Introduction
Integrating Solar Power Battery Systems with the grid is a critical step toward achieving a reliable, sustainable, and efficient energy infrastructure. Solar battery storage systems not only enhance the utilization of solar energy but also support grid stability and resilience. This article explores the importance of grid integration with solar battery storage, the benefits, key components, challenges, and future trends.
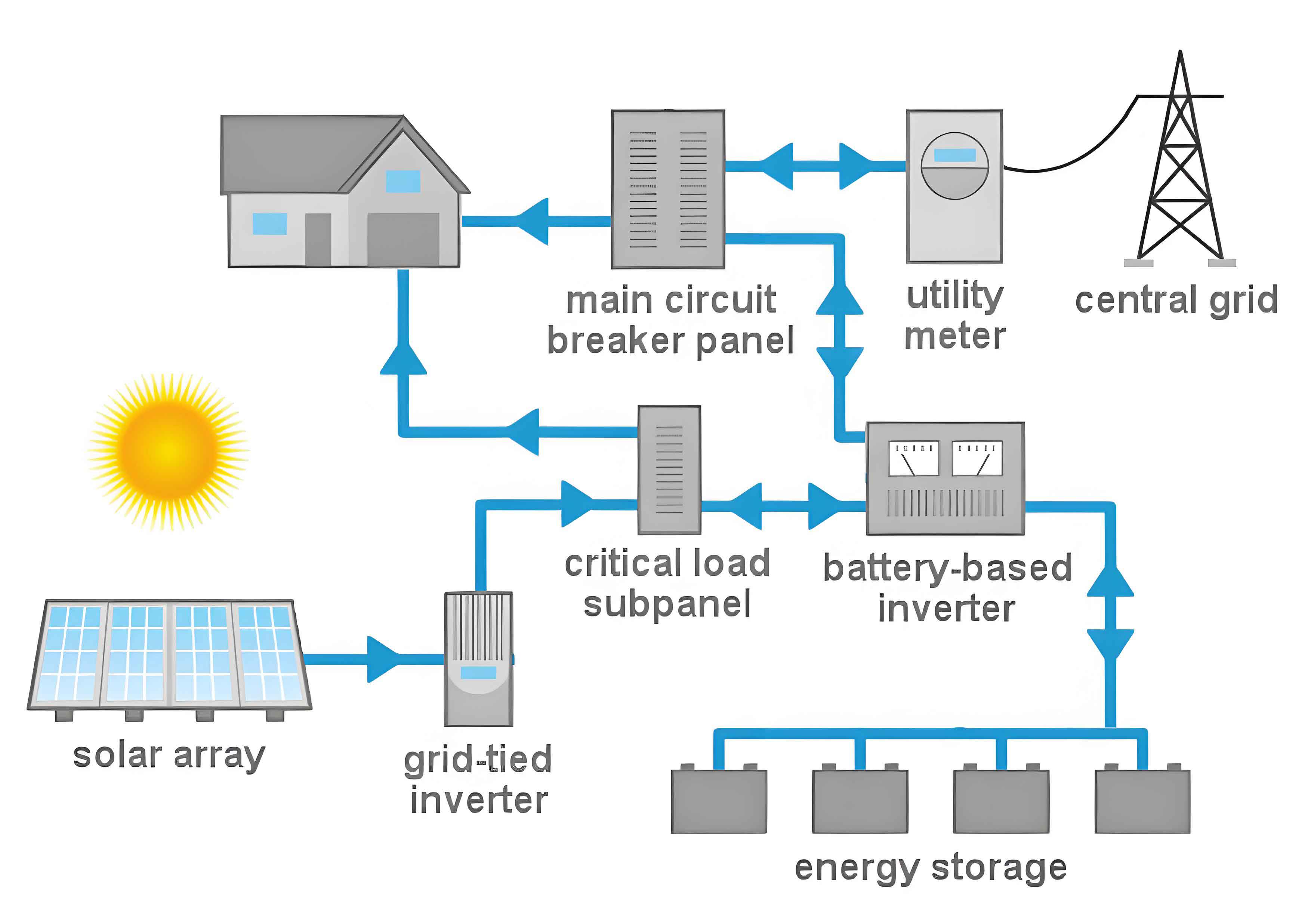
Importance of Grid Integration with Solar Battery Storage
Grid integration of Solar Power Battery Systems ensures that the generated solar energy is efficiently stored and distributed, optimizing energy use and supporting grid operations. This integration is vital for:
- Balancing Supply and Demand: Ensuring a steady supply of electricity by storing excess energy and releasing it during peak demand.
- Enhancing Grid Stability: Providing ancillary services such as frequency regulation and voltage support.
- Facilitating Renewable Energy Penetration: Enabling higher integration of renewable energy sources into the grid.
Benefits of Grid Integration with Solar Battery Storage
1. Enhanced Energy Efficiency
Grid-integrated Solar Power Battery Systems optimize the use of solar energy by storing excess production and utilizing it when needed, reducing energy waste.
Key Points:
- Energy Utilization: Maximizes the use of solar-generated energy.
- Reduced Transmission Losses: Locally stored energy reduces losses during transmission.
Table 1: Energy Efficiency Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Energy Utilization | Maximizes use of solar-generated energy |
| Reduced Transmission Losses | Decreases energy loss during transmission |
2. Grid Stability and Reliability
Solar battery storage systems contribute to grid stability and reliability by providing essential grid services.
Key Points:
- Frequency Regulation: Maintains stable grid frequency by absorbing or releasing energy as needed.
- Voltage Support: Provides reactive power to maintain voltage levels within acceptable ranges.
