Chapter 1: Determine the Needs of Home Energy Storage Systems
Deciding how much electricity you want your home energy storage system to store and its purpose involves considering your energy needs, goals, and local conditions. Here’s a step-by-step approach to help you determine the right capacity and purpose for your home energy storage system:
1. Assess Your Energy Needs:
- Calculate your average daily electricity consumption. Review your utility bills to understand your usage patterns over time.
- Identify peak consumption hours when electricity rates are highest or when you experience the most frequent power outages.
2. Define Your Goals:
- Backup Power: If your primary goal is to have backup power during outages, determine how long you need the energy storage system to provide power for critical appliances. This will help you estimate the required capacity.
- Bill Reduction: If you want to reduce your electricity bills, consider peak shaving and load shifting. Analyze how much energy you want to store during off-peak hours to use during high-cost periods.
- Self-Sufficiency: If you aim to become more self-sufficient, evaluate how much of your daily energy needs you want to cover using stored energy.
3. Calculate Storage Capacity:
- Backup Power: Calculate the watt-hours needed to power critical appliances during an outage. Multiply this by the estimated duration of the outage to determine the required capacity.
- Bill Reduction: Estimate the amount of energy you want to store during off-peak hours and use it during peak hours. Consider both daily and seasonal variations in energy usage.
- Self-Sufficiency: Calculate the portion of your daily electricity consumption you want to cover using stored energy.
4. Consider System Efficiency and Depth of Discharge:
- Keep in mind that not all stored energy can be used due to system inefficiencies and limitations on how deeply batteries can be discharged. Factor in round-trip efficiency and the recommended depth of discharge for your chosen battery technology.
5. Evaluate Local Conditions:
- Research your region’s solar irradiance (if you plan to integrate solar panels) and weather patterns. This will affect the amount of energy you can generate and store.
6. Consult Professionals:
- If you’re unsure about your calculations or the technical aspects, consult with energy professionals, energy storage system providers, or solar installers. They can help you design an optimal system for your needs.
7. Balance Cost and Benefit:
- Determine your budget for the energy storage system, including installation costs. Compare the costs of different system capacities and technologies against the potential benefits, such as bill savings, resilience, and reduced carbon footprint.
In conclusion, the size and purpose of your home energy storage system depend on your energy goals, usage patterns, and local conditions. Careful planning and consideration of your needs will help you make an informed decision that aligns with your objectives and budget.
Chapter 2: Choose the Appropriate Home Energy Storage System Technology
Selecting the right home energy storage system technology involves understanding the strengths and limitations of different options and aligning them with your specific needs and goals. Consulting professionals, such as energy experts or energy storage system providers, can provide valuable insights tailored to your situation. Here’s an overview of some common home energy storage technologies to consider:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries:
- Advantages: Widely available, high energy density, good power density, established technology, suitable for various applications, and decreasing costs.
- Considerations: While lithium-ion batteries are versatile and commonly used, they may have limited cycle life in some cases and require proper management for safety.
- Sodium Sulfur (NaS) Batteries:
- Advantages: High energy density, long cycle life, and well-suited for stationary applications with daily cycling.
- Considerations: NaS batteries operate at high temperatures, requiring thermal management and safety precautions. They might be better suited for larger-scale applications.
- Flow Batteries (Vanadium Redox, Zinc-Flow, etc.):
- Advantages: Long cycle life, decoupled energy and power capacity, scalable, and suited for longer-duration energy storage.
- Considerations: Typically have lower energy density and higher system complexity, making them more suitable for grid-scale or larger residential installations.
- Lead-Acid Batteries (Advanced and AGM):
- Advantages: Relatively lower cost, mature technology, good for short-duration backup applications.
- Considerations: Lead-acid batteries have lower energy density, shorter cycle life, and maintenance requirements compared to newer technologies.
- Supercapacitors (Ultracapacitors):
- Advantages: Extremely fast charging and discharging, long cycle life, suitable for rapid power bursts.
- Considerations: Supercapacitors have lower energy density compared to batteries, making them better suited for short-term, high-power applications.
- Hybrid Systems:
- Advantages: Combining different technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries with supercapacitors, can provide benefits of both high energy density and rapid power delivery.
- Considerations: Hybrid systems might be more complex to design and control, requiring careful integration.
