As the demand for renewable energy continues to rise, Solar Power for Home integration is experiencing significant advancements. Homeowners are increasingly seeking efficient, cost-effective, and aesthetically pleasing solutions to harness solar energy. This article explores the emerging trends in Solar Power for Home integration, highlighting innovative technologies, design improvements, and the impact of policy and market dynamics.
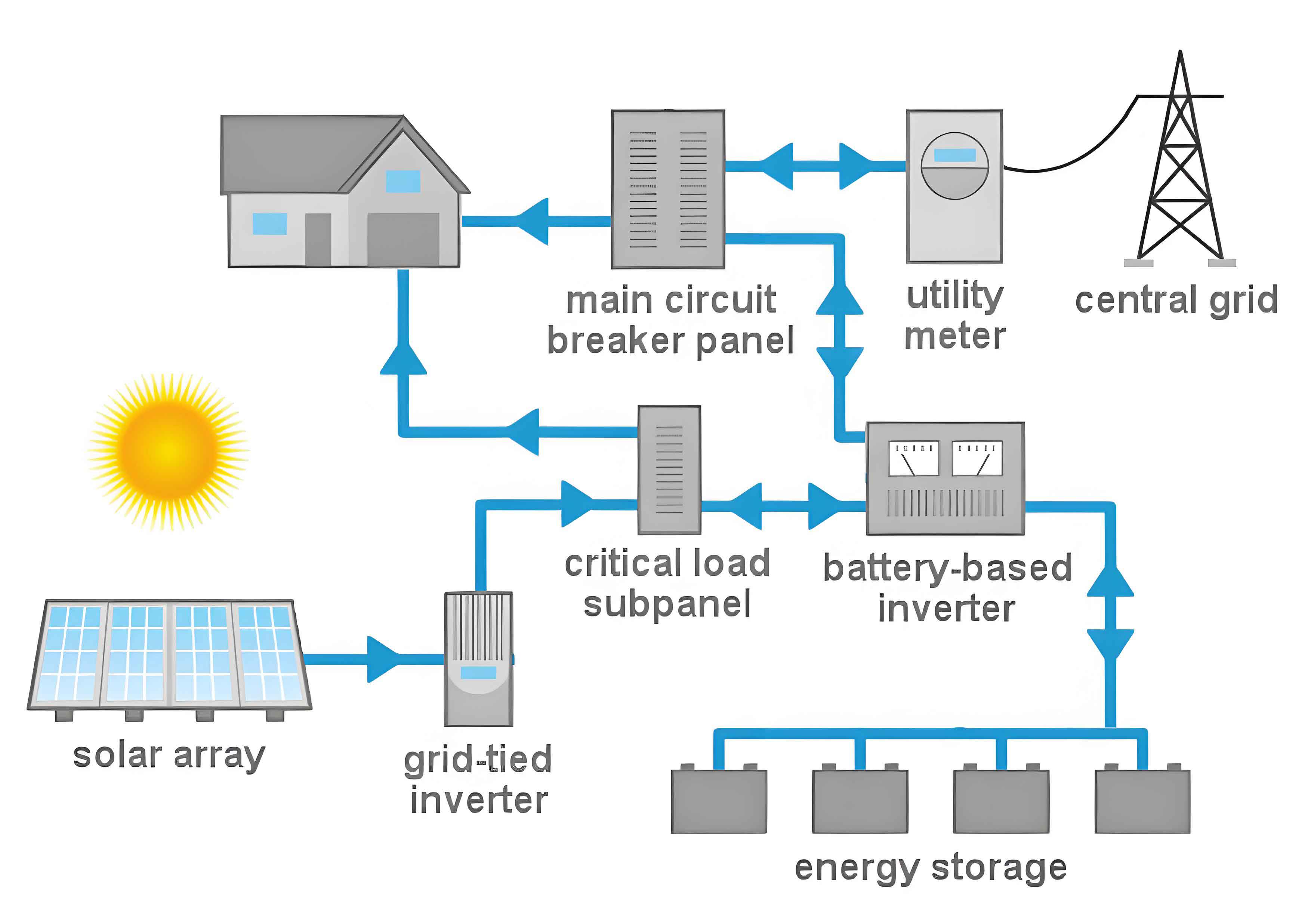
Technological Advancements in Solar Power for Home
1. Advanced Photovoltaic Materials
Recent developments in photovoltaic materials are enhancing the efficiency and performance of Solar Power for Home systems. Innovations such as perovskite solar cells, organic photovoltaics, and tandem solar cells are pushing the boundaries of what is possible in residential solar energy.
Key Innovations:
- Perovskite Solar Cells: Known for high efficiency and low production costs.
- Organic Photovoltaics: Flexible and lightweight, suitable for a variety of applications.
- Tandem Solar Cells: Combining different materials to achieve higher efficiency.
2. Smart Solar Inverters
Smart solar inverters are revolutionizing Solar Power for Home integration by providing real-time monitoring, energy management, and optimization. These inverters can communicate with other smart home devices, ensuring efficient energy use and maximizing solar energy production.
Key Features:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Provides homeowners with data on energy production and consumption.
- Energy Management: Optimizes energy use based on demand and availability.
