In the world of solar energy systems, the choice of solar power inverter plays a critical role in determining the overall efficiency, reliability, and performance of the installation. There are three primary types of solar power inverters used in solar energy systems: string inverters, central inverters, and microinverters. Each type has its own unique advantages and disadvantages, making them suitable for different applications and system sizes. This article provides a comparative analysis of string, central, and micro solar power inverters, highlighting their features, benefits, and ideal use cases.
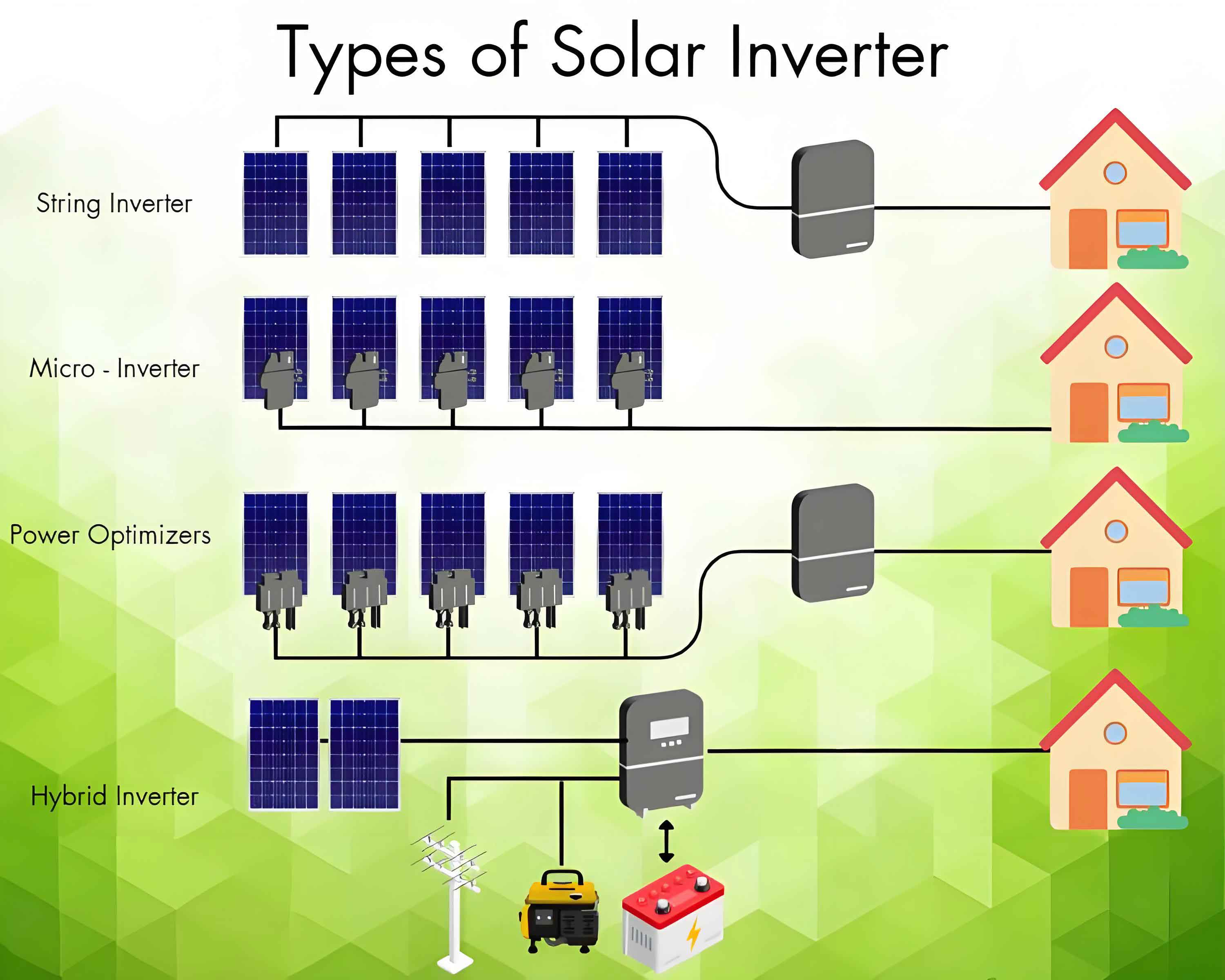
Overview of Solar Power Inverters
- String Solar Power Inverter:
- A string solar power inverter connects a series of solar panels (known as a string) into one single inverter.
- It converts the direct current (DC) produced by the solar panels into alternating current (AC) for use in homes and businesses.
