Introduction
Solar energy has become a cornerstone in the quest for renewable and sustainable energy solutions. A crucial component in harnessing solar power is the solar power inverter, which converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) that can be used by household appliances and fed into the power grid. Solar power inverters are broadly classified into two categories: on-grid and off-grid. Understanding the differences between these two types of solar power inverters is essential for choosing the right system for your energy needs.
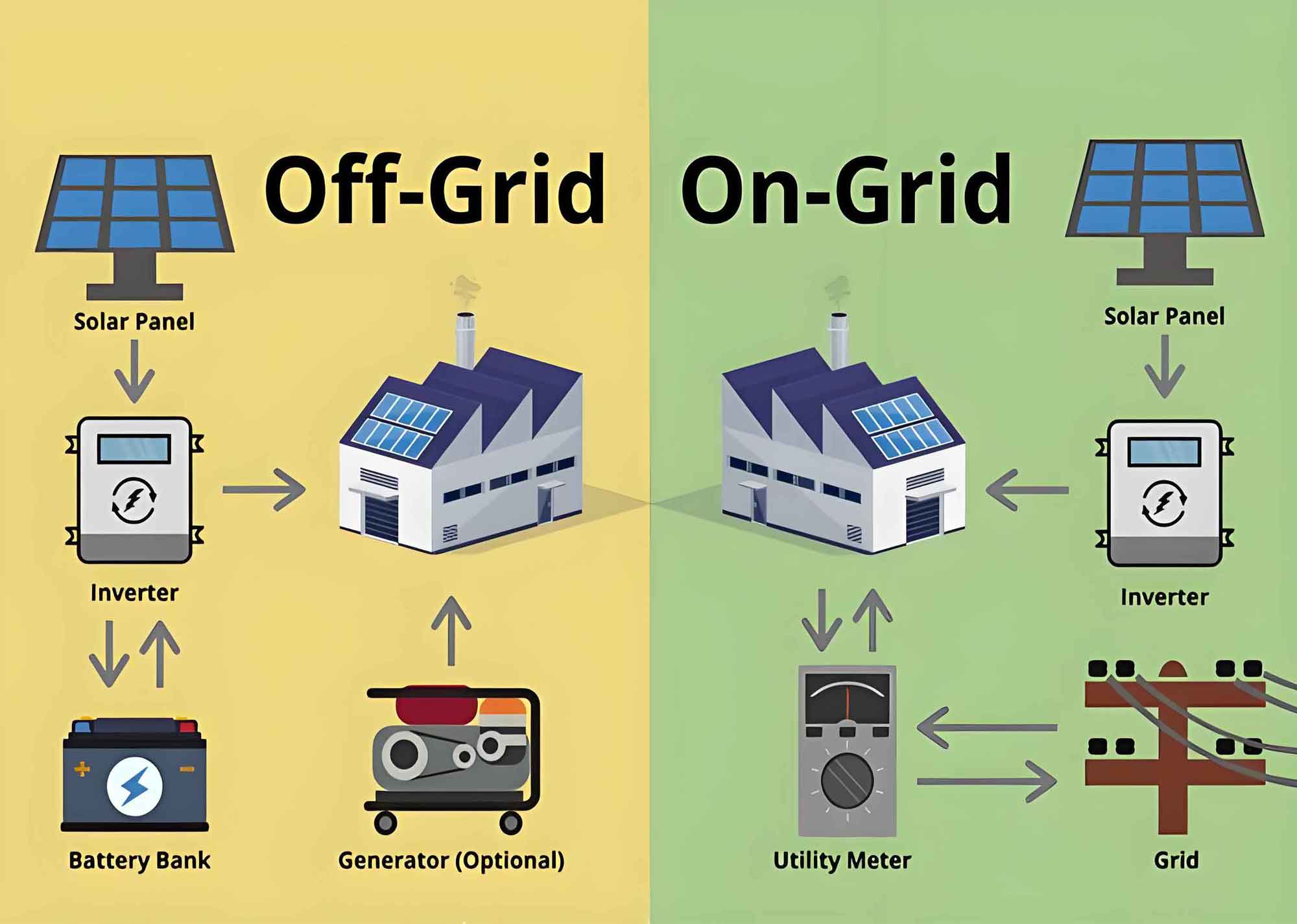
What is an On-Grid Solar Power Inverter?
