The global push for sustainable and renewable energy sources has propelled the adoption of solar energy system to the forefront of the energy transition. Solar energy system, which convert sunlight into electricity, offer a clean, abundant, and sustainable energy solution. This article explores the factors driving the adoption of solar energy system worldwide, the challenges faced, and the strategies that can accelerate their deployment.
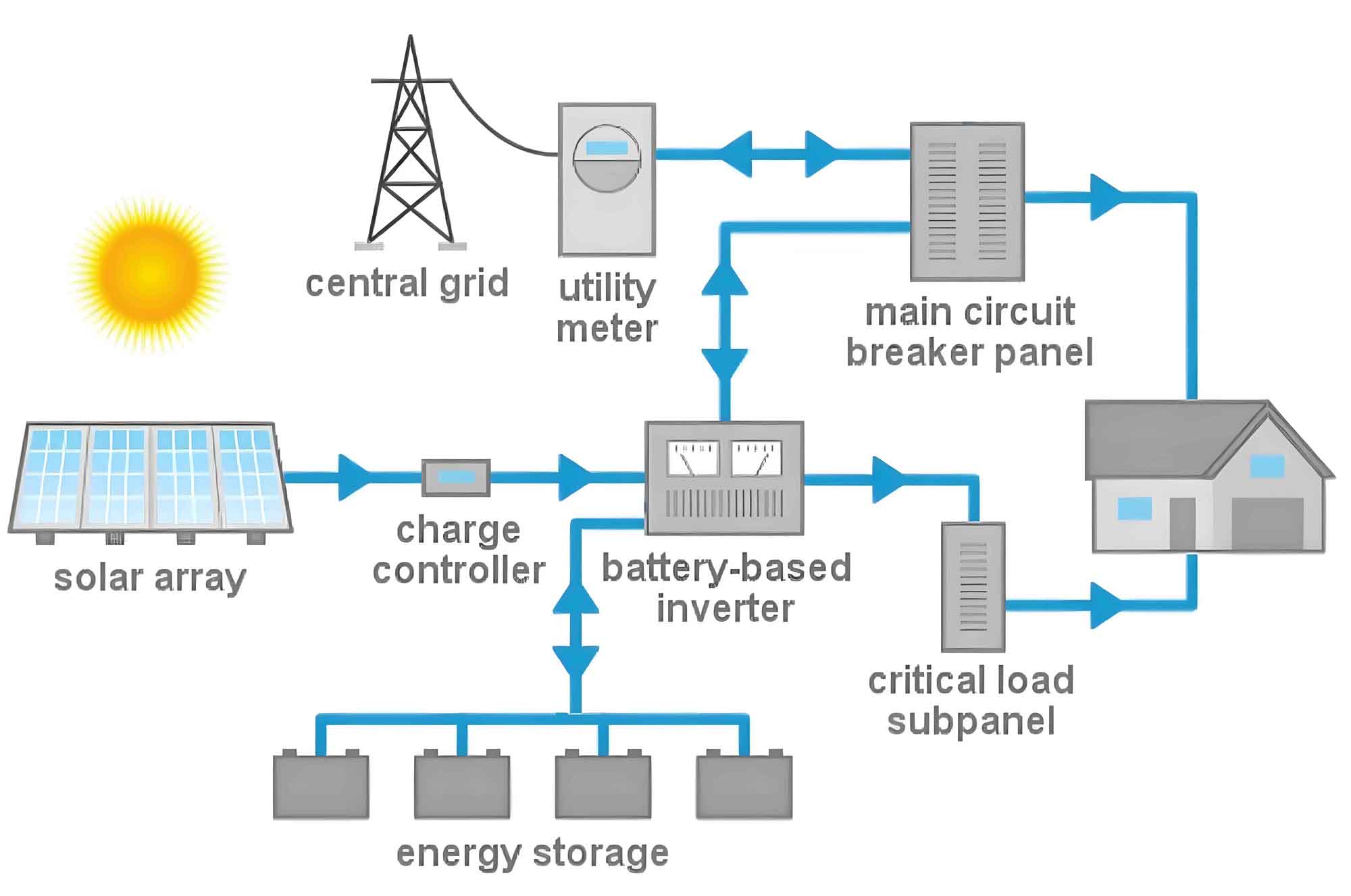
Factors Driving Solar Energy System Adoption
Several factors are contributing to the rapid adoption of solar energy system across the globe. These factors range from environmental and economic benefits to technological advancements and supportive policies.
1. Environmental Benefits
Solar energy system offer significant environmental advantages by reducing greenhouse gas emissions and dependence on fossil fuels.
- Reduction in Carbon Footprint: Solar energy system generate electricity without emitting carbon dioxide, helping to combat climate change.
- Decreased Air Pollution: Unlike conventional power plants, solar energy system do not produce air pollutants, contributing to cleaner air and improved public health.
- Conservation of Water Resources: Solar energy system require minimal water for operation compared to traditional power plants, conserving valuable water resources.
| Environmental Benefit | Solar Energy System | Conventional Power Plant |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon Emissions | Zero | High |
| Air Pollution | None | Significant |
| Water Usage | Minimal | High |
2. Economic Advantages
The economic benefits of solar energy system is driving their adoption in both developed and developing countries.
- Cost Savings: Solar energy system reduce electricity bills for households and businesses by providing a free source of energy after the initial investment.
- Job Creation: The solar energy industry creates jobs in manufacturing, installation, maintenance, and research and development.
