Electrochemical energy storage refers to the use of chemical elements as energy storage media, and the charging and discharging processes are accompanied by chemical reactions in the energy storage medium. Mainly including lithium-ion batteries, sodium ion batteries, flow batteries, lead-acid batteries, etc. According to the “White Paper on Energy Storage Industry Research 2023” released by the Zhongguancun Energy Storage Industry Technology Alliance, in 2022, the installed capacity of newly added power storage projects in China exceeded 15 GW for the first time, reaching 16.5 GW. The new energy storage capacity reached a historic high of 7.3 GW/15.9 GWh, with a year-on-year increase of 200% in power and 280% in energy. Among the new energy storage projects, lithium-ion batteries occupy an absolute dominant position, with a weight ratio of 97%. As of the end of 2022, the cumulative installed capacity of China’s power storage projects that have been put into operation is 59.8 GW, accounting for 25% of the global market size and an annual growth rate of 38%. The cumulative installed capacity of new energy storage has exceeded 10 GW for the first time, reaching 13.1 GW/27.1 GWh, with an annual growth rate of 128% for power scale and 141% for energy scale. Among the new energy storage, lithium-ion batteries account for 94%. It can be seen that the vast majority of energy storage technologies involved in new energy storage projects are lithium-ion batteries.
The structure of lithium-ion batteries includes a positive electrode, a negative electrode, a separator, and an electrolyte, which has the same priority as the design of the positive electrode, negative electrode, and the entire battery. As one of the key materials for batteries, the electrolyte should have high ionic conductivity, electrochemical stability, and thermal stability, be able to form a stable and sustainable solid electrolyte interface (SEI) film, and be non-toxic and cost-effective.
Battery energy storage patent information, as an important carrier of technological innovation achievements, can reflect the current status and history of innovation and development in a certain technological field. Battery energy storage patent information has become an important form of technological intelligence. In recent years, scholars have continuously conducted analysis and research on energy storage technology and its related sub fields from the perspective of battery energy storage patents. By analyzing the dimensions of application volume, applicants, maintenance period, classification number, and technology source country, the development trend of energy storage technology has been revealed, providing reference for strategic decision-making and industrial development of governments, enterprises, and others.
Based on the perspective of battery energy storage patents, the Incopat patent data retrieval system is used to analyze the application volume, applicants, inventors, legal status, and other single or multiple dimensions in the field of electrochemical energy storage electrolytes, revealing the development trend and technological development trend of battery energy storage patents in the field of electrochemical energy storage electrolytes, providing reference for the research and development decisions, industrial layout, and other aspects of the Chinese government and enterprises in the field of electrochemical energy storage.
1. Data Sources and Methods
Using the Incopat patent data retrieval system, with a search date of April 11, 2023, the scope of the search data is Chinese invention patent applications. The search method uses a combination of keywords and IPC classification number to retrieve battery energy storage patent data, specifically using lithium-ion batteries, lithium-ion secondary batteries, lithium-ion batteries, lithium-ion secondary batteries, sodium ion batteries, and sodium ion secondary batteries under the “Title/Abstract/Claims” item Search for keywords such as sodium batteries, sodium secondary batteries, and secondary batteries to obtain the first dataset. Use keywords such as electrolyte and electrolyte under the “title” item or use classification numbers such as H01M10/0566, H01M10/0567, H01M10/0568, H01M10/0569 under the “IPC” item to obtain the second dataset. The first and second datasets are combined to obtain the third dataset. The title of the third dataset only includes electrodes, negative electrodes Patents for positive electrodes, active materials, and separators were removed, and after manual processing, a total of 6267 electrolyte patents were obtained for analysis. Due to an 18 month lag from the application date to the publication date of battery energy storage patents, a large number of battery energy storage patents are still in an undisclosed state. Therefore, data from October 2022 onwards are only for comparative reference.
