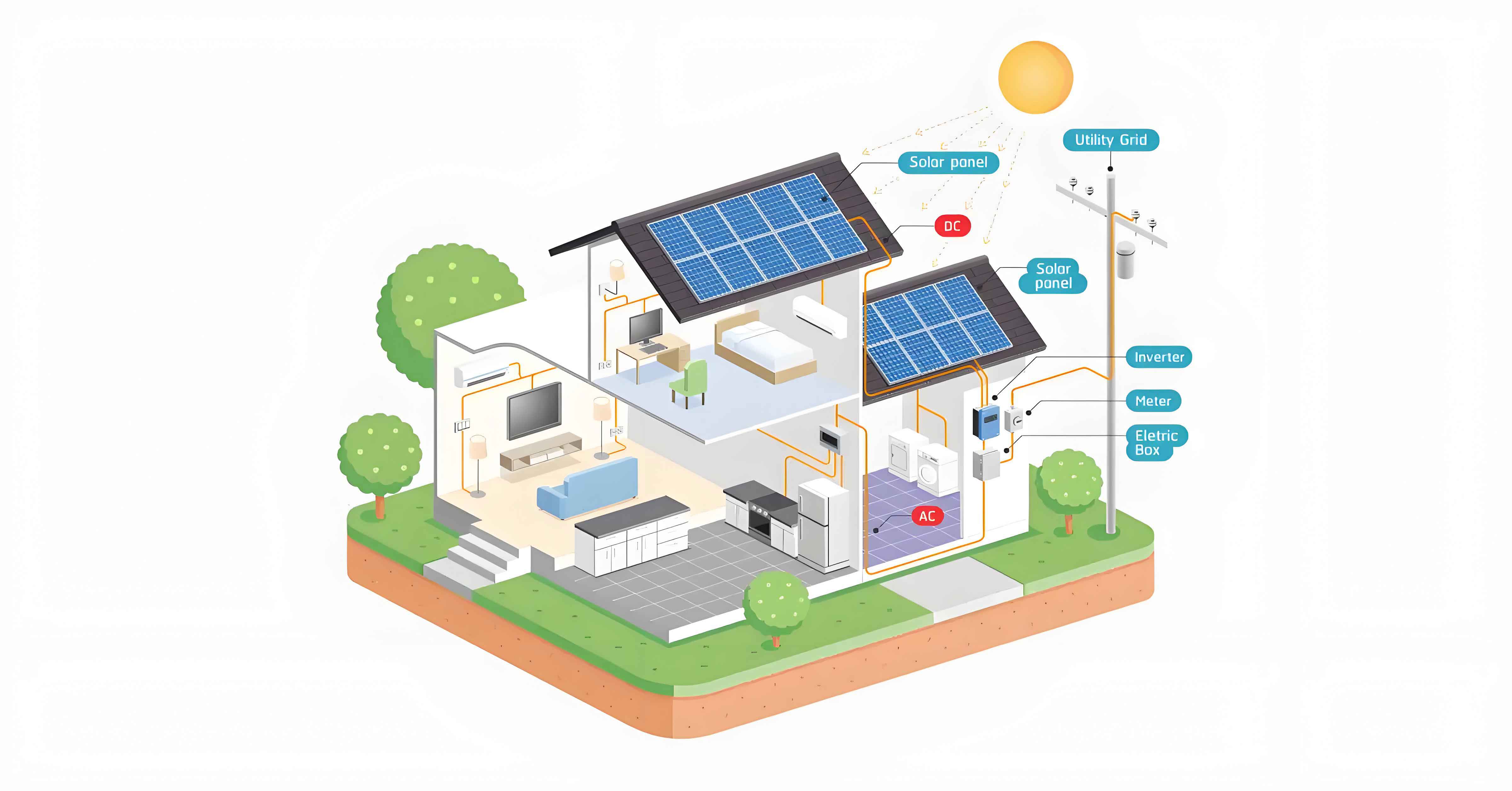
Introduction
The adoption of home solar battery system in remote and rural areas is rapidly increasing as more people seek reliable, sustainable, and independent energy solutions. Home solar battery system offer a viable alternative to traditional grid electricity, especially in areas where grid access is limited or non-existent. This article delves into the importance of home solar battery system, their components, design considerations, and benefits for remote and rural areas.
