Since the 1980s, the solar photovoltaic power generation industry has grown at a rate of 30% to 40% annually, and solar photovoltaic power generation technology is attracting attention from countries around the world. In the long run, solar energy can replace conventional energy sources such as coal, oil, and natural gas as a new energy source in the future. According to the forecast of the Joint Research Center (JRC) of the European Union, by 2030, renewable energy will account for more than 30% of total energy, and the solar photovoltaic industry will generate more than 10% of total electricity; By 2040, the proportion of renewable energy will reach 50%, and the proportion of solar power generation will reach 20%; By the end of the 21st century, this number will reach over 80%, and solar power generation will account for over 60%, truly reflecting the core position of solar power generation. According to data from the China Photovoltaic Industry Association (CPIA), the global increase in solar photovoltaic installed capacity from 2011 to 2015 is shown in Figure 1.
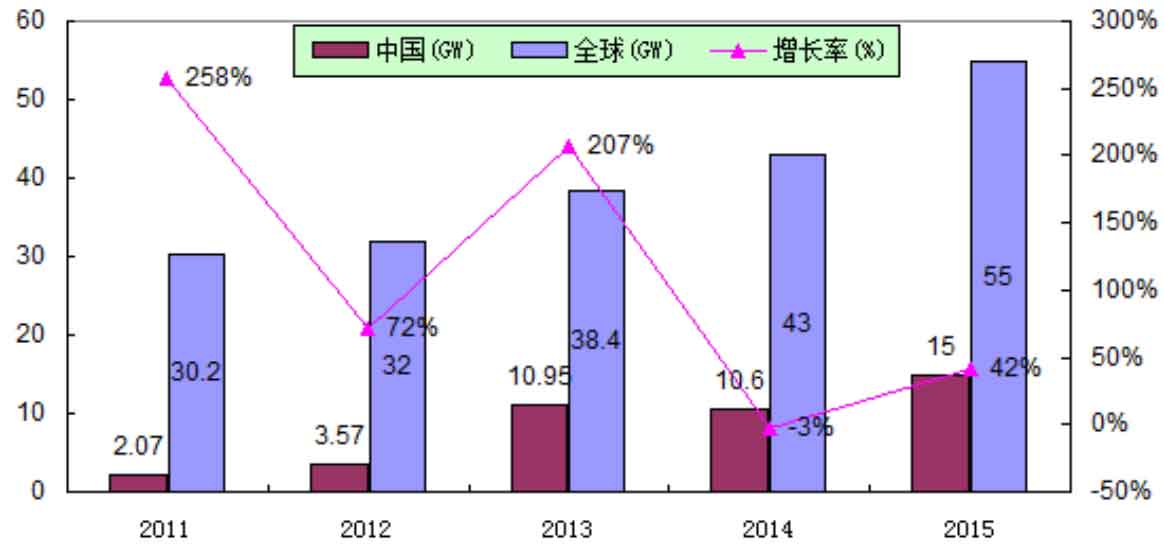
Driven by the rise of major markets such as China, the United States, and Japan, as well as other emerging markets, the demand for solar energy continued to grow in 2015. According to the latest report from Trend Force, the top five global solar energy markets in the first half of the year were ranked in order by China, Japan, the United States, the United Kingdom, and Germany. Although the highly anticipated Indian market is catching up this year, it has not yet entered the top five due to its late start. It is estimated that the installation volume in the UK and Germany will remain stable in the second half of the year, while China and the US will enter the peak of installation, so overall demand remains strong.
Under the premise of unchanged policies, global market demand will continue to increase in 2016, with Asia, the Americas, Europe, and the Middle East region accounting for 57%, 25%, 11%, and 7% respectively. The global demand is expected to reach approximately 58GW. Under the continuous promotion of China’s 13th Five Year Plan and the Leading Plan, even though demand in Asia may decrease after next year due to Japan’s gradual reduction in subsidies, the gap can still be filled; Although India developed relatively late, its local manufacturing capacity continues to expand due to the participation of Chinese manufacturers, and it will become the fourth largest market in the world next year; Other Asian countries such as South Korea, Thailand, and the Philippines also have a certain amount of demand, and it is expected that the Asian market will reach about 33.1GW next year.
The Americas region, on the other hand, will experience a significant increase in demand due to the end of US subsidies. In addition, California has recently raised the Renewable Portfolio Standard (RPS) for 2020 to 50%, giving the US market more potential for growth in the future; The short-term targets of South American countries, including Brazil, Chile, Honduras, Uruguay, etc., are all in the hundreds of MW, so it is expected to reach about 14.6 GW in 2016, which should not be underestimated.
In the European, African, and Middle Eastern regions, including Arabia, Israel, South Africa, Algeria, etc., the demand for power plants with a capacity of over 50MW continued to increase in 2015. Although countries such as the UK, Germany, and Greece have seen a decrease in demand for solar photovoltaics due to declining subsidies and economic issues, it is estimated that the total installed solar photovoltaics in Europe, Africa, and the Middle East will remain stable in 2016, reaching approximately 10.3GW.
As a resource rich country, although China has abundant resources, the rational utilization planning of resources started relatively late, especially renewable energy shows high installation costs and lack of competitiveness. But after more than 30 years of efforts, China’s solar photovoltaic industry has entered a new stage of rapid development. Driven by national projects such as the “Bright Project” and “Sending Electricity to Countryside”, as well as the global solar photovoltaic market, China’s solar photovoltaic industry has developed rapidly.