- Energy Independence: By generating electricity locally, solar energy system reduce reliance on imported fossil fuels and enhance energy security.
| Economic Advantage | Impact |
|---|---|
| Cost Savings | Reduced electricity bills |
| Job Creation | Employment in solar industry |
| Energy Independence | Reduced fuel imports |
3. Technological Advancements
Technological innovations are making solar energy system more efficient, affordable, and versatile.
- Improved Efficiency: Advances in solar cell technology, such as perovskite and bifacial solar cells, have significantly increased the efficiency of solar energy system.
- Energy Storage Solutions: Enhanced energy storage technologies, including lithium-ion and solid-state batteries, are improving the reliability and usability of solar energy.
- Smart Grid Integration: Smart grid technologies enable better integration of solar energy system into the electrical grid, enhancing grid stability and efficiency.
| Technology | Advancement | Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Solar Cells | Higher efficiency | Increased energy output |
| Energy Storage | Improved storage solutions | Reliable energy supply |
| Smart Grid | Enhanced integration | Grid stability |
4. Supportive Policies and Incentives
Government policies and incentives play a crucial role in promoting the adoption of solar energy system.
- Subsidies and Tax Credits: Financial incentives such as subsidies, tax credits, and rebates lower the cost of installing solar energy system.
- Renewable Energy Targets: National and regional governments are setting ambitious renewable energy targets, driving the deployment of solar energy system.
- Net Metering: Policies that allow solar energy system owners to sell excess electricity back to the grid make solar investments more attractive.
| Policy | Incentive |
|---|---|
| Subsidies | Reduced installation costs |
| Renewable Energy Targets | Increased solar deployment |
| Net Metering | Financial returns |
Challenges to Solar Energy System Adoption
Despite the numerous benefits, the adoption of solar energy system faces several challenges that need to be addressed to achieve widespread deployment.
1. Initial Investment Costs
The upfront cost of purchasing and installing solar energy system can be a significant barrier, especially in developing countries.
- High Installation Costs: The initial investment for solar panels, inverters, and installation can be substantial.
- Financing Options: Limited access to financing options can hinder the adoption of solar energy system.
2. Technological Barriers
While technological advancements have improved solar energy system, certain barriers still exist.
- Efficiency Variability: Solar energy system efficiency can vary based on geographic location, weather conditions, and shading.
- Energy Storage Limitations: Current energy storage technologies may not provide sufficient capacity for large-scale solar energy system.
3. Regulatory and Policy Hurdles
Inconsistent and restrictive policies can impede the growth of solar energy system.
- Regulatory Barriers: Complex permitting processes and regulatory hurdles can delay solar energy system installations.
- Policy Uncertainty: Uncertainty around government policies and incentives can deter investment in solar energy system.
Strategies to Accelerate Solar Energy System Adoption
To overcome these challenges and accelerate the adoption of solar energy system, a multifaceted approach is needed. The following strategies can help promote the widespread deployment of solar energy system.
1. Financial Mechanisms and Incentives
- Innovative Financing Models: Implementing financing models such as solar leases, power purchase agreements (PPAs), and community solar programs can make solar energy system more accessible.
- Microfinancing: Providing microfinancing options can help individuals and small businesses afford solar energy system.
- International Funding: Leveraging international funding and grants can support solar energy projects in developing countries.
| Financial Mechanism | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Solar Leases | Affordable access to solar |
| Power Purchase Agreements | Cost savings and investment |
| Microfinancing | Accessibility for low-income |
2. Technological Innovation and Research
- Research and Development: Investing in research and development can lead to breakthroughs in solar cell efficiency, energy storage, and system integration.
- Grid Modernization: Upgrading grid infrastructure and implementing smart grid technologies can enhance the integration of solar energy system.
- Hybrid Systems: Developing hybrid systems that combine solar energy with other renewable sources can improve reliability and efficiency.
| Innovation Area | Focus |
|---|---|
| Solar Cell Efficiency | Higher energy conversion |
| Energy Storage | Improved capacity and cost |
| Grid Integration | Stability and smart grids |
3. Policy and Regulatory Support
- Streamlined Permitting: Simplifying the permitting process can reduce installation time and costs.
- Long-Term Policy Commitment: Governments should commit to long-term renewable energy policies to provide stability and confidence for investors.
- Public Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the benefits of solar energy system can increase adoption rates.
| Policy Action | Impact |
|---|---|
| Simplified Permitting | Faster installations |
| Long-Term Policy Commitment | Investor confidence |
| Public Awareness | Increased adoption |
4. Capacity Building and Training
- Workforce Development: Training programs for installers, technicians, and engineers can ensure a skilled workforce for the solar energy industry.
- Educational Programs: Incorporating solar energy education into school curriculums can raise awareness and interest among future generations.
- Knowledge Sharing: International collaboration and knowledge sharing can accelerate the adoption of best practices and technologies.
| Capacity Building | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Workforce Training | Skilled labor force |
| Educational Programs | Awareness and interest |
| Knowledge Sharing | Adoption of best practices |
Conclusion
The adoption of solar energy system worldwide is being driven by a combination of environmental, economic, technological, and policy factors. While challenges such as high initial costs, technological barriers, and regulatory hurdles exist, strategic approaches can accelerate the deployment of solar energy system. Financial mechanisms, technological innovation, supportive policies, and capacity building are essential to overcoming these challenges and promoting the widespread use of solar energy system. As the world continues to shift towards renewable energy, solar energy system will play a crucial role in achieving a sustainable and energy-efficient future.