Importance of Home Solar Battery System
Home solar battery system play a crucial role in enhancing energy security and sustainability in remote and rural areas. Key benefits include:
- Energy Independence:
- Provides a reliable energy source without relying on the grid.
- Environmental Sustainability:
- Utilizes renewable solar energy, reducing carbon footprint.
- Cost Savings:
- Eliminates the need for expensive grid extensions and reduces energy bills.
- Reliability:
- Ensures a continuous power supply, crucial for essential services and daily living.
Key Components of Home Solar Battery System
An effective home solar battery system comprises several essential components that work together to generate, store, and distribute electricity.
Table 1: Key Components of Home Solar Battery System
| Component | Function |
|---|---|
| Solar Panels | Convert sunlight into direct current (DC) electricity |
| Charge Controller | Regulates the voltage and current from the solar panels to the batteries |
| Batteries | Store energy for use during periods without sunlight |
| Inverter | Converts DC electricity from the batteries to alternating current (AC) for household use |
| System Monitoring | Tracks performance and ensures optimal operation |
Designing a Home Solar Battery System
Designing a home solar battery system for remote and rural areas involves several critical steps to ensure it meets the energy needs of the household efficiently and reliably.
1. Assessing Energy Needs
Steps to Assess Energy Needs:
- Calculate Total Energy Consumption:
- List all electrical appliances and devices to be powered.
- Determine the wattage of each device and estimate the daily usage in hours.
- Calculate the total daily energy consumption in watt-hours (Wh).
Table 2: Example Energy Consumption Calculation
| Device | Wattage (W) | Daily Usage (hours) | Daily Consumption (Wh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator | 150 | 24 | 3600 |
| LED Lights (10) | 10 each | 5 | 500 |
| Laptop | 50 | 4 | 200 |
| TV | 100 | 3 | 300 |
| Water Pump | 500 | 1 | 500 |
| Total Daily Consumption | 5100 |
2. Sizing Solar Panels
Factors to Consider:
- Daily Solar Irradiance:
- Determine the average daily solar irradiance (kWh/m²/day) for the location.
- System Efficiency:
- Consider system losses due to inverter efficiency, battery charging, and temperature.
Calculation:
- Required Solar Panel Capacity (W):
- Divide the total daily energy consumption by the average daily solar irradiance.
- Adjust for system efficiency (typically around 75-85%).
Example Calculation:
- Daily energy consumption: 5100 Wh
- Average daily solar irradiance: 5 kWh/m²/day
- System efficiency: 80%
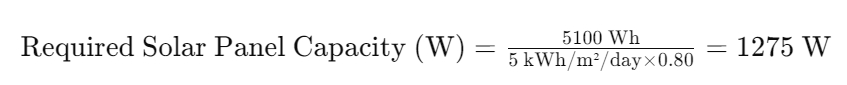
3. Sizing the Battery Bank
Factors to Consider:
- Autonomy Days:
- Number of days the system should operate without sunlight.
- Depth of Discharge (DoD):
- Maximum allowable discharge level to prolong battery life.
Calculation:
- Required Battery Capacity (Wh):
- Multiply the daily energy consumption by the number of autonomy days.
- Divide by the depth of discharge.
Example Calculation:
- Daily energy consumption: 5100 Wh
- Autonomy days: 3
- Depth of discharge: 50%
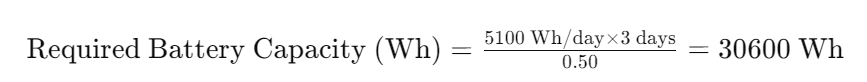
4. Selecting the Inverter
Factors to Consider:
- Total Load:
- Ensure the inverter can handle the peak load of all devices simultaneously.
- Surge Capacity:
- Inverters should manage temporary surges from devices like pumps and motors.
Example Calculation:
- Peak load: 1500 W (considering all devices running simultaneously)
- Surge capacity: At least 2000 W
Applications of Home Solar Battery System in Remote and Rural Areas
Home solar battery system is versatile and can be tailored for various applications in remote and rural areas:
1. Residential Applications
Benefits:
- Reliable Power:
- Provides electricity for lighting, appliances, and electronic devices in areas without grid access.