When consulting professionals, be prepared to discuss:
- Your Energy Needs: Outline your primary goals, whether it’s backup power, bill reduction, self-sufficiency, or a combination of these.
- Usage Patterns: Provide information about your daily energy consumption, peak usage times, and expected backup duration (if applicable).
- Budget: Specify your budget for the energy storage system, including installation costs.
- Local Conditions: Discuss factors like available space, solar potential (if you plan to integrate solar panels), and any regulations or restrictions.
Professionals can help you evaluate these factors and recommend the most suitable technology for your home energy storage system based on your unique requirements.
Chapter 3: Budget Planning for Home Energy Storage Systems
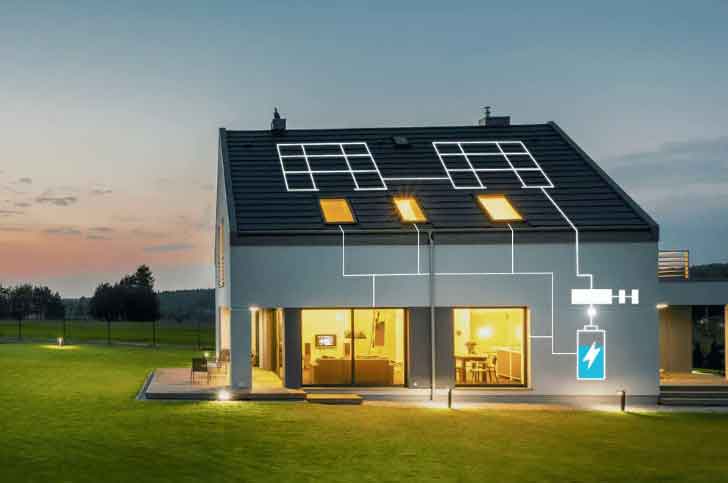

Creating a comprehensive budget plan for your home energy storage system involves considering the purchase cost of the system, installation expenses, and potential maintenance costs. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you budget effectively:
1. Determine Your Budget:
- Start by setting a total budget for your home energy storage system. Consider how much you’re willing to invest in the system, keeping in mind potential long-term savings and benefits.
2. Research energy storage system Options:
- Research different energy storage system technologies and brands to get an idea of their costs. The purchase cost can vary based on the type of technology, capacity, and brand.
3. Purchase Cost:
- Estimate the purchase cost of the energy storage system itself. This includes the cost of batteries, inverters, control systems, and any required accessories.
4. Installation Cost:
- Installation expenses can vary based on factors like system complexity, labor rates in your area, and whether you’re integrating the energy storage system with other systems (e.g., solar panels).
- If you’re not comfortable with DIY installation, get quotes from professional installers. They can provide a more accurate estimate based on your specific situation.
5. Additional Costs:
- Permit Fees: Depending on your local regulations, you might need to obtain permits for installing the energy storage system. Factor in potential permit fees.
- Electrical Work: If your home’s electrical system needs upgrades or modifications to accommodate the energy storage system, consider the associated costs.
6. Maintenance Costs:
- Different energy storage system technologies have varying maintenance requirements. Research the expected maintenance needs for the technology you’re considering.
- Include potential costs for battery replacements, routine inspections, and any required maintenance services.
7. Energy Savings and Benefits:
- Consider potential long-term benefits, such as reduced electricity bills, potential revenue from grid services (if applicable), and increased energy self-sufficiency.
8. Financial Incentives:
- Research available incentives, rebates, tax credits, or grants in your area that could help offset your costs.
9. Contingency Fund:
- It’s a good idea to allocate a small percentage of your budget as a contingency fund for unexpected expenses.
10. Total Budget Calculation:
- Add up the purchase cost, installation cost, maintenance estimates, permit fees, and any other additional costs. Subtract any potential incentives or benefits.
- The resulting total will give you an estimate of the overall budget required for your home energy storage system.
By carefully estimating and planning your budget, you’ll be better prepared to make an informed decision about the type of energy storage system that fits your needs while staying within your financial means.
Chapter 4: Choose Excellent Supplier of Home Energy Storage Systems
Choosing an excellent supplier for your home energy storage system is a crucial step to ensure the quality, performance, and reliability of the system. Here are some effective methods to find and select a reputable energy storage system supplier:
1. Internet Searches and Reviews:
- Search for energy storage system suppliers in your region using search engines or online directories.
- Look for customer reviews, testimonials, and ratings to gauge the experiences of others who have purchased from the supplier.