2. Result analysis
2.1 Development Trend Analysis
As of April 11, 2023, the total number of patent applications for electrolytes in China is 6267. As shown in Figure 1, there have been gradually applied for battery energy storage patents since 1994. It has been 30 years now and can be divided into four development stages: 1994-1999 was the embryonic stage of technology, with only sporadic battery energy storage patent applications during this stage, and electrolyte technology began to sprout; The period from 2000 to 2010 was a period of slow technological development, during which the number of patent applications for battery energy storage slowly increased, with an annual application volume exceeding 100; 2011-2020 is a period of rapid technological development, during which the number of patent applications for battery energy storage rapidly increased, especially in the six years from 2014 to 2019, where the number of patent applications increased by 212%; In 2021, the number of patent applications for battery energy storage has decreased, showing a trend towards technological maturity.
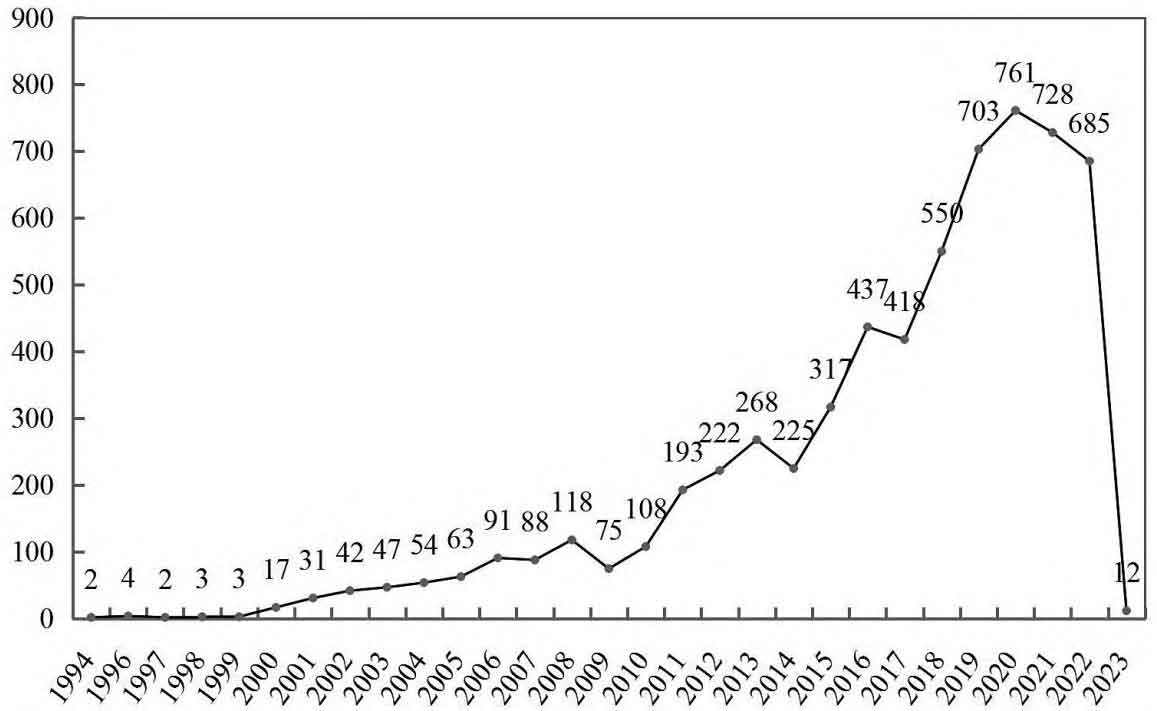
Figure 2 shows the lifecycle diagram. Prior to 2010, the maximum number of applications for battery energy storage patents was 118 per year, and the maximum number of patent applicants was 51 per year. Both the number of applications for battery energy storage patents and the number of patent applications were not high. In 2014, 2017, and 2021, there was a slight decrease in the number of battery energy storage patent applications and the number of patent applicants. In 2022, there was a slight increase in the number of battery energy storage patent applicants, but the number of patent applications still decreased, indicating that there are still new applicants joining the electrolyte field, but innovation work has become increasingly difficult. In 2021, there is a trend towards technological maturity.