- Energy Self-Sufficiency:
- Reduces reliance on the grid by storing excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night.
List of Commonly Powered Devices:
- Lighting
- Refrigeration
- Water pumps
- Communication devices
- Small household appliances
2. Agricultural Applications
Benefits:
- Irrigation Systems:
- Powers water pumps for irrigation, enhancing crop yields in remote farms.
- Livestock Operations:
- Provides energy for automated feeding systems, electric fences, and lighting.
Table 3: Agricultural Energy Consumption Examples
| Application | Wattage (W) | Daily Usage (hours) | Daily Consumption (Wh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water Pump | 1000 | 3 | 3000 |
| Electric Fence | 50 | 24 | 1200 |
| Automated Feeder | 200 | 2 | 400 |
| Total Daily Consumption | 4600 |
3. Commercial Applications
Benefits:
- Remote Businesses:
- Supports energy needs for small businesses, shops, and kiosks in off-grid areas.
- Telecommunication Towers:
- Powers telecommunication equipment to ensure connectivity in remote regions.
List of Commonly Powered Devices:
- Communication equipment
- Computers and office equipment
- Refrigeration units
- Lighting systems
4. Emergency and Disaster Relief
Benefits:
- Portable Systems:
- Provides immediate power supply for medical equipment, communication devices, and lighting in disaster-stricken areas.
- Community Centers:
- Establishes reliable energy sources for shelters and relief centers during emergencies.
Table 4: Emergency Energy Consumption Examples
| Device | Wattage (W) | Daily Usage (hours) | Daily Consumption (Wh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Medical Refrigerator | 200 | 24 | 4800 |
| Communication Radio | 50 | 12 | 600 |
| Lighting (10 units) | 10 each | 8 | 800 |
| Total Daily Consumption | 6200 |
Advanced Technologies in Home Solar Battery System
1. Hybrid Systems
Description:
- Combines solar energy with other renewable sources such as wind or hydro, or with conventional generators to ensure a continuous power supply.
Benefits:
- Enhances system reliability and flexibility.
- Reduces dependency on a single energy source.
2. Smart Energy Management
Description:
- Utilizes advanced software and monitoring systems to optimize energy use and storage.
Benefits:
- Improves system efficiency by dynamically adjusting to energy demand and supply.
- Provides real-time data for better decision-making and maintenance.
3. Advanced Battery Technologies
Description:
- Incorporates newer battery technologies such as lithium-ion, flow batteries, and advanced lead-acid batteries.
Benefits:
- Increases energy storage capacity and lifespan.
- Enhances overall system efficiency and reliability.
Future Trends in Home Solar Battery System
The role of home solar battery system in remote and rural areas is expected to grow significantly in the coming years, driven by technological advancements and increasing demand for renewable energy solutions.
1. Advancements in Battery Technology
Trends:
- Higher Energy Density:
- Development of batteries with higher energy density to store more energy in a smaller space.
- Improved Lifespan:
- Research into materials and designs that enhance the lifespan and durability of batteries.
Example Technologies:
- Solid-state batteries
- Advanced lithium-sulfur batteries
2. Cost Reductions
Trends:
- Economies of Scale:
- Increasing production volumes and technological advancements are driving down the cost of battery storage.
- Innovation:
- Continued innovation in battery technology and manufacturing processes is expected to further reduce costs.
Table 5: Projected Cost Reductions in Battery Storage
| Year | Lithium-ion Cost ($/kWh) | Lead-acid Cost ($/kWh) | Flow Battery Cost ($/kWh) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 350 | 150 | 600 |
| 2026 | 300 | 140 | 550 |
| 2028 | 250 | 130 | 500 |
3. Integration with Smart Grids
Trends:
- Smart Energy Management:
- Integration of battery storage with smart grids to optimize energy distribution and usage.
- Grid Services:
- Use of battery storage for grid services such as frequency regulation, voltage support, and load balancing.
Conclusion
Home solar battery system is transformative for remote and rural areas, providing reliable, sustainable, and cost-effective energy solutions. By understanding the components, design considerations, and applications, individuals and communities can harness the full potential of solar energy to enhance their quality of life and ensure energy security. With ongoing advancements in technology and decreasing costs, the adoption of home solar battery system is set to expand, making renewable energy accessible to even the most remote regions.
