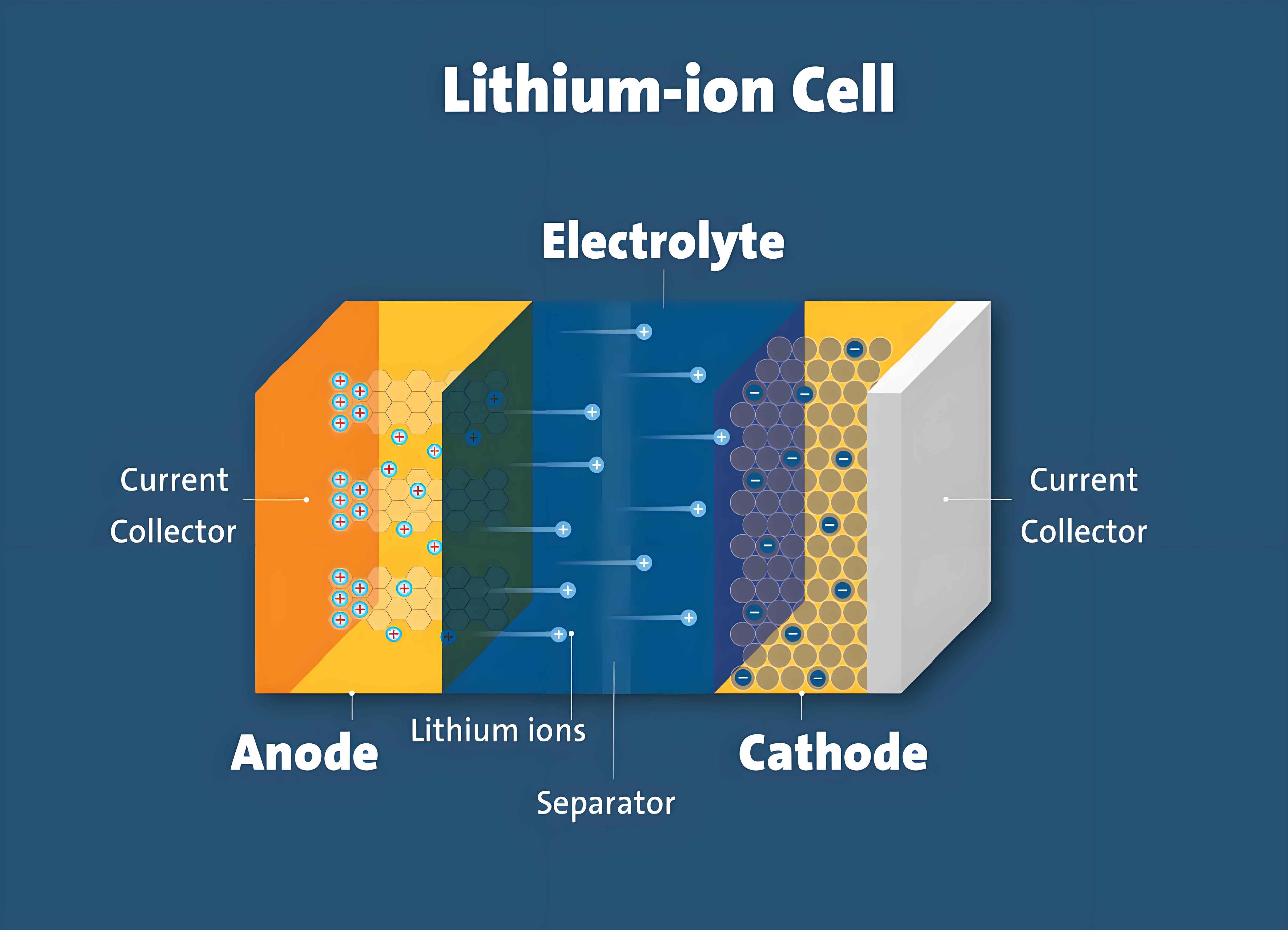
Lithium-Ion cells have revolutionized energy storage and are widely recognized for their pivotal role in the electric vehicle industry. However, their potential extends far beyond this application. With advancements in technology, Lithium-Ion cells are finding new and innovative uses in various sectors. This article explores emerging markets and applications for Lithium-Ion cells beyond electric vehicles, highlighting their transformative impact on energy storage solutions across different industries.
Key Properties of Lithium-Ion Cells
Lithium-Ion cells are favored for their unique properties that make them suitable for diverse applications:
- High Energy Density: Lithium-Ion cells can store a large amount of energy in a compact form.
- Long Cycle Life: These cells can endure many charge-discharge cycles with minimal capacity degradation.
- Rapid Charge and Discharge Rates: Lithium-Ion cells can quickly absorb and release energy.
- High Efficiency: They offer high round-trip efficiency, meaning most of the stored energy is retrievable.
- Lightweight: Lithium-Ion cells are relatively lightweight compared to other battery technologies.
Emerging Markets for Lithium-Ion Cells
1. Renewable Energy Storage
Lithium-Ion cells are increasingly used in renewable energy storage systems to manage the intermittent nature of solar and wind power.
Applications:
- Residential Energy Storage: Homeowners use Lithium-Ion cells to store excess solar energy generated during the day for use at night.