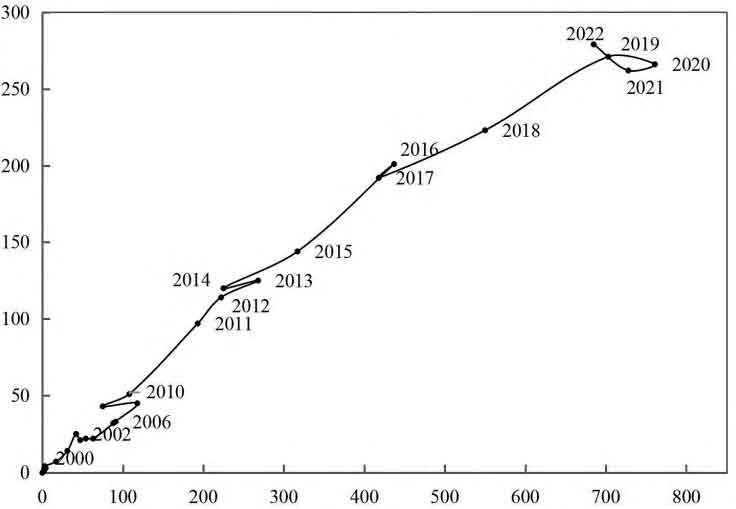
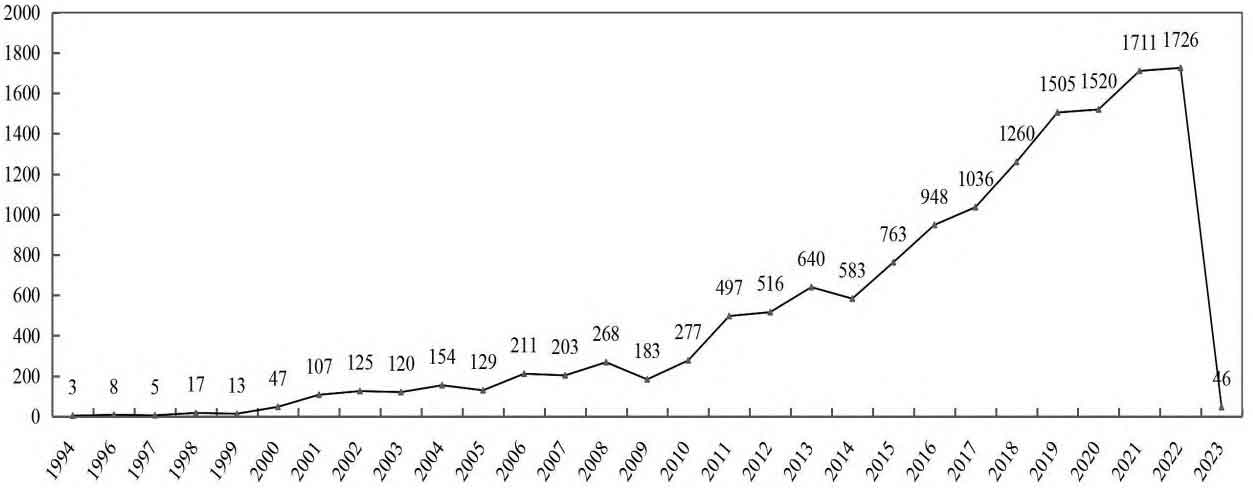
Figure 3 shows the annual distribution of the number of inventors, showing an increasing trend year by year. From 2010 to 2022 (except for 2014), the number of inventors has been increasing year by year, and fresh blood has been continuously added to the field of electrolytes, indicating that the field of electrolytes remains a hot topic at present. From 1994 to 2022, the average ratio of the number of inventors to the number of battery energy storage patent applications was 2.6, which means 2.6 individuals completed one patent application. From 2010 to 2022, the ratio was 2.4, which means 2.4 individuals completed one patent application. Throughout the entire development stage of electrolytes, there has been a certain improvement in innovation capabilities during the rapid technological development stage.