- Integration with Smart Home Systems: Enhances overall home energy efficiency.
3. Energy Storage Solutions
Energy storage is a critical component of Solar Power for Home systems, allowing homeowners to store excess energy for use during non-sunny periods or power outages. Advanced battery technologies, such as lithium-ion, solid-state, and flow batteries, are making energy storage more efficient and affordable.
Key Technologies:
- Lithium-Ion Batteries: Widely used for their high energy density and reliability.
- Solid-State Batteries: Promising higher energy density and improved safety.
- Flow Batteries: Offering scalability and long cycle life.
Design Improvements in Solar Power for Home
1. Aesthetic Solar Panels
Aesthetic solar panels are designed to blend seamlessly with the home’s architecture, addressing one of the main concerns of homeowners regarding the visual impact of solar installations. These panels come in various colors and designs, including solar shingles and tiles.
Key Features:
- Solar Shingles: Look like traditional roofing materials while generating electricity.
- Customizable Colors: Panels available in colors that match the home’s exterior.
- Integrated Designs: Panels that blend with architectural elements.
2. Bifacial Solar Panels
Bifacial solar panels capture sunlight from both sides, increasing the overall energy production. These panels are particularly effective in areas with high albedo surfaces, such as snowy regions or rooftops with reflective coatings.
Key Advantages:
- Dual-Sided Energy Generation: Higher total energy output.
- Increased Efficiency: Improved performance in various installation environments.
- Durability: Enhanced resistance to environmental factors.
Policy and Market Dynamics
1. Government Incentives
Government incentives play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of Solar Power for Home systems. These incentives include tax credits, rebates, and grants that can significantly reduce the initial installation costs.
Key Incentives:
- Federal Tax Credits: Reduce the overall tax liability for homeowners installing solar systems.
- State and Local Rebates: Additional financial support from state and local governments.
- Grants and Subsidies: Funding opportunities for renewable energy projects.
2. Net Metering Policies
Net metering policies allow homeowners to sell excess solar energy back to the grid, providing a financial return on their solar investment. These policies vary by region but generally support the financial viability of Solar Power for Home systems.
Key Points:
- Financial Incentives: Credits for excess energy fed back into the grid.
- Increased ROI: Higher return on investment for solar installations.
- Policy Variations: Different regulations and benefits depending on location.
3. Market Growth and Cost Reduction
The solar market is experiencing rapid growth, leading to economies of scale and reductions in the cost of solar technology. Increased competition and technological advancements are making Solar Power for Home more accessible and affordable.
Market Trends:
- Decreasing Costs: Lower prices for solar panels and installation.
- Increased Competition: More options and better prices for consumers.
- Technological Advancements: Continuous improvements driving efficiency and affordability.
Comparative Table of Emerging Technologies
| Technology | Key Features | Advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Perovskite Solar Cells | High efficiency, low production costs | Cost-effective, efficient |
| Organic Photovoltaics | Flexible, lightweight | Versatile, adaptable |
| Tandem Solar Cells | Combining materials for higher efficiency | Enhanced performance |
| Smart Solar Inverters | Real-time monitoring, energy management | Optimized energy use |
| Lithium-Ion Batteries | High energy density, reliability | Efficient storage |
| Solid-State Batteries | Higher energy density, improved safety | Advanced storage solution |
| Flow Batteries | Scalability, long cycle life | Flexible and durable storage |
| Aesthetic Solar Panels | Customizable colors, integrated designs | Improved aesthetics |
| Bifacial Solar Panels | Dual-sided energy generation, increased efficiency | Higher energy output |
Comparative Table of Policy and Market Dynamics
| Policy/Dynamic | Description | Impact on Solar Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Government Incentives | Tax credits, rebates, grants | Lower installation costs |
| Net Metering Policies | Selling excess energy back to the grid | Increased financial return |
| Market Growth and Cost Reduction | Economies of scale, increased competition | More affordable options |
Summary List of Key Trends
Technological Advancements:
- Development of advanced photovoltaic materials like perovskite and tandem solar cells.
- Emergence of smart solar inverters with real-time monitoring and energy management.
- Advancements in energy storage solutions including lithium-ion, solid-state, and flow batteries.
Design Improvements:
- Introduction of aesthetic solar panels such as solar shingles and customizable color panels.
- Adoption of bifacial solar panels for dual-sided energy generation.
Policy and Market Dynamics:
- Availability of government incentives including tax credits, rebates, and grants.
- Implementation of net metering policies allowing financial returns on excess energy.
- Market growth leading to cost reductions and increased competition.
Conclusion
The integration of Solar Power for Home is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements, design improvements, and supportive policy and market dynamics. Innovations in photovoltaic materials, smart inverters, and energy storage solutions are making solar energy more efficient and accessible. Design improvements such as aesthetic solar panels and bifacial panels are addressing homeowner concerns about the visual impact of solar installations. Government incentives, net metering policies, and market growth are further encouraging the adoption of Solar Power for Home, making it a viable and attractive option for homeowners seeking sustainable and cost-effective energy solutions. As these trends continue to develop, Solar Power for Home will play an increasingly important role in achieving energy independence and environmental sustainability.
