In the realm of solar energy, photovoltaic panels are a crucial component for harnessing the power of the sun. Among the various types of photovoltaic panels available, two of the most commonly used are monocrystalline photovoltaic panels and polycrystalline photovoltaic panels. This article delves into the differences, advantages, and disadvantages of these two types of photovoltaic panels, helping homeowners and businesses make informed decisions about their solar energy investments.
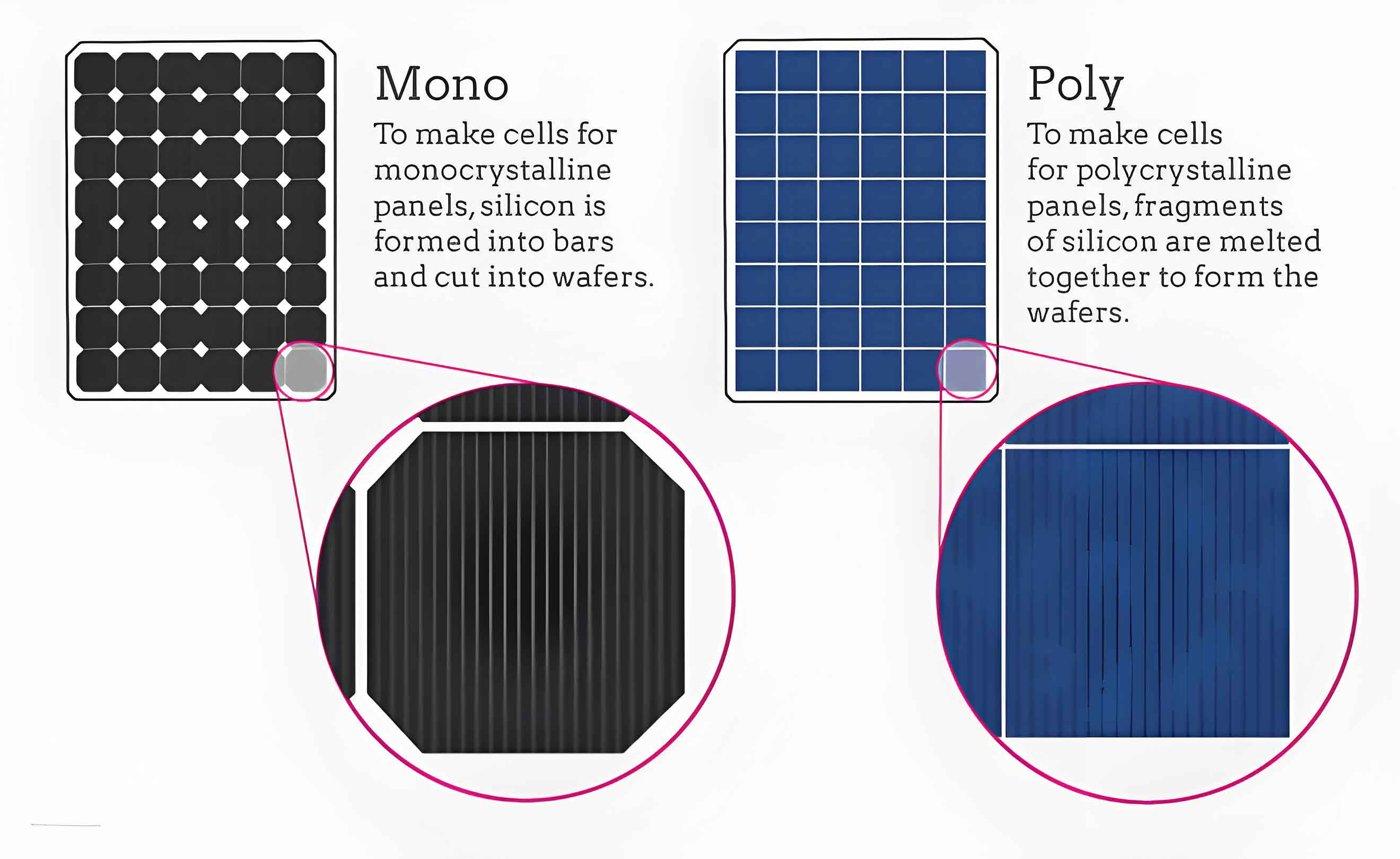
Overview of Photovoltaic Panels
Photovoltaic panels convert sunlight into electricity through the photovoltaic effect. Both monocrystalline and polycrystalline photovoltaic panels serve this purpose, but they differ in their manufacturing processes, efficiency, and cost.