2.2 Analysis of Competitive Situation
2.2.1 Analysis of R&D strength
The distribution of technology source countries is shown in Table 1. According to Table 1, China is the first technology source country for Chinese patent applications, with a total of 4542 patent applications, accounting for 72.47%; Secondly, Japan has 1004 patent applications for battery energy storage, accounting for 16.02%; South Korea ranks third, with 517 battery energy storage patent applications, accounting for 8.25%; The United States and Germany, ranked fourth and fifth, have only applied for about 1% of battery energy storage patents. From this perspective, China, Japan, and South Korea are the main source countries for electrolyte technology.
| Serial number | Country | Application volume | Proportion |
| 1 | China | 4542 | 72.47% |
| 2 | Japan | 1004 | 16.02% |
| 3 | Korea | 517 | 8.25% |
| 4 | United States | 90 | 1.44% |
| 5 | Germany | 63 | 1.01% |
| 6 | France | 23 | 0.37% |
| 7 | Belgium | 18 | 0.29% |
| 8 | Canada | 3 | 0.05% |
| 9 | Britain | 2 | 0.03% |
| 10 | Finland | 1 | 0.02% |
| 11 | Mexico | 1 | 0.02% |
| 12 | Switzerland | 1 | 0.02% |
| 13 | Singapore | 1 | 0.02% |
| 14 | Italy | 1 | 0.02% |
| Provincial administrative regions | Number of patent layouts | Provincial administrative regions | Number of patent layouts |
| Guangdong | 1497 | Shaanxi | 33 |
| Jiangsu | 505 | Guangxi | 16 |
| Fujian | 436 | Heilongjiang | 16 |
| Zhejiang | 350 | Gansu | 15 |
| Beijing | 235 | Taiwan | 15 |
| Shandong | 193 | Jilin | 14 |
| Hunan | 174 | Shanxi | 9 |
| Anhui | 172 | Chongqing | 8 |
| Hubei | 145 | Guizhou | 7 |
| Shanghai | 142 | Ningxia | 5 |
| Hebei | 118 | Xizang | 5 |
| Henan | 105 | Hong Kong | 5 |
| Tianjin | 105 | Qinghai | 4 |
| Sichuan | 90 | Yunnan | 4 |
| Jiangxi | 70 | Hainan | 2 |
| Liaoning | 46 | Inner Mongolia | 1 |
The distribution of provincial-level administrative regions of Chinese applicants is shown in Table 2. Out of 32 provinces, autonomous regions, and municipalities in China, only Xinjiang has no patent applications. Guangdong Province ranks first in the number of patent applications for battery energy storage, with 1497 applications, accounting for 33%; Next is Jiangsu Province, with 505 applications, accounting for 11%; Ranked third is Fujian Province, with a total of 436 applications, accounting for 10%; Zhejiang Province ranks fourth with 350 applications, accounting for 8%; Beijing ranks fifth with 235 applications, accounting for 5%. Shandong Province ranks sixth with 193 applications, accounting for 4%. Hunan Province, Anhui Province, Hubei Province, and Shanghai City rank seventh, eighth, ninth, and tenth respectively. Ranked 11th is Hebei Province, with 118 applications, accounting for 3%. Tianjin ranked 12th with 105 applications, accounting for 2%. The top twelve are mostly the eastern coastal provinces, autonomous regions, or municipalities directly under the central government. Among the inland provincial-level administrative regions, Hunan Province, Anhui Province, Hubei Province, Henan Province, Sichuan Province, Jiangxi Province, and Shaanxi Province have the majority of battery energy storage patent applications, with 174, 172, 145, 105, 90, 70, and 33 applications in sequence.
