Abstract:
This comprehensive article delves into the safety standards for battery energy storage system in three major regions: Europe, North America, and China. Through detailed comparisons of the IEC, UL, and GB/T series of standards, this study examines the various aspects of battery safety, including mechanical safety, environmental adaptability, electrical safety, and thermal runaway. The analysis highlights the strengths and weaknesses of each standard and provides recommendations for the energy storage industry.
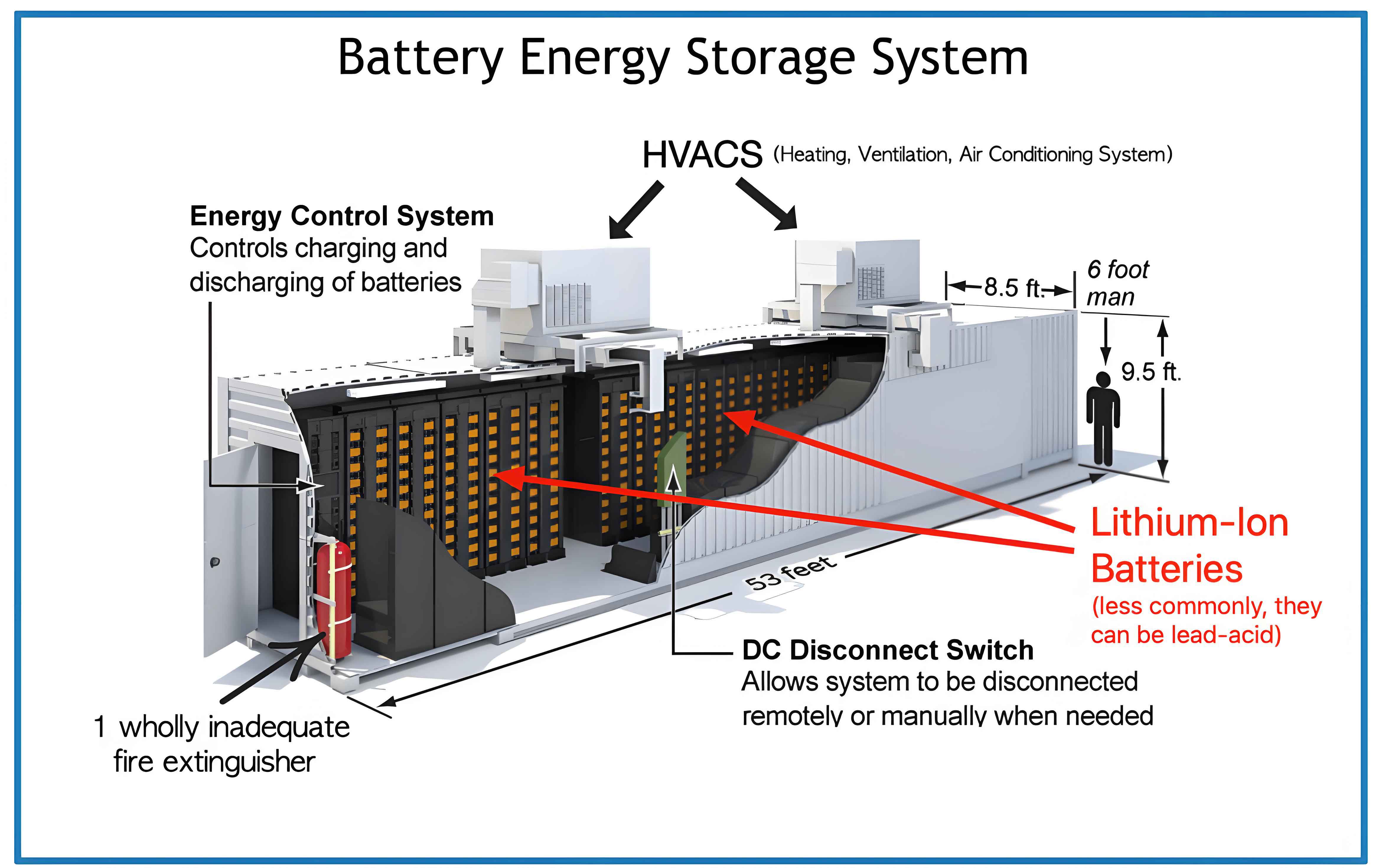
1. Introduction
With the global push towards carbon neutrality, battery energy storage system have become ubiquitous in various applications, ranging from renewable energy integration to grid stability. However, the increasing adoption of these systems has also led to a surge in battery-related incidents, particularly fires and explosions. To mitigate these risks, various countries have developed comprehensive safety standards tailored to their local needs and conditions. This article compares and contrasts the key safety standards for battery energy storage system in Europe, North America, and China.