An on-grid solar power inverter, also known as a grid-tied inverter, is designed to work in conjunction with the power grid. It converts the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity, which is then either used to power household appliances or fed back into the grid. The key characteristics and advantages of on-grid solar power inverters include:
- Grid Synchronization: On-grid solar power inverters are synchronized with the grid, ensuring that the frequency and voltage of the generated electricity match those of the grid.
- Net Metering: One of the significant benefits of on-grid solar power inverters is the ability to participate in net metering programs. Excess electricity generated by the solar panels is fed into the grid, and the owner receives credits, which can offset the cost of electricity drawn from the grid during periods of low solar production.
- No Need for Batteries: On-grid systems do not require batteries for energy storage, reducing the overall cost and maintenance requirements.
- Efficiency: These systems are typically more efficient because they do not incur the energy losses associated with battery storage.
What is an Off-Grid Solar Power Inverter?
An off-grid solar power inverter, also known as a standalone inverter, is designed to operate independently of the power grid. It converts the DC electricity generated by solar panels into AC electricity and stores excess energy in batteries for later use. The key characteristics and advantages of off-grid solar power inverters include:
- Independence from the Grid: Off-grid solar power inverters provide complete energy independence, making them ideal for remote locations where access to the power grid is limited or nonexistent.
- Battery Storage: Off-grid systems rely on batteries to store excess solar energy. This stored energy can be used during periods of low solar production, such as at night or during cloudy days.
- Self-Sufficiency: Off-grid solar power inverters allow users to be self-sufficient in their energy needs, reducing reliance on external power sources.
- Backup Power: These systems provide a reliable backup power source during grid outages, ensuring continuous power supply for critical appliances and systems.
Key Differences Between On-Grid and Off-Grid Solar Power Inverters
| Feature | On-Grid Solar Power Inverter | Off-Grid Solar Power Inverter |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Connection | Connected to the power grid | Operates independently of the power grid |
| Energy Storage | Does not require batteries; feeds excess energy into the grid | Requires batteries to store excess energy |
| Net Metering | Eligible for net metering programs | Not eligible for net metering |
| Cost | Generally lower initial cost due to the absence of batteries | Higher initial cost due to the need for batteries |
| Efficiency | Higher efficiency without battery losses | Potential energy losses due to battery storage |
| Ideal Use Case | Urban and suburban areas with reliable grid access | Remote areas with no grid access or frequent grid outages |
| Backup Power | Does not provide backup power during grid outages | Provides reliable backup power |
Choosing the Right Solar Power Inverter System
Selecting the right solar power inverter system depends on several factors, including your energy needs, location, and budget. Here are some considerations to help you make an informed decision:
- Energy Needs: Assess your daily energy consumption and peak energy requirements. On-grid systems are suitable for homes with consistent energy needs and reliable grid access, while off-grid systems are ideal for locations with variable energy consumption or unreliable grid access.
- Location: Consider the availability and reliability of the power grid in your area. On-grid systems are best suited for urban and suburban areas, whereas off-grid systems are more appropriate for remote locations without grid access.
- Budget: Evaluate the initial cost and long-term savings of each system. On-grid systems typically have lower upfront costs but may result in ongoing grid electricity costs. Off-grid systems have higher initial costs due to the need for batteries but can provide long-term savings by eliminating electricity bills.
- Backup Power: Determine if you need a reliable backup power source. If continuous power supply is critical, an off-grid system with battery storage may be the better option.
- Environmental Impact: Consider the environmental benefits of each system. Both on-grid and off-grid systems reduce reliance on fossil fuels, but off-grid systems offer greater self-sufficiency and independence from the grid.
Conclusion
Understanding the differences between on-grid and off-grid solar power inverters is crucial for choosing the right system for your energy needs. On-grid solar power inverters are ideal for locations with reliable grid access and offer the benefits of net metering and lower initial costs. Off-grid solar power inverters, on the other hand, provide complete energy independence and are well-suited for remote areas or locations with unreliable grid access.
By carefully evaluating your energy needs, location, budget, and backup power requirements, you can make an informed decision that will maximize the benefits of solar energy for your home or business. Whether you choose an on-grid or off-grid system, investing in solar power inverters is a step towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