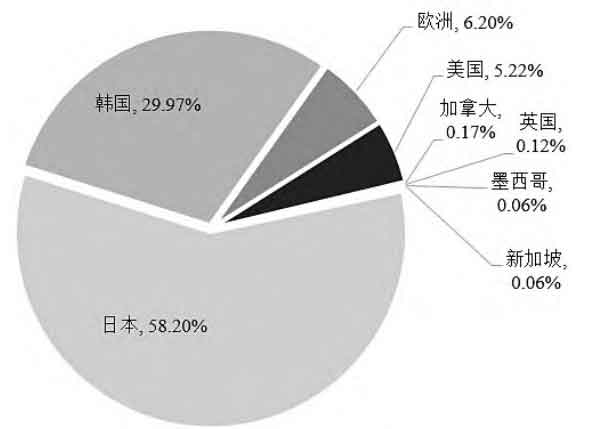
Figure 4 shows the proportion of patent applications from other countries or regions in China, with Japan accounting for 58.20%, South Korea accounting for 29.97%, Europe accounting for 6.2%, and the United States accounting for 5.22%. Japan and South Korea have a patent application volume of 88.17%, making them the top two overseas countries in terms of electrolyte patents in China.
In terms of the number of patent applications for battery energy storage by applicants, the top 100 applicants have 4625 patent applications, accounting for 73.8% of the total. The top 50 applicants have applied for 3854 battery energy storage patents, accounting for 61.5% of the total. The top 20 applicants have applied for 2747 battery energy storage patents, accounting for 43.8% of the total. The top 10 applicants have applied for 1793 battery energy storage patents, accounting for 28.6% of the total. From this perspective, the application for battery energy storage patents is relatively concentrated. Among the top 100 applicants, there are 71 Chinese applicants, accounting for 71%; There are 21 Japanese applicants, accounting for 21%. Among the top 50 applicants, there are 38 Chinese applicants, accounting for 76%; There are 9 Japanese applicants, accounting for 18%. Among the top 20 applicants, there are 14 Chinese applicants, accounting for 70%; There are 4 Japanese applicants, accounting for 20%. Among the top 10 applicants, there are 7 Chinese applicants, accounting for 70%; There is one Japanese applicant, accounting for 10%; There are two Korean applicants, accounting for 20%. The top 20 applicants for battery energy storage patents and their patent numbers are shown in Table 3.
| Serial number | Applicant | Number of patents |
| 1 | LG Group Company (hereinafter referred to as LG) | 241 |
| 2 | Panasonic Group Corporation (hereinafter referred to as Panasonic) | 198 |
| 3 | Ningde Times New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Ningde Times) | 195 |
| 4 | Shenzhen New Zebang Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as New Zebang) | 195 |
| 5 | Samsung Group Company (hereinafter referred to as Samsung) | 191 |
| 6 | Dongguan Shanshan Battery Materials Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Shanshan) | 172 |
| 7 | Dongguan New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as ATL) | 171 |
| 8 | Guangzhou Tianci High tech Materials Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Tianci) | 165 |
| 9 | Zhuhai Guanyu Battery Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Guanyu) | 140 |
| 10 | BYD Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as BYD) | 125 |
| 11 | Sony Corporation (hereinafter referred to as Sony) | 124 |
| 12 | Zhangjiagang Guotai Huarong Chemical New Materials Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Guotai) | 121 |
| 13 | Mitsubishi Chemical Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Mitsubishi) | 114 |
| 14 | Zhuhai Saiwei Electronic Materials Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Saiwei) | 109 |
| 15 | Hefei Guoxuan High tech Power Energy Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Guoxuan) | 101 |
| 16 | Xianghe Kunlun New Energy Materials Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Kunlun Materials) | 93 |
| 17 | Xinwangda Electronics Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Xinwangda) | 79 |
| 18 | Huizhou Yiwei Lithium Energy Co., Ltd. (hereinafter referred to as Yiwei) | 74 |
| 19 | Yuanjing Technology Group Company (hereinafter referred to as Yuanjing Technology) | 70 |
| 20 | Toyota Corporation (hereinafter referred to as Toyota) | 69 |
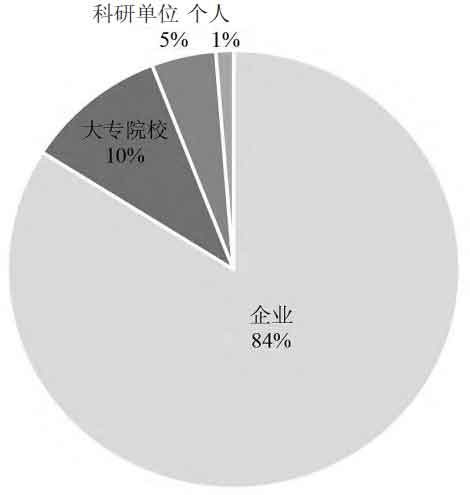
The distribution of patent applicant types is shown in Figure 5. Among them, 84% are enterprise applicants, 10% are college applicants, 5% are research unit applicants, and 1% are individual applicants. Among the top 50 applicants, there are 6 universities and colleges, including South China Normal University, Central South University, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Xiamen University, Tsinghua University, and Beijing University of Technology. There are no college or university applicants among the top 20 applicants.