2. Word-of-Mouth Recommendations:
- Ask friends, family, neighbors, or colleagues if they have installed an energy storage system and inquire about their experiences with the supplier they used.
- Personal recommendations can provide valuable insights into the reliability and quality of a supplier.
3. Consulting Experts:
- Reach out to energy professionals, solar installers, or consultants who are knowledgeable about energy storage system technologies.
- Experts can recommend reputable suppliers based on your specific needs and circumstances.
4. Industry Conferences and Trade Shows:
- Attend energy storage industry events, trade shows, or conferences where energy storage system suppliers showcase their products.
- These events offer opportunities to interact with suppliers, learn about their offerings, and gather information.
5. Supplier Websites:
- Visit the websites of potential suppliers to learn about their product offerings, technology specifications, case studies, and contact information.
- Look for suppliers with transparent information and a strong online presence.
6. Request Quotes and Information:
- Contact shortlisted suppliers to request detailed information, quotes, and product specifications.
- A supplier’s responsiveness and willingness to address your questions can be indicative of their commitment to customer service.
7. Check Certifications and Quality Standards:
- Look for suppliers that adhere to industry standards and certifications for safety, quality, and environmental responsibility.
8. Warranty and Support:
- Inquire about warranty terms, post-purchase support, and after-sales services offered by the supplier.
9. Visit Showrooms or Installations:
- If possible, visit showrooms or installations where the supplier’s energy storage system products are in use.
- This allows you to see the technology in action and assess its performance firsthand.
10. Compare Multiple Options:
- Don’t settle for the first option you come across. Compare offerings from different suppliers in terms of technology, cost, warranty, and customer reviews.
11. Local Regulations and Compatibility:
- Ensure that the supplier’s products comply with local regulations and standards.
- Verify that the chosen energy storage system technology is compatible with your electrical system and any other systems you plan to integrate (e.g., solar panels).
By utilizing a combination of these methods, you can gather a well-rounded understanding of various energy storage system suppliers and make an informed decision that aligns with your needs and preferences.
Chapter 5: Customizing Suitable Home Energy Storage System for You
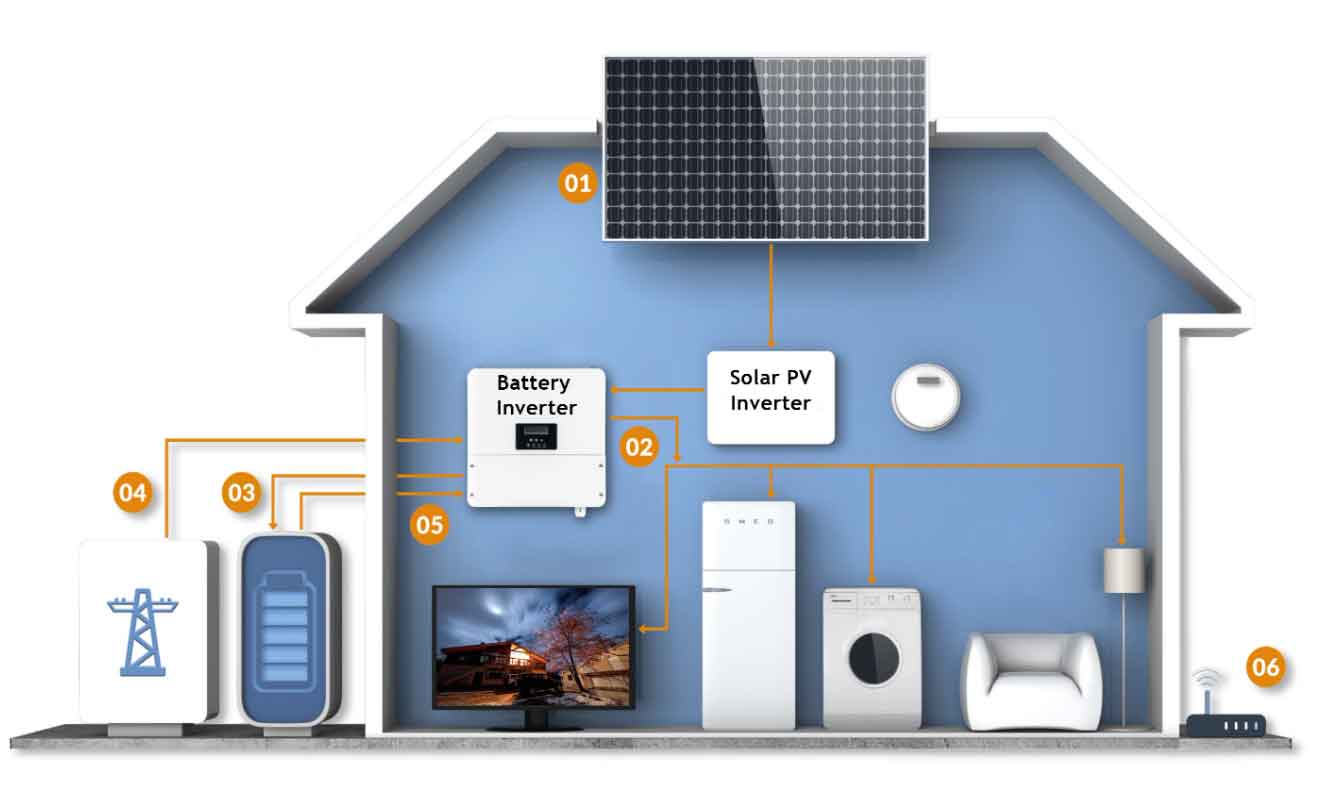
Customizing an energy storage system for your family’s needs involves several key decisions to ensure the system aligns with your energy goals, usage patterns, and budget. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you navigate the customization process:
1. Assess Your Energy Needs:
- Calculate your average daily electricity consumption and identify peak usage times.
- Determine if you want the energy storage system to provide backup power during outages, reduce electricity bills, or increase self-sufficiency.
2. Battery Capacity:
- Based on your energy needs, select a battery capacity that can store enough energy to meet your requirements.
- Consider both usable capacity (taking into account depth of discharge) and total capacity.
