Introduction
As the world moves towards a more sustainable and efficient energy future, the integration of solar battery storage with smart grids represents a pivotal development. Smart grids, equipped with advanced communication and control technologies, enable two-way communication between utilities and consumers, optimizing the distribution and consumption of electricity. Integrating solar battery storage with smart grids not only enhances the reliability and efficiency of power systems but also paves the way for greater renewable energy adoption. This article delves into the challenges and opportunities associated with this integration, providing a comprehensive overview of its potential impact on the energy landscape.
Understanding Smart Grids and Solar Battery Storage
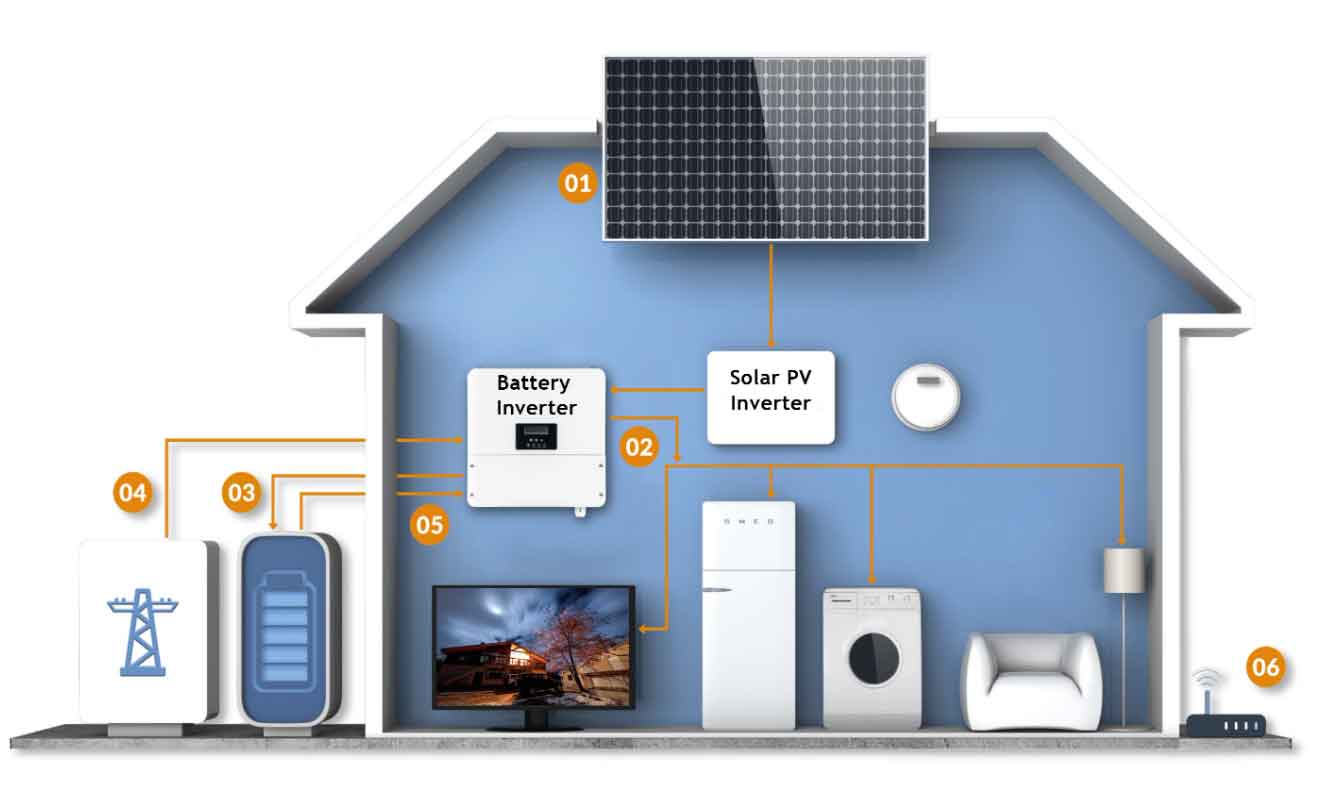
Smart grids are modernized electrical grids that use information and communication technologies to improve the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of electricity services. Key features include automated meter reading, real-time monitoring, and dynamic demand-response capabilities.