2.2.2 Analysis of the Competitiveness of Main Applicants
Table 4 shows the annual distribution of the number of battery energy storage patent applications by the top 20 applicants in the past decade. The top ranked applicant is LG, with a total of 241 applications. The number of applications in the past decade has shown an upward trend, with a higher number of battery energy storage patent applications in 2013, 2018-2021, and an average annual application volume of 25 in these five years. The second ranked applicant is Panasonic, with a total of 198 applications. In the past decade, the number of applications has shown an upward trend. In 2019 and 2020, there were many applications for battery energy storage patents, with an average annual application volume of 20 in these two years. Ningde Times and New Zebang both ranked third, with a total of 195 applications. In the past decade, Ningde Times has shown a trend of first increasing and then decreasing in application volume, with 72.8% of applications for battery energy storage patents from 2016 to 2019; In the past decade, the application volume of New Zebang has shown an upward trend, with the highest application volume in 2022, reaching 29. The total number of applications from Samsung, ranked fifth, is 191. In the past decade, the number of applications has shown a slow upward trend and then a downward trend. The year with the highest number of applications was 2018-2020, with annual applications exceeding 10 in all three years. The total number of ATL applications ranked sixth is 172, with a decreasing trend in the past decade. From 2013 to 2016, there were many applications for battery energy storage patents, accounting for 64% of the total. The average annual application volume for these four years was 27.5. Shanshan ranks seventh with a total of 171 applications, and the number of applications has been on the rise in the past 10 years. From 2018 to 2021, there were many applications for battery energy storage patents, with the highest number of applications in 2019, with 65 applications, accounting for 38% of the total. Tianci ranks eighth with a total of 165 applications. Since 2014, the number of applications has been relatively stable, with the highest number of applications in 2016, at 32. Guanyu ranks ninth with a total of 140 applications. Prior to 2018, there were sporadic applications for battery energy storage patents, and 97.9% of battery energy storage patents were filed from 2018 to 2022. BYD, ranked 10th, has a total of 125 applications and an average annual application volume for battery energy storage patents.
| Applicant | Total number of patents |
| LG | 241 |
| Panasonic | 198 |
| Ningde Times | 195 |
| New Zebang | 195 |
| Samsung | 191 |
| ATL | 172 |
| Cunninghamia lanceolata | 171 |
| Heavenly gift | 165 |
| Guanyu | 140 |
| BYD | 125 |
| Sony | 124 |
| Guotai | 121 |
| Mitsubishi | 114 |
| Saiwei | 109 |
| Guoxuan | 101 |
| Kunlun Materials | 93 |
| Xinwangda | 79 |
| Yiwei | 74 |
| Vision Technology | 70 |
| Toyota | 69 |
Among the applicants ranked 11th to 20th, Sony, Mitsubishi, and Toyota have had relatively stable application volume in the past decade, with Sony accounting for 48% of their total application volume in the past decade; Mitsubishi has accounted for 19% of its total applications in the past decade; Toyota has accounted for 81% of its total applications in the past decade. In the past decade, Cathay Pacific’s application volume has shown a trend of first increasing and then slowly decreasing, accounting for 79% of its total application volume. Saiwei, Guoxuan, Kunlun Materials, Xinwangda, Yiwei, and Yuanjing Technology have shown an upward trend in application volume in the past decade. These six enterprises have accounted for 96%, 94%, 97%, 100%, 96%, and 100% of their total application volume in the past decade, respectively.