Monocrystalline Photovoltaic Panels
Monocrystalline photovoltaic panels are made from a single, continuous crystal structure. This type of photovoltaic panel is known for its high efficiency and sleek appearance.
Table 1: Key Characteristics of Monocrystalline Photovoltaic Panels
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficiency | Typically between 15% and 20% |
| Manufacturing Process | Made from single silicon crystals, cut into wafers |
| Appearance | Uniform black color with rounded edges |
| Space Efficiency | Requires less space for the same power output compared to polycrystalline photovoltaic panels |
| Lifespan | Typically 25 to 30 years |
| Cost | Higher initial cost compared to polycrystalline photovoltaic panels |
Advantages of Monocrystalline Photovoltaic Panels
- High Efficiency: Monocrystalline photovoltaic panels offer the highest efficiency rates due to their high-purity silicon content.
- Space Efficiency: Due to their higher efficiency, monocrystalline photovoltaic panels require less space to produce the same amount of electricity.
- Longevity: These photovoltaic panels generally have a longer lifespan and often come with extended warranties.
Disadvantages of Monocrystalline Photovoltaic Panels
- Cost: The initial cost of monocrystalline photovoltaic panels is higher than that of polycrystalline photovoltaic panels.
- Temperature Sensitivity: Performance can decrease in extremely high temperatures.
Polycrystalline Photovoltaic Panels
Polycrystalline photovoltaic panels are made from silicon crystals that are melted together. These photovoltaic panels are known for their lower cost and blue, speckled appearance.
Table 2: Key Characteristics of Polycrystalline Photovoltaic Panels
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Efficiency | Typically between 13% and 16% |
| Manufacturing Process | Made from multiple silicon crystals melted together |
| Appearance | Blue color with a speckled, less uniform look |
| Space Efficiency | Requires more space for the same power output compared to monocrystalline photovoltaic panels |
| Lifespan | Typically 20 to 25 years |
| Cost | Lower initial cost compared to monocrystalline photovoltaic panels |
Advantages of Polycrystalline Photovoltaic Panels
- Cost: Polycrystalline photovoltaic panels are less expensive to produce and purchase.
- Durability: These photovoltaic panels are less affected by high temperatures compared to monocrystalline photovoltaic panels.
- Environmental Impact: The manufacturing process is simpler and generates less waste.
Disadvantages of Polycrystalline Photovoltaic Panels
- Lower Efficiency: Polycrystalline photovoltaic panels generally have lower efficiency rates.
- Space Requirements: They require more space to generate the same amount of electricity as monocrystalline photovoltaic panels.
- Aesthetic Appeal: The blue, speckled appearance may be less visually appealing to some homeowners.
Comparative Analysis
To better understand the differences between monocrystalline and polycrystalline photovoltaic panels, it is useful to compare them side-by-side.
Table 3: Comparison of Monocrystalline and Polycrystalline Photovoltaic Panels
| Feature | Monocrystalline Photovoltaic Panels | Polycrystalline Photovoltaic Panels |
|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 15% – 20% | 13% – 16% |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | Lower initial cost |
| Space Efficiency | More efficient, requires less space | Less efficient, requires more space |
| Appearance | Uniform black | Blue with speckled appearance |
| Lifespan | 25 – 30 years | 20 – 25 years |
| Temperature Sensitivity | More sensitive | Less sensitive |
Conclusion
Choosing between monocrystalline and polycrystalline photovoltaic panels depends on various factors, including budget, space availability, efficiency requirements, and aesthetic preferences. Monocrystalline photovoltaic panels are ideal for those seeking high efficiency and a sleek appearance, despite their higher cost. On the other hand, polycrystalline photovoltaic panels offer a cost-effective solution with slightly lower efficiency and a distinct blue appearance.
Ultimately, both types of photovoltaic panels provide a sustainable way to harness solar energy, contributing to reduced electricity bills and a lower carbon footprint. By understanding the differences and weighing the pros and cons, homeowners and businesses can make informed decisions that best suit their energy needs and financial considerations.
