy crisis. Although China is a resource rich country, it is also a major energy consuming country, and the phenomenon of energy shortage is becoming increasingly prominent. In today’s rapidly developing Chinese economy, energy consumption increased nearly 13 times in 2015 compared to 1965, making China the world’s second largest energy consumer. However, China’s non renewable energy reserves are not as abundant as imagined. According to the latest data, China’s proven total reserves of exploitable energy account for about 10.1% of the world’s total, with coal accounting for 58.8%, oil accounting for 3.4%, natural gas accounting for 1.3%, and water resources accounting for 36.5%. The comparison between China’s proven non renewable energy reserves (storage/extraction) and the world’s remaining reserves is shown in Figure. It can be seen that the exploitable lifespan of energy in our country is lower than the world level, so our energy demand will face more severe challenges.
With the significant consumption of non renewable energy, the economic constraints and environmental impacts of traditional non renewable energy have also received increasing attention worldwide. Due to its uneven distribution worldwide, it seriously restricts economic development; At the same time, a large amount of carbon dioxide emissions have caused the global greenhouse effect. The greenhouse effect causes melting of polar glaciers and rising sea levels, gradually reducing land area while also reducing species diversity, which will have a devastating impact on human activities. Therefore, the development of renewable energy has gradually received attention from countries around the world.
Solar energy combines various advantages such as inexhaustible, environmentally friendly, and affordable, making it an ideal choice for human energy utilization. If calculated based on a conversion rate of 5% and converting 0.1% of the Earth’s surface solar energy into electricity, the annual power generation can reach 5.6 × 1012kWh, approximately 40 times the current energy consumption in the world. The abundant solar energy resources and suitable development environment indicate the current and future direction of resource development for people around the world. It is speculated that by 2050, the utilization ratio of solar energy on a global scale will reach 13-15%, accounting for more than 50% of renewable energy in energy, as shown in Table 1. This fully reflects the important role that solar energy plays in the human energy structure.
| Time period | 2010 | 2020 | 2030 | 2040 | 2050 | |
| Japan Forecast | Renewable energy | 20.2 | 23.5 | 33.6 | 42.7 | 53.4 |
| Japan Forecast | Solar energy | — | — | 1.9 | 7.9 | 13.5 |
| SHELL prediction | Renewable energy | 22.2 | 20.9 | 32.3 | 43.3 | 54.6 |
| SHELL prediction | Solar energy | — | — | 2.6 | 8.4 | 14.9 |
| Average | Renewable energy | 21.2 | 22.2 | 33.0 | 43.0 | 54.0 |
| Average | Solar energy | — | — | 2.3 | 8.2 | 14.0 |
China has a land area of over 9.6 million square kilometers, therefore it has a vast illuminated land area. Every year, China’s land receives about 50% of the solar radiation energy × 1018kJ, which is equivalent to the energy brought by 1700 billion tons of standard coal. The abundant lighting resources have created unique conditions for the development of China’s photovoltaic industry. Therefore, among the renewable energy sources defined in the Renewable Energy Law of the People’s Republic of China, solar energy is the most widely concerned.
The distribution of solar energy resources in China shows a relatively concentrated energy trend with fewer in the east and relatively concentrated in the west. The radiation and sunshine hours in Xizang, Qinghai, Gansu, the Inner Mongolian Plateau, Ningxia and other regions in China are relatively highest in China, and the above regions are all rich in solar energy resources in the world; The distribution of solar energy resources in Sichuan Basin, Hunan, and Hubei is relatively low; The distribution of solar energy resources in the eastern, central, southern, and northeastern regions of China is relatively balanced. Such resource distribution facilitates the centralized development of solar energy resources. The distribution of resources in various regions is shown in Table 2.
| Type | Region | Annual exposure time (h) | Annual radiation amount (kcal/cm2) |
| 1 | Western Xizang, Western Qinghai, Western Gansu, Southeast Xinjiang | 2800-3300 | 160-200 |
| 2 | Southeast Xizang, southern Xinjiang, eastern Qinghai, southern Ningxia, Inner Mongolia, northern Shanxi, northwestern Hebei, central Gansu | 3000-3200 | 140-160 |
| 3 | Eastern Hebei, Henan, Liaoning, Southern Fujian, Southern Shanxi, Northern Xinjiang, Eastern Gansu, Southern Guangdong, Northern Anhui | 2200-3000 | 120-140 |
| 4 | Hunan, Zhejiang, southern Anhui, Hubei, Heilongjiang, northern Fujian, southern Shanxi, southern Jiangsu | 1400-2200 | 100-120 |
| 5 | Sichuan and Guizhou | 1000-1400 | 80-100 |
The depletion of non renewable energy has provided enormous development space for renewable energy. Solar energy, as the most abundant clean energy, is of great concern to everyone. Conducting research on solar photovoltaic power generation, expanding the vast photovoltaic power generation market, mastering key technologies in the photovoltaic field, improving the efficiency of photovoltaic power generation systems, has significant theoretical and practical significance for the development of the world economy and the improvement of environmental issues.
