The growing interest in renewable energy has led to widespread adoption of solar energy systems in both residential and commercial settings. A crucial component of these systems is the solar inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) used by home appliances and the electrical grid. Solar inverter play a vital role in both on-grid and off-grid solar energy systems, but their applications and benefits differ significantly depending on the system type. This article provides a comprehensive analysis of solar inverter applications in on-grid and off-grid solar energy systems, highlighting the differences, advantages, and key considerations for each system.
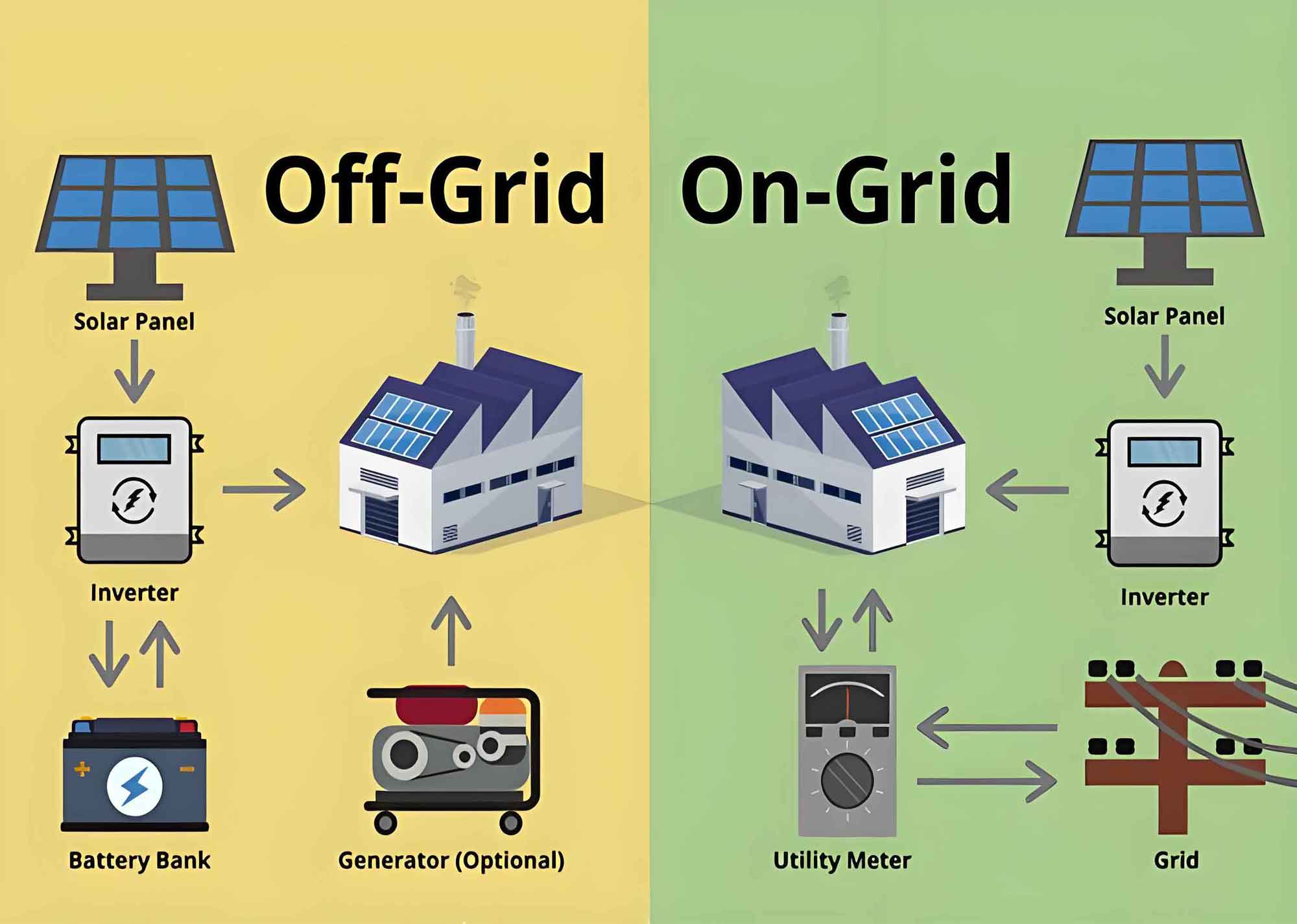
Understanding On-Grid Solar Energy Systems
On-grid solar energy systems, also known as grid-tied systems, are connected to the public electricity grid. These systems allow homeowners to use solar power when it is available and draw electricity from the grid when solar power is insufficient, such as during nighttime or cloudy days. On-grid systems are the most common type of solar energy systems and offer several benefits:
- Grid Integration: On-grid solar energy systems seamlessly integrate with the electrical grid, allowing excess solar power to be fed back into the grid. This results in energy credits for the homeowner through net metering, reducing electricity bills.