Among the top 20 Chinese companies, BYD has accounted for 50% to 60% of their total application volume in the past decade, Cathay Pacific has accounted for 70% to 80%, ATL and Shanshan have accounted for 80% to 90%, and New Zebang, Tianci, Guoxuan, Saiwei, Yiwei, Kunlun Materials, Ningde Times, Guanyu, Xinwangda, and Yuanjing Technology have accounted for 90% to 100% of their total application volume. Among the top 20 Japanese companies, Mitsubishi has accounted for 10-20% of their total application volume in the past decade, Panasonic and Sony have accounted for 40-50%, and Toyota has accounted for 80-90%. Among the top 20 Korean companies, Samsung accounts for 50% to 60% of their total application volume in the past decade, while LG accounts for 70% to 80%.
2.2.3 Analysis of Patent Legal Status
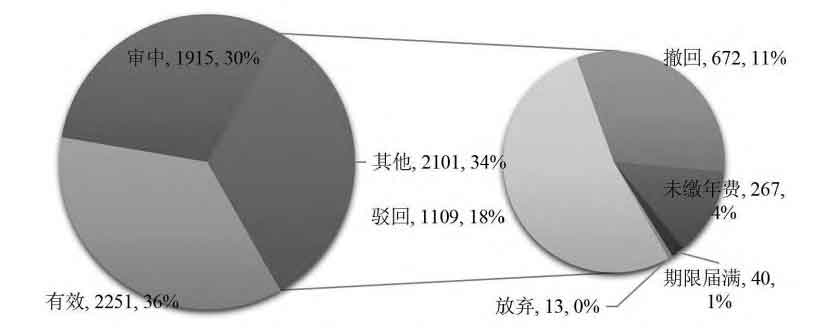
Figure 6 shows the distribution of the legal status of battery energy storage patents, with 2251 patents remaining valid, accounting for 36%. There are 1915 battery energy storage patents under review, accounting for 30%. There are 2101 expired battery energy storage patents, accounting for 34%. Among them, 18% were rejected, 11% were withdrawn, 4% were expired without paying annual fees, and 1% were expired.
2.3 Analysis of representative enterprises
This section analyzes Ningde Times as a representative enterprise. In the patents for electrochemical energy storage electrolytes in Ningde Times, 75% of the invention points to the synergistic effect of multi-component mixing, and 25% of the invention points to the effect of single component. From this, it can be seen that Ningde Era focuses on the development of electrolyte technology by mixing multiple components, while also taking into account the creation of new substances. From the perspective of solvents and additives, the innovation point is that the proportion of additive improvement is 86%, the proportion of additives and solvent improvement is 9%, and the proportion of solvent improvement is 5%. The research on electrochemical energy storage electrolytes in Ningde Times mainly focuses on additive improvement.