Solar battery storage systems, on the other hand, store excess energy generated by solar panels, making it available for use during periods of low solar output. When integrated with smart grids, these systems can enhance grid stability, reduce energy costs, and facilitate the seamless incorporation of renewable energy sources.
Opportunities of Integration
1. Enhanced Grid Stability and Reliability
The integration of solar battery storage with smart grids can significantly enhance grid stability and reliability. During peak demand periods, stored solar energy can be dispatched to alleviate stress on the grid, reducing the likelihood of blackouts and power outages.
2. Optimized Energy Management
Smart grids enable dynamic energy management, allowing for real-time adjustments based on consumption patterns and supply conditions. Solar battery storage systems can store excess solar energy during periods of low demand and release it during peak demand, optimizing energy use and reducing reliance on fossil fuels.
3. Increased Renewable Energy Adoption
Integrating solar battery storage with smart grids facilitates the integration of renewable energy sources. By storing excess energy and managing its distribution, these systems can help overcome the intermittent nature of solar power, making it a more reliable and consistent energy source.
4. Economic Benefits
The integration can lead to significant economic benefits for both utilities and consumers. By reducing peak demand, utilities can defer or avoid costly infrastructure investments. Consumers can benefit from lower energy costs and potential revenue streams from selling stored energy back to the grid.
5. Environmental Impact
Reducing reliance on fossil fuels through optimized use of solar energy directly contributes to lower greenhouse gas emissions. This integration supports broader environmental goals and helps combat climate change.
Challenges of Integration
1. Technical Challenges
Integrating solar battery storage with smart grids involves several technical challenges, including:
- Interoperability: Ensuring that different systems and technologies can communicate and work together seamlessly.
- Grid Stability: Managing the variability and unpredictability of solar power to maintain grid stability.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting the grid from cyber-attacks and ensuring data security.
2. Regulatory and Policy Barriers
The regulatory landscape for energy systems is often complex and can hinder the integration of new technologies. Policies need to be updated to support the deployment of smart grids and solar battery storage, including incentives for adoption and clear guidelines for grid interconnection.
3. Cost and Financing
While the costs of solar battery storage have been declining, the initial investment remains significant. Access to financing and incentives is crucial to make these technologies affordable for consumers and businesses.
4. Consumer Awareness and Acceptance
For successful integration, consumers need to be aware of the benefits and functionalities of smart grids and solar battery storage. Education and outreach programs are essential to increase acceptance and participation.
Comparative Analysis
The following table provides a comparative analysis of the opportunities and challenges associated with the integration of solar battery storage with smart grids:
| Aspect | Opportunities | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Grid Stability | Enhanced stability and reliability | Managing variability of solar power |
| Energy Management | Optimized energy use and reduced costs | Interoperability of different technologies |
| Renewable Energy Adoption | Increased adoption of renewable sources | Regulatory and policy barriers |
| Economic Benefits | Cost savings for utilities and consumers | High initial investment and financing needs |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced greenhouse gas emissions | Ensuring consumer awareness and acceptance |
| Cybersecurity | Improved security measures through smart systems | Protecting against cyber-attacks |
Future Outlook
The integration of solar battery storage with smart grids holds immense potential for transforming the energy landscape. As technology continues to advance, costs are expected to decrease, making these systems more accessible. Policymakers and industry stakeholders must work together to address the challenges and create a conducive environment for this integration.
Conclusion
The integration of solar battery storage with smart grids presents a unique opportunity to enhance the efficiency, reliability, and sustainability of power systems. While there are several challenges to overcome, the potential benefits in terms of grid stability, economic savings, increased renewable energy adoption, and environmental impact are significant. By addressing technical, regulatory, and consumer-related barriers, we can pave the way for a more resilient and sustainable energy future. As the energy landscape continues to evolve, the synergistic integration of these technologies will play a crucial role in achieving global energy and environmental goals.