- Lower Initial Cost: On-grid systems typically have a lower initial cost compared to off-grid systems because they do not require energy storage solutions like batteries.
- Simplicity and Reliability: On-grid systems are relatively simple to install and maintain. They provide reliable power supply by leveraging the grid as a backup source.
Understanding Off-Grid Solar Energy Systems
Off-grid solar energy systems operate independently of the public electricity grid. These systems are designed to provide all the energy needs of a home or facility using solar power, often in combination with energy storage solutions such as batteries. Off-grid systems are ideal for remote locations where access to the electrical grid is unavailable or unreliable. Key benefits of off-grid solar energy systems include:
- Energy Independence: Off-grid systems offer complete energy independence, ensuring a continuous power supply even in remote or underserved areas.
- Environmental Impact: Off-grid systems eliminate reliance on fossil fuels and reduce carbon footprint by utilizing renewable solar energy exclusively.
- Customization: Off-grid systems can be tailored to meet specific energy needs and can include backup generators or other renewable energy sources for added reliability.
Solar Inverter Applications in On-Grid Systems
In on-grid solar energy systems, solar inverter perform several critical functions:
- Grid Synchronization: Solar inverter synchronize the output of the solar panels with the grid frequency and voltage, ensuring smooth integration with the public electricity grid.
- Energy Export: Solar inverter facilitate the export of excess solar energy to the grid, enabling homeowners to earn energy credits through net metering.
- Safety Features: On-grid solar inverter is equipped with safety mechanisms such as anti-islanding protection, which prevents the inverter from supplying power to the grid during an outage, ensuring the safety of utility workers.
Solar Inverter Applications in Off-Grid Systems
In off-grid solar energy systems, solar inverter play a different but equally critical role:
- Energy Storage Management: Off-grid solar inverter manage the charging and discharging of batteries, ensuring optimal energy storage and usage.
- Power Conversion: Off-grid solar inverter convert the DC output from solar panels and batteries into AC for use in home appliances, providing a reliable power supply.
- System Monitoring: Off-grid solar inverter include monitoring capabilities to track energy production, storage, and consumption, helping homeowners manage their energy resources efficiently.
Comparative Table of On-Grid vs. Off-Grid Solar Inverter Features
| Feature | On-Grid Solar Inverter | Off-Grid Solar Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Integration | Yes | No |
| Energy Storage | Optional | Required |
| Initial Cost | Lower | Higher |
| Energy Independence | No | Yes |
| Net Metering | Yes | No |
| Safety Features | Anti-Islanding Protection | Battery Management |
| Complexity | Simpler | More Complex |
Key Considerations for Choosing Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Inverter
When deciding between on-grid and off-grid solar energy systems, several factors should be considered:
- Location and Accessibility: For remote locations without reliable access to the electrical grid, off-grid systems are the only viable option.
- Energy Independence: Homeowners seeking complete energy independence should opt for off-grid systems, while those comfortable with partial grid reliance may prefer on-grid systems.
- Initial Investment: On-grid systems generally have a lower initial cost, making them more accessible for budget-conscious homeowners.
- Energy Needs: The size and energy consumption of the household will influence the choice of system. Off-grid systems require careful planning to ensure sufficient energy storage and supply.
Advantages and Disadvantages of On-Grid Solar Inverter
Advantages:
- Lower initial cost compared to off-grid systems.
- Simplified installation and maintenance.
- Ability to earn energy credits through net metering.
- Reliable power supply with grid backup.
Disadvantages:
- Dependence on the public electricity grid.
- Lack of energy independence.
- No power supply during grid outages without additional battery backup.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Off-Grid Solar Inverter
Advantages:
- Complete energy independence.
- Ideal for remote or underserved areas.
- Reduced environmental impact with exclusive use of renewable energy.
Disadvantages:
- Higher initial cost due to the need for energy storage solutions.
- More complex installation and maintenance.
- Requires careful management of energy resources to ensure continuous supply.
Conclusion
Solar inverter is pivotal component in both on-grid and off-grid solar energy systems, transforming solar power into usable electricity for homes and facilities. The choice between on-grid and off-grid solar energy systems depends on various factors, including location, energy independence, initial investment, and energy needs. On-grid systems offer simplicity, lower initial costs, and the benefit of net metering, while off-grid systems provide complete energy independence and are ideal for remote locations. By understanding the differences and applications of solar inverter in these systems, homeowners can make informed decisions to harness the power of solar energy effectively and sustainably.