2. Overview of Safety Standards
2.1 European Standards (IEC Series)
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) has formulated several key standards related to battery energy storage system, including IEC 62619 and IEC 63056. These standards focus on the safety requirements for secondary lithium cells and batteries used in industrial applications, including battery energy storage system. IEC standards are widely recognized and adopted across Europe and beyond, providing a solid foundation for battery safety.
2.2 North American Standards (UL Series)
In North America, Underwriters Laboratories (UL) has developed a series of standards for battery energy storage system, including UL 1973, UL 9540A, and UL 9540. These standards emphasize the evaluation of safety hazards, such as thermal runaway fire propagation, and cover a broader range of testing scenarios, making them more stringent and applicable to real-world conditions.
2.3 Chinese Standards (GB/T Series)
China has established a comprehensive set of national standards for battery energy storage system, primarily represented by the GB/T series, including GB/T 36276 and GB/T 34131. These standards focus on various aspects of battery safety, including lithium-ion battery performance, battery management systems, and inverter technology requirements, tailored to China’s specific battery energy storage system needs.
3. Detailed Comparison of Safety Standards
3.1 Mechanical Safety Testing
Mechanical safety testing assesses the performance of battery energy storage system under various physical conditions. The following table summarizes the key mechanical safety tests across the IEC, UL, and GB/T standards.
| Testing Project | IEC | UL | GB/T |
|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Test | √ | √ | – |
| Drop Test | √ | √ | √ |
| Vibration Test | √ | √ | √ |
| Wall Mount Fixture/ | – | √ | √ |
| Support Structure/ | |||
| Handle Test |
Key Insights:
- UL Series: Provides the most comprehensive coverage of mechanical safety tests, including tests for wall mount fixtures, support structures, and handles.
- GB/T Series: Includes basic mechanical safety tests but lacks specific tests for wall mount fixtures and handles.
- IEC Series: Focuses more on traditional mechanical safety tests but may lack tests specific to installation conditions.
3.2 Environmental Adaptability Testing
Environmental adaptability testing evaluates the performance of battery energy storage system under extreme conditions. The following table summarizes the key environmental tests across the IEC, UL, and GB/T standards.
| Testing Project | IEC | UL | GB/T |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal Cycling | – | √ | – |
| Humidity Test | – | √ | √ |
| Salt Spray Test | – | √ | √ |
Key Insights:
- UL Series: Offers the most comprehensive environmental testing, including thermal cycling, humidity, and salt spray tests.
- GB/T Series: Includes humidity and salt spray tests but lacks thermal cycling.
- IEC Series: Typically references other IEC standards for environmental testing, such as IEC 60529, but may include additional tests like vibration and shock resistance, depending on the specific product application.
- MIL-STD Series: Focused on military-grade environmental testing, often involving more rigorous conditions such as extreme temperatures, high humidity, and mechanical stresses like vibration and shock, ensuring products can withstand harsh environments.
- IP Code (Ingress Protection): Rates the degree of protection provided by enclosures against the intrusion of solid objects (including dust) and water, using a two-digit code; for instance, IP67 signifies complete protection against dust and immersion in water up to 1 meter for 30 minutes.
Each series serves different industries and applications, with varying levels of stringency in their testing protocols. Choosing the appropriate series for environmental testing depends on the intended use of the product, the expected environmental conditions it will encounter, and the required durability and reliability standards.