3. Technology Selection:
- Choose an energy storage system technology that suits your goals. For example, lithium-ion batteries offer high energy density, while flow batteries provide longer-duration storage.
4. Inverter Selection:
- Select an inverter that’s compatible with the chosen battery technology and capable of handling the power demands of your household.
- Determine whether you want an integrated inverter or a separate unit.
5. System Layout:
- Consider the physical space available for the energy storage system installation. If you’re integrating solar panels, ensure there’s sufficient space for both components.
- Decide if you want the energy storage system to be wall-mounted or floor-standing.
6. Integration with Solar Panels (If Applicable):
- If you plan to install solar panels, ensure that the energy storage system and solar system are compatible and can work together seamlessly.
- Determine the solar capacity needed to charge the energy storage system effectively.
7. Energy Management and Control:
- Research energy management systems (EMS) or software solutions that allow you to monitor and control your energy storage system remotely.
- Consider EMS features such as real-time monitoring, energy scheduling, and integration with smart home systems.
8. Backup Power Configuration:
- If backup power is a priority, decide which critical appliances or circuits you want to power during outages.
- Configure the energy storage system and inverter to prioritize backup power when the grid is down.
9. Budget Considerations:
- Balance your customization choices with your budget. Opt for the features and capacities that align with your financial resources.
10. Professional Consultation:
- If you’re unsure about the technical aspects, consult with energy storage system providers, energy professionals, or installers. They can provide expert advice on customization.
11. Future Expansion:
- Consider future expansion options. Some systems allow you to add more batteries as your energy needs evolve.
12. Safety Considerations:
- Ensure that your customized energy storage system adheres to safety guidelines and regulations. Battery installation and integration should be done following proper safety practices.
By carefully customizing your energy storage system, you’ll be able to create a solution that meets your family’s energy goals, enhances your energy independence, and contributes to a more sustainable energy future.
Chapter 6: License to Install Home Energy Storage Systems.
The installation of a household energy storage system, especially when connected to the power grid, is subject to regulations and may require obtaining licenses, permits, or approvals. The specific requirements vary depending on your location, local regulations, and the capacity of the energy storage system. Here are some key considerations:
1. Local Regulations:
- Research and understand the regulations and guidelines specific to your region or country. These regulations can include safety standards, grid interconnection rules, and environmental requirements.
2. Grid Connection Rules:
- If you plan to connect your energy storage system to the power grid, you may need to adhere to grid connection rules set by your utility company or grid operator. These rules ensure the safe and reliable integration of your system into the grid.