- Black Start Capability: Restores grid operation after a blackout by providing the initial power required.
Table 2: Grid Stability Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Frequency Regulation | Maintains stable grid frequency |
| Voltage Support | Ensures voltage levels are within acceptable ranges |
| Black Start Capability | Restores grid operation after a blackout |
3. Economic Benefits
Integrating Solar Power Battery Systems with the grid provides significant economic advantages.
Key Points:
- Peak Shaving: Reduces peak demand charges by using stored energy during high-demand periods.
- Load Shifting: Shifts energy usage from peak to off-peak times, optimizing energy costs.
- Reduced Infrastructure Costs: Minimizes the need for additional grid infrastructure investments.
Table 3: Economic Benefits
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Peak Shaving | Reduces peak demand charges |
| Load Shifting | Optimizes energy costs by shifting usage |
| Reduced Infrastructure Costs | Minimizes need for additional grid investments |
Key Components of Grid-Integrated Solar Power Battery Systems
1. Batteries
Batteries are the core component of Solar Power Battery Systems, storing the energy generated by solar panels.
Types of Batteries:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: High energy density and efficiency, commonly used in residential and commercial applications.
- Lead-Acid Batteries: Cost-effective but lower energy density and shorter lifespan.
- Flow Batteries: Suitable for large-scale applications due to their scalability and long-duration storage capabilities.
Table 4: Types of Batteries
| Battery Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | High energy density and efficiency |
| Lead-Acid Batteries | Cost-effective but lower energy density |
| Flow Batteries | Scalable and long-duration storage |
2. Inverters
Inverters convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) electricity used by most household appliances.
Key Points:
- DC to AC Conversion: Essential for making solar energy usable in homes and businesses.
- Efficiency: High-efficiency inverters minimize energy loss during conversion.
- Grid-Tie Capability: Allows the system to feed excess power back to the grid.
Table 5: Inverter Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| DC to AC Conversion | Converts solar-generated DC electricity to AC |
| Efficiency | Minimizes energy loss during conversion |
| Grid-Tie Capability | Feeds excess power back to the grid |
3. Battery Management System (BMS)
A Battery Management System (BMS) monitors and manages the performance and safety of the batteries.
Key Points:
- Health Monitoring: Tracks battery health and performance.
- Safety Management: Prevents overcharging, overheating, and other safety issues.
- Optimization: Ensures optimal performance and longevity of the battery system.
Table 6: BMS Functions
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Health Monitoring | Tracks battery health and performance |
| Safety Management | Prevents overcharging and overheating |
| Optimization | Ensures optimal performance and longevity |
Challenges of Grid Integration with Solar Power Battery Systems
1. Technical Challenges
Integrating Solar Power Battery Systems with the grid presents several technical challenges.
Key Points:
- Grid Compatibility: Ensuring that solar battery storage systems are compatible with existing grid infrastructure.
- Intermittency Management: Managing the variability of solar energy production.
- Cybersecurity: Protecting grid-integrated systems from cyber threats.
Table 7: Technical Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| Grid Compatibility | Ensuring compatibility with existing infrastructure |
| Intermittency Management | Managing variability in solar energy production |
| Cybersecurity | Protecting systems from cyber threats |
2. Economic Challenges
Economic challenges also play a significant role in the grid integration of solar battery storage systems.
Key Points:
- High Initial Costs: The upfront cost of solar battery storage systems can be substantial.
- Economic Viability: Ensuring the long-term economic viability of solar battery storage investments.
- Market Regulations: Navigating complex energy market regulations and policies.
Table 8: Economic Challenges
| Challenge | Description |
|---|---|
| High Initial Costs | Significant upfront cost of battery systems |
| Economic Viability | Ensuring long-term viability of investments |
| Market Regulations | Navigating complex energy market policies |
Future Trends in Grid Integration with Solar Battery Storage
1. Advanced Grid Management Technologies
The integration of advanced grid management technologies will enhance the efficiency and reliability of grid-integrated solar battery storage systems.
Key Points:
- Smart Grids: Leveraging smart grid technologies for real-time energy management.
- AI and Machine Learning: Using AI and machine learning for predictive analytics and optimization.
- Blockchain: Implementing blockchain for secure and transparent energy transactions.
Table 9: Advanced Grid Management Technologies
| Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Smart Grids | Real-time energy management |
| AI and Machine Learning | Predictive analytics and optimization |
| Blockchain | Secure and transparent energy transactions |
2. Policy and Regulatory Support
Supportive policies and regulations will play a crucial role in promoting the integration of solar battery storage systems with the grid.
Key Points:
- Incentives and Subsidies: Providing financial incentives for solar battery storage investments.
- Standardization: Developing standards for interoperability and safety.
- Long-Term Planning: Implementing long-term energy planning strategies.
Table 10: Policy and Regulatory Support
| Support | Description |
|---|---|
| Incentives and Subsidies | Financial incentives for investments |
| Standardization | Standards for interoperability and safety |
| Long-Term Planning | Long-term energy planning strategies |
Conclusion
Grid integration of Solar Power Battery Systems is essential for optimizing energy use, enhancing grid stability, and supporting the transition to a sustainable energy future. By addressing technical and economic challenges, and leveraging advanced technologies and supportive policies, the integration of solar battery storage systems with the grid can unlock significant benefits for energy markets and consumers alike.
As technology continues to evolve, and as the adoption of renewable energy sources accelerates, the role of solar battery storage in grid integration will become increasingly critical. Embracing these advancements and fostering a collaborative approach among stakeholders will be key to achieving a resilient, efficient, and sustainable energy system for the future.