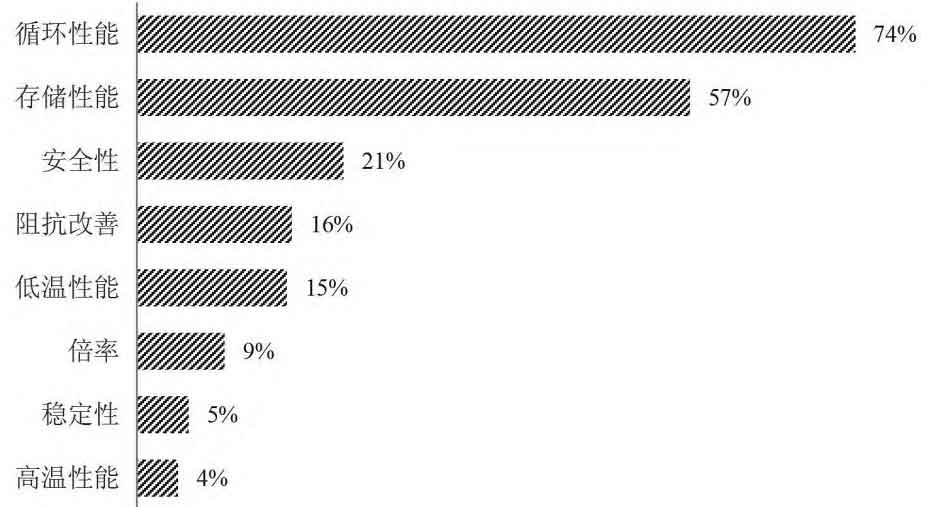
By analyzing the technical effects of Ningde Era’s electrochemical energy storage electrolyte patents, it was found that 74% of patents improved battery cycling performance, 57% improved battery storage performance, 21% improved battery safety performance, 16% improved impedance performance, and 15% improved low-temperature performance. Patents improved battery rate performance, stability performance, and high-temperature performance accounted for 9%, 5%, and 4% respectively, See Figure 7. From this, it can be seen that as a leading battery enterprise, Ningde Times pays particular attention to the cycling and storage performance of batteries.
From the perspective of battery energy storage patent text, in order to improve high-temperature cycling performance and high-temperature storage performance, Ningde Times has laid out 19 Chinese battery energy storage patents around polynitrile based six membered nitrogen heterocyclic compounds, all of which are in valid legal status. The invention layout of these 19 Chinese battery energy storage patents is the combination of polynitrile based six membered nitrogen heterocyclic compounds with various positive electrode active materials and various additives. The research and development mechanism lies in the fact that each six membered nitrogen heterocyclic molecule with multiple nitrile groups simultaneously possesses two or more nitrile groups. The lone pair electrons contained in the nitrogen atoms in the nitrile groups can strongly complex with the three-dimensional empty orbitals of the transition metal on the surface of the positive electrode material, reducing the surface activity of the positive electrode while isolating direct contact between the electrolyte and the positive electrode surface, greatly reducing surface side reactions and consuming lithium ions in the side reactions.
3. Conclusion
Research and development institutions usually use various means such as battery energy storage patents and trade secrets to protect innovative technologies, so a single battery energy storage patent information cannot accurately determine the technological leadership of research and development institutions. This article analyzes and studies the development trend of electrochemical energy storage electrolyte technology from the perspective of battery energy storage patent analysis, and draws the following conclusions for reference by researchers, decision-makers, and enterprises in related fields.
(1) The application for Chinese battery energy storage patents related to electrochemical energy storage electrolyte technology began in 1994, followed by a brief period of technological germination. Since 2000, the number of battery energy storage patents has slowly increased, entering a period of slow technological development; The number of battery energy storage patents has rapidly increased from 2011 to 2020, and this technology has entered a period of rapid technological development; After 2021, the number of battery energy storage patents has decreased and is gradually entering a period of technological maturity.
(2) From the perspective of the number of applicants and inventors, there is an upward trend with the year, indicating that electrochemical energy storage electrolyte technology is still a hot field at present.
(3) From a national perspective, China, Japan, and South Korea account for the vast majority of battery energy storage patents, accounting for 96.7%. Electrochemical energy storage electrolyte technology mainly comes from these three countries.
(4) From the perspective of applicants, LG, Panasonic, Ningde Times, New Zebang, Samsung, Shanshan, ATL, Tianci, Guanyu, and BYD rank among the top 10 in terms of patent applications for battery energy storage. Among them, LG and New Zebang have good R&D sustainability and strong strength.
(5) From the perspective of legal status, the effective patents, pending battery energy storage patents, and expired battery energy storage patents in the electrochemical energy storage electrolyte technology patents are almost evenly distributed, and the innovation ability in this technology field is still acceptable.
(6) From the perspective of the representative company Ningde Times, the research on electrochemical energy storage electrolytes mainly focuses on the mixing of additives, taking into account the creation of new additive substances, and improving the cycling and storage performance of batteries is the main technical effect pursued by battery companies.