3. Building Codes:
- Some jurisdictions have building codes or zoning regulations that dictate the installation and placement of energy storage systems. Ensure compliance with these codes to ensure safety and structural integrity.
4. Electrical Codes:
- Electrical codes ensure the safe installation of electrical systems, including energy storage system. Compliance with these codes helps prevent hazards and ensures proper electrical connections.
5. Permits and Approvals:
- Depending on the size and type of your energy storage system, you may need to obtain permits or approvals from local authorities before installation. This could include building permits, electrical permits, or renewable energy system permits.
6. Utility Approval:
- If you’re connecting to the grid, your utility company might require you to go through an approval process to ensure the compatibility of your energy storage system with their infrastructure.
7. Licensing and Certification:
- In some cases, individuals or installers may need to hold specific licenses or certifications to work on energy storage systems. Verify if your installer is properly certified.
8. Environmental Impact:
- Depending on the type of energy storage system and its components, there might be environmental regulations to consider, such as proper disposal of batteries or hazardous materials.
9. Interconnection Agreements:
- If you plan to participate in grid services, such as providing ancillary services or participating in demand response programs, you might need to sign interconnection agreements with the grid operator.
10. Professional Assistance:
- Consult with local energy professionals, installers, or renewable energy experts who are familiar with the regulations in your area. They can guide you through the regulatory process.
11. Insurance and Liability:
- Review your insurance policies to ensure coverage for your energy storage system. Some policies may require updates to cover the new installation.
It’s crucial to thoroughly research and understand the regulatory landscape in your location before proceeding with the installation of a household energy storage system. Failure to comply with regulations can result in safety hazards, legal issues, or challenges with grid integration. Consulting with professionals and engaging with local authorities will help ensure a smooth and compliant installation process.
Chapter 7: Installation of Home Energy Storage Systems
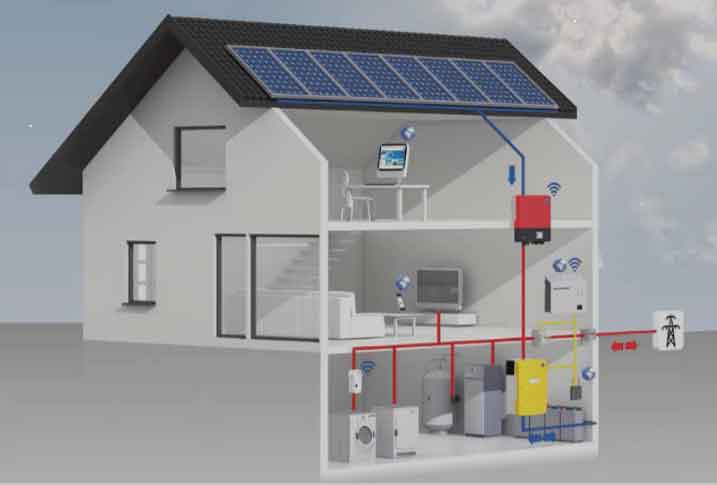

Selecting qualified and experienced professionals for the installation of your home energy storage system is essential to ensure the safety, reliability, and optimal performance of the system. Here are some steps to help you choose the right professionals for the job:
1. Research and Shortlisting:
- Research local installers or companies that specialize in energy storage system installations. Look for those with a track record of successful installations and positive customer reviews.
2. Qualifications and Certifications:
- Verify that the installers or technicians have the necessary qualifications and certifications to handle energy storage systems. Look for certifications related to electrical work, battery installation, and renewable energy systems.
3. Experience and Expertise:
- Choose professionals who have experience working with the specific type of energy storage system technology you’ve chosen. Different technologies might have varying installation requirements.
4. Licensing and Insurance:
- Ensure that the professionals hold valid licenses to perform electrical or renewable energy installations in your area.
- Check if the installer has liability insurance to cover any potential damages or accidents during the installation.
5. References and Portfolio:
- Ask for references from previous clients who have had energy storage system installations done by the professionals. This can provide insights into their work quality and customer satisfaction.
- Review their portfolio to see if they have successfully completed similar projects.
6. Knowledge of Local Regulations:
- Professionals should be familiar with local building codes, electrical codes, and grid interconnection requirements. They should ensure that the installation complies with all regulations.
7. On-Site Assessment:
- Invite potential installers to your property to assess the site and gather information about your energy needs, available space, and electrical infrastructure.