- Central Solar Power Inverter:
- A central solar power inverter is similar to a string inverter but is designed for larger solar installations.
- It connects multiple strings of solar panels into one large inverter, typically used in commercial or utility-scale solar projects.
- Micro Solar Power Inverter:
- A micro solar power inverter is a small inverter installed on each individual solar panel.
- It converts the DC from each panel directly to AC, allowing for modular and independent operation of each panel.
Comparative Analysis
Table 1: Key Features of String, Central, and Micro Solar Power Inverter
| Feature | String Solar Power Inverter | Central Solar Power Inverter | Micro Solar Power Inverter |
|---|---|---|---|
| System Size | Suitable for residential and small commercial | Ideal for large commercial and utility-scale | Suitable for residential and small commercial |
| Installation Complexity | Moderate | High | Low |
| Initial Cost | Moderate | High | High per panel |
| Maintenance Requirements | Moderate | High | Low |
| Efficiency | High | High | Highest (individual optimization) |
| Shading Impact | High (one panel affects entire string) | High (one string affects entire system) | Low (each panel operates independently) |
| Scalability | Moderate | High | High |
String Solar Power Inverter
Advantages:
- Cost-Effective:
- String solar power inverters are generally less expensive compared to microinverters, making them a cost-effective choice for many residential and small commercial installations.
- Simplicity:
- The installation process for string solar power inverters is relatively straightforward, requiring fewer components and less wiring than central inverters.
- High Efficiency:
- String inverters offer high efficiency and are capable of converting a large amount of energy with minimal losses.
Disadvantages:
- Shading Sensitivity:
- The performance of a string solar power inverter can be significantly affected by shading on any single panel in the string, reducing the overall system efficiency.
- Limited Flexibility:
- Expansion of the system may be limited, as adding more panels might require additional string inverters.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Residential installations with minimal shading.
- Small commercial installations where cost is a primary concern.
Central Solar Power Inverter
Advantages:
- High Capacity:
- Central solar power inverters are designed to handle large volumes of power, making them ideal for large commercial and utility-scale solar projects.
- Economies of Scale:
- While the initial cost is high, central inverters benefit from economies of scale, reducing the per-watt cost for large installations.
- Simplified Maintenance:
- Maintenance is centralized, simplifying the process for large installations.
Disadvantages:
- Installation Complexity:
- Central inverters require complex installation procedures, including extensive wiring and large infrastructure.
- Shading Impact:
- Similar to string inverters, shading on one string can affect the entire system’s performance.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Large commercial installations.
- Utility-scale solar farms.
Micro Solar Power Inverter
Advantages:
- Maximized Energy Harvest:
- Each solar panel operates independently, maximizing energy production and minimizing the impact of shading or panel failures.
- Scalability:
- Microinverters offer excellent scalability, allowing for easy system expansion by adding more panels and microinverters as needed.
- Monitoring and Diagnostics:
- Microinverters provide panel-level monitoring, offering detailed insights into the performance of each individual panel.
Disadvantages:
- Higher Initial Cost:
- The cost per watt is higher for microinverters compared to string and central inverters, which can make them less cost-effective for large installations.
- Increased Component Count:
- More components and connections mean a higher potential for installation errors and increased maintenance requirements.
Ideal Use Cases:
- Residential installations with shading issues.
- Small commercial installations requiring high reliability and detailed performance monitoring.
Comparative Summary
Table 2: Comparative Summary of String, Central, and Micro Solar Power Inverter
| Criteria | String Solar Power Inverter | Central Solar Power Inverter | Micro Solar Power Inverter |
|---|---|---|---|
| Installation Cost | Moderate | High | High (per panel) |
| Maintenance | Moderate | Centralized but high | Low |
| Shading Tolerance | Low | Low | High |
| Efficiency | High | High | Highest |
| System Expansion | Moderate | High | High |
| Monitoring Capability | System-level | System-level | Panel-level |
| Best Use Case | Residential, Small Commercial | Large Commercial, Utility-scale | Residential, Small Commercial |
Conclusion
The choice between string, central, and micro solar power inverters depends on various factors including system size, shading conditions, budget, and desired monitoring capabilities. String solar power inverters offer a balanced solution for residential and small commercial applications with minimal shading. Central solar power inverters are best suited for large commercial and utility-scale projects due to their high capacity and centralized maintenance. Micro solar power inverters provide the highest efficiency and flexibility, making them ideal for installations with shading challenges and the need for detailed performance monitoring. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each type of solar power inverter, system designers and homeowners can make informed decisions to optimize the performance and longevity of their solar energy systems.