- Commercial Energy Storage: Businesses implement large-scale storage systems to balance energy loads and reduce dependency on the grid.
- Grid Stabilization: Utilities use Lithium-Ion cells to stabilize the grid, manage peak loads, and integrate renewable energy sources.
2. Portable Electronics
The demand for longer-lasting, more efficient power sources for portable electronics continues to grow.
Applications:
- Smartphones and Tablets: Enhanced energy density and rapid charging capabilities make Lithium-Ion cells ideal for mobile devices.
- Laptops and Wearable Devices: Lightweight and compact Lithium-Ion cells extend the battery life and usability of portable electronics.
- Power Tools: Lithium-Ion cells provide high power output and quick recharging for cordless power tools.
3. Medical Devices
Lithium-Ion cells are critical in powering various medical devices, offering reliability and long-lasting energy.
Applications:
- Implantable Devices: Pacemakers and other implantable medical devices rely on the long life and stability of Lithium-Ion cells.
- Portable Medical Equipment: Devices such as defibrillators, ventilators, and infusion pumps use Lithium-Ion cells for their portability and reliability.
- Wearable Health Monitors: Fitness trackers and health monitoring devices benefit from the lightweight and efficient energy storage of Lithium-Ion cells.
4. Aerospace and Defense
Lithium-Ion cells are used in aerospace and defense applications due to their high energy density and reliability.
Applications:
- Satellites: Lithium-Ion cells provide reliable power for satellites, supporting various functions in space.
- Unmanned Aerial Vehicles (UAVs): UAVs, or drones, utilize Lithium-Ion cells for longer flight times and efficient energy use.
- Military Equipment: Portable military equipment, such as communication devices and night vision goggles, depend on the durability and efficiency of Lithium-Ion cells.
5. Marine Applications
The marine industry is exploring Lithium-Ion cells for energy storage solutions in boats and ships.
Applications:
- Electric Boats: Lithium-Ion cells power electric boats, providing a clean and efficient energy source.
- Submarines: Advanced Lithium-Ion cells are used in submarines for reliable, long-lasting power.
- Offshore Platforms: Energy storage systems on offshore oil and gas platforms benefit from the high capacity and reliability of Lithium-Ion cells.
Comparative Table of Emerging Applications
| Market | Application | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy Storage | Residential, Commercial, Grid Stabilization | Enhanced energy management, reduced grid dependency | High initial cost, recycling challenges |
| Portable Electronics | Smartphones, Laptops, Wearable Devices | Longer battery life, rapid charging | Limited lifespan, potential for overheating |
| Medical Devices | Implantable, Portable Medical Equipment | Reliability, long-lasting energy | Safety regulations, size constraints |
| Aerospace and Defense | Satellites, UAVs, Military Equipment | High energy density, reliability | Extreme operating conditions, cost |
| Marine Applications | Electric Boats, Submarines, Offshore Platforms | Clean energy, high capacity | Environmental impact, safety standards |
List of Factors Driving the Adoption of Lithium-Ion Cells
- Technological Advancements: Continuous improvements in Lithium-Ion cell technology enhance performance, safety, and cost-effectiveness.
- Environmental Concerns: The push for cleaner energy solutions drives the adoption of Lithium-Ion cells in various sectors.
- Regulatory Support: Government policies and incentives promoting renewable energy and energy storage technologies bolster the market for Lithium-Ion cells.
- Consumer Demand: Increasing demand for portable, reliable, and efficient power sources in consumer electronics and medical devices.
- Industry Innovation: Ongoing innovation in applications such as electric boats, drones, and satellites expands the market for Lithium-Ion cells.
Future Prospects for Lithium-Ion Cells
The future of Lithium-Ion cells looks promising as they continue to evolve and adapt to new applications. Several trends and developments are expected to shape their trajectory:
1. Solid-State Lithium-Ion Cells
Solid-state Lithium-Ion cells, which use a solid electrolyte instead of a liquid one, promise higher energy density, improved safety, and longer cycle life. These advancements could further expand the applications of Lithium-Ion cells.
2. Enhanced Recycling Technologies
Developing efficient and cost-effective recycling technologies for Lithium-Ion cells will address environmental concerns and reduce the need for raw material extraction.
3. Integration with Renewable Energy
The integration of Lithium-Ion cells with renewable energy systems will continue to grow, driven by the need for efficient energy storage solutions to balance supply and demand.
4. Expansion into New Markets
Emerging markets, such as smart cities, advanced transportation systems, and the Internet of Things (IoT), present new opportunities for the deployment of Lithium-Ion cells.
Conclusion
Lithium-Ion cells have proven to be a versatile and transformative energy storage technology, extending far beyond their initial application in electric vehicles. Their unique properties make them suitable for a wide range of emerging markets and applications, from renewable energy storage and portable electronics to medical devices and aerospace. As technology continues to advance, and as the demand for efficient and reliable energy storage solutions grows, Lithium-Ion cells will play an increasingly critical role in shaping the future of energy storage across various industries. By focusing on innovation, sustainability, and adaptability, Lithium-Ion cells will continue to drive progress and enable new possibilities in the ever-evolving energy landscape.