8. Clear Communication:
- Choose professionals who communicate clearly, answer your questions, and provide detailed information about the installation process, timeline, and costs.
9. Written Quotes and Contracts:
- Request written quotes from shortlisted installers detailing the scope of work, costs, and any warranties offered.
- Sign a contract that outlines the terms and conditions of the installation, including payment terms, timeline, and warranty coverage.
10. Warranty and After-Sales Support:
- Inquire about the warranty provided for the installation work. A reputable installer should stand behind their work and offer support in case of any issues.
11. Visit Previous Installations (if possible):
- If feasible, visit homes where the installer has previously completed energy storage system installations. This can give you a sense of their work quality and attention to detail.
By taking the time to research and select qualified professionals, you can ensure that your home energy storage system is installed correctly, adheres to safety regulations, and operates effectively over the long term.
Chapter 8: Testing of Home Energy Storage Systems
Testing your home energy storage system after installation is a crucial step to ensure its proper functioning, safety, and seamless integration with your home’s power system. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you test and verify the normal operation of your energy storage system:
1. Pre-Installation Checks:
- Before testing, ensure that all necessary permits, approvals, and interconnection agreements have been obtained.
2. Safety Precautions:
- Ensure that safety protocols are followed during testing. This includes wearing appropriate personal protective equipment and working in a safe environment.
3. System Connection and Integration:
- Verify that the energy storage system is properly connected to your home’s power system according to the manufacturer’s instructions and local electrical codes.
4. Initial Power-Up:
- Power up the energy storage system and ensure that all components, including batteries and inverters, are functioning and displaying the expected indicators.
5. Grid Connection (if applicable):
- If your energy storage system is connected to the grid, ensure that the connection is established properly and follows grid interconnection rules.
6. Functionality Testing:
- Test various functions of the energy storage system, such as charging, discharging, and switching between grid and backup modes (if applicable).
7. Emergency Power Test (Backup Systems):
- If your energy storage system is intended for backup power during outages, simulate an outage and verify that the energy storage system switches to backup mode seamlessly and powers the designated circuits or appliances.
8. Load Testing:
- Gradually increase and decrease the load on the energy storage system to verify that it responds correctly and maintains stable power supply.
9. Energy Management System (EMS):
- If your energy storage system has an energy management system, test its features, such as scheduling, remote monitoring, and optimization.
10. Charging and Discharging Efficiency:
- Measure the efficiency of the energy storage system by comparing the energy input during charging to the energy output during discharging.
11. Voltage and Frequency Regulation (Grid-Connected Systems):
- If your energy storage system provides grid services, test its ability to regulate voltage and frequency within the acceptable range.
12. Monitoring and Reporting:
- Monitor the system’s performance through any provided monitoring interface or software. Check for accurate data and alerts.
13. Documentation and Reports:
- Keep records of the testing process, including any test results, observations, and issues encountered.
14. Final Verification:
- Verify that the energy storage system meets your initial energy goals and requirements, and that it operates as intended.
15. Professional Assistance:
- If you’re not familiar with the technical aspects of testing an energy storage system, consider consulting with the installer or an expert to ensure accurate testing and proper functioning.
Completing thorough testing and verification ensures that your home energy storage system is ready to provide reliable backup power, energy savings, or other benefits as intended. It also helps identify and address any issues early, ensuring a smooth and trouble-free experience with your energy storage system.
Chapter 9: Monitoring of Home Energy Storage Systems

Monitoring and regular maintenance are essential practices to ensure the optimal performance, safety, and longevity of your home energy storage system. Here’s how you can effectively monitor your energy storage system and perform routine maintenance:
1. Monitoring:
- Most modern energy storage systems come with monitoring interfaces or software that allow you to track the system’s performance, energy flows, state of charge, and more.
- Regularly check the monitoring platform to ensure that the energy storage system is operating within expected parameters.
2. Monitoring Parameters:
- Monitor key parameters such as state of charge (SoC), state of health (SoH), charging and discharging rates, voltage levels, and system temperatures.
3. Data Logging and Alerts:
- Set up data logging to record historical performance data. Configure alerts to notify you of any abnormalities or system errors.
4. Remote Monitoring:
- Many energy storage systems offer remote monitoring capabilities, allowing you to access real-time data and alerts through your smartphone or computer.
5. Regular Maintenance:
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommended maintenance schedule to ensure the energy storage system remains in good condition.