Affected by favorable factors such as the continuous release of policies and air pollution control, China’s solar photovoltaic industry has gradually emerged from a downturn since 2013. The China Institute of Electronic Information Industry Development released the “White Paper on the Development of Solar Photovoltaic Industry (2015 Edition)”, which shows that in terms of market development in 2014, the Chinese solar photovoltaic market maintained a growth rate of over 10GW for two consecutive years. In 2014, the newly installed solar photovoltaic capacity reached 10.6 million kilowatts, of which 2.05 million kilowatts were distributed solar photovoltaic systems, accounting for 19.3% of the total installed capacity, a year-on-year increase of 13%, The cumulative installed capacity of solar photovoltaic connected to the grid is 28.05 million kilowatts, with an annual power generation of about 25 billion hours, a year-on-year increase of over 200%. According to data from the National Energy Administration, as of the end of 2015, China’s cumulative installed capacity of solar photovoltaic power generation was 43.18 million kilowatts, making it the country with the largest installed capacity of solar photovoltaic power generation in the world. Among them, solar photovoltaic power stations are 37.12 million kilowatts, distributed 6.06 million kilowatts, and annual power generation is 39.2 billion kilowatt hours. In 2015, a new installed capacity of 15.13 million kilowatts was added, achieving the goal of adding 15 million kilowatts of grid connected installed capacity in 2015, accounting for more than a quarter of the global new installed capacity and one-third of the annual production of solar photovoltaic modules in China. This provides effective market support for China’s solar photovoltaic manufacturing industry. The cumulative installed capacity of solar photovoltaics in China from 2010 to 2015 is shown in Figure 2.
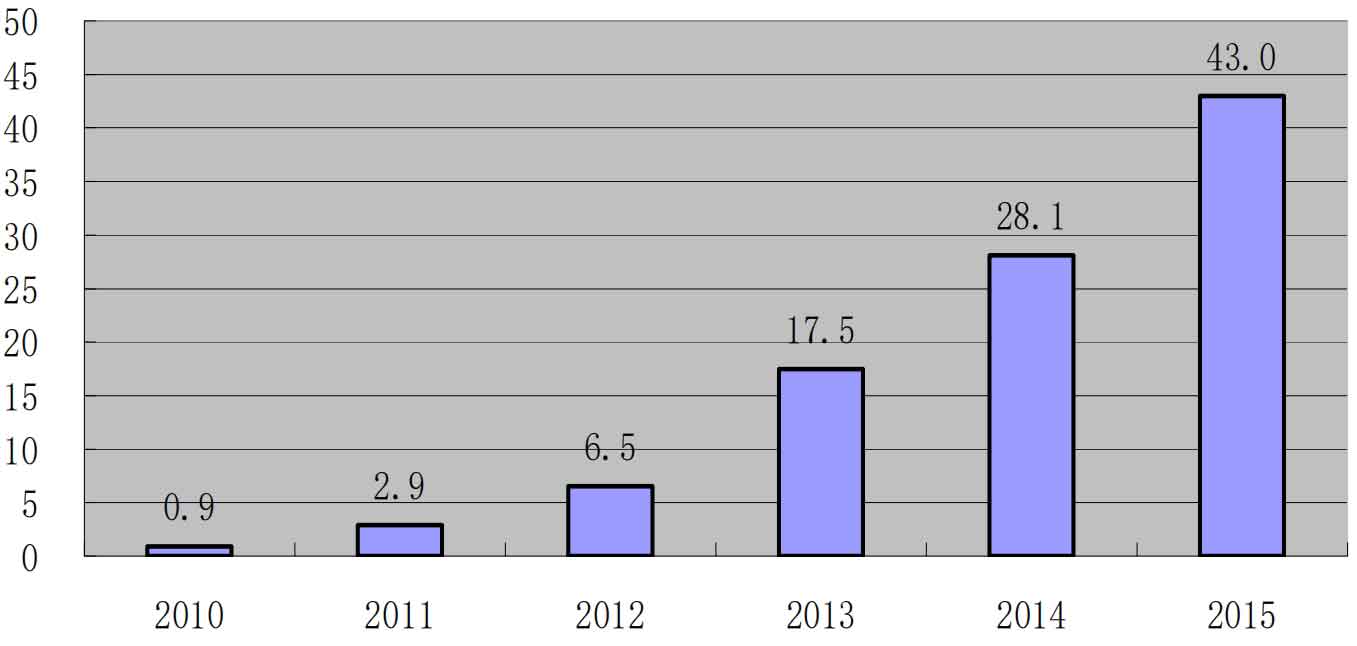
Looking ahead to the future, with the release of the 13th Five Year Plan for energy, the coal reduction target has been clearly proposed for the first time, reducing the proportion of coal consumption from the current 66% to 60%. This means that China’s solar photovoltaic market will definitely continue to expand. However, due to the impact of solar photovoltaic power generation costs, consumption capacity, and subsidy policies, the solar photovoltaic industry is bound to develop from the current “extensive” to “refined” direction, and in-depth research and development of solar photovoltaic inverters is particularly important.