6. Visual Inspection:
- Regularly inspect the physical components of the energy storage system, including batteries, inverters, and wiring, for signs of damage or wear.
7. Cooling and Ventilation:
- Ensure that the energy storage system is properly ventilated and cooled to prevent overheating, which can degrade battery performance and lifespan.
8. Cleaning:
- Keep the energy storage system and its surroundings clean and free from dust and debris that can affect performance.
9. Battery Maintenance:
- If your energy storage system includes batteries, follow the manufacturer’s guidelines for battery maintenance, which may include periodic balancing, equalization, and cleaning.
10. Firmware Updates:
- Regularly update the firmware of your energy storage system components to benefit from performance improvements, bug fixes, and security updates.
11. Professional Inspection:
- Schedule periodic professional inspections by certified technicians or ESS experts to assess the system’s health and address any issues.
12. Address Issues Promptly:
- If you notice any anomalies or performance deviations during monitoring, take action promptly. Investigate and address the issue to prevent further complications.
13. Safety Precautions:
- When performing maintenance, always follow safety guidelines provided by the manufacturer. Ensure proper shutdown procedures and use appropriate personal protective equipment.
14. Documentation:
- Keep detailed records of maintenance activities, including dates, performed tasks, and any issues encountered.
15. Warranty Considerations:
- Adhering to the recommended maintenance schedule is important to maintain warranty coverage for your energy storage system components.
By monitoring your home energy storage system and conducting regular maintenance, you can ensure that your system operates efficiently, delivers the intended benefits, and remains in good condition over its lifespan. Regular monitoring and maintenance help catch potential issues early and contribute to the long-term reliability of your energy storage system.
Chapter 10: Familiar with Guidelines for Using Home Energy Storage Systems
Familiarity with the guidelines for using home energy storage systems is crucial for ensuring safe and efficient operation. Here are some key guidelines to understand regarding charging and discharging, battery maintenance, and handling faults:
1. Charging and Discharging:
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions for charging and discharging your energy storage system. This might involve setting charge and discharge thresholds to prevent overcharging or overdischarging.
- Avoid rapid and extreme charge and discharge cycles, as they can impact the battery’s lifespan.
2. Battery Maintenance:
- Adhere to the maintenance recommendations provided by the manufacturer for the specific battery technology used in your energy storage system.
- Some battery technologies might require periodic balancing or equalization to ensure consistent performance across cells.
3. Proper Charging:
- Ensure that the energy storage system is charged using the correct voltage and current specifications provided by the manufacturer. Incorrect charging can damage the battery.
4. Cooling and Ventilation:
- Maintain proper cooling and ventilation for the energy storage system, especially if it contains batteries. High temperatures can degrade battery performance and lifespan.
5. Avoid Overloading:
- Do not overload the energy storage system by connecting appliances or devices that exceed the system’s rated capacity.
6. Handling Faults:
- Familiarize yourself with the system’s fault indicators and error codes. In case of a fault, consult the manufacturer’s documentation to understand the issue and potential remedies.
7. Safety Precautions:
- Always follow safety guidelines and precautions provided by the manufacturer when operating, maintaining, or troubleshooting the energy storage system.
8. Emergency Shut-Off:
- Be aware of the emergency shut-off procedures for the energy storage system. This is crucial in case of any unexpected issues or emergencies.
9. User Manual:
- Thoroughly read and understand the user manual provided by the manufacturer. It contains important information on system operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting.
10. Professional Assistance:
- If you encounter issues or are unsure about any aspect of using your energy storage system, seek assistance from professionals, installers, or the manufacturer’s support.
11. Maintenance Schedule:
- Stick to the recommended maintenance schedule for your energy storage system, including regular inspections, cleaning, and any necessary battery maintenance.
12. Warranty Considerations:
- Following the manufacturer’s guidelines for using and maintaining the energy storage system is often a requirement to maintain warranty coverage.
13. Regular Monitoring:
- Continuously monitor the performance and status of your energy storage system through the provided monitoring interface or software.
14. Update Knowledge:
- Stay updated with the latest information and guidelines provided by the manufacturer. Technology and best practices can evolve over time.
By thoroughly understanding and adhering to the guidelines for using your home energy storage system, you can maximize its efficiency, prolong its lifespan, ensure safety, and enjoy the benefits it offers.
