Under the global carbon neutrality initiative, energy storage batteries have become critical components in renewable energy systems. This article analyzes safety standards from Europe, North America, and China through four technical dimensions while integrating MPPT optimization strategies to enhance system safety.
1. Mechanical Safety Requirements
Mechanical robustness directly impacts battery structural integrity during transportation and operation. Table 1 compares key parameters across standards:
| Test Item | IEC 62619 | UL 1973 | GB/T 36276 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Shock Test | 50g, 11ms | 75g, 6ms | 25g, 16ms |
| Vibration | 5-500Hz, 3h/axis | 10-2000Hz, 12h | 5-200Hz, 6h |
MPPT algorithms can mitigate mechanical stress through dynamic power adjustment:
$$P_{MPPT} = V_{oc} \times I_{sc} \times FF$$
where fill factor (FF) determines the maximum power extraction efficiency under mechanical deformation conditions.
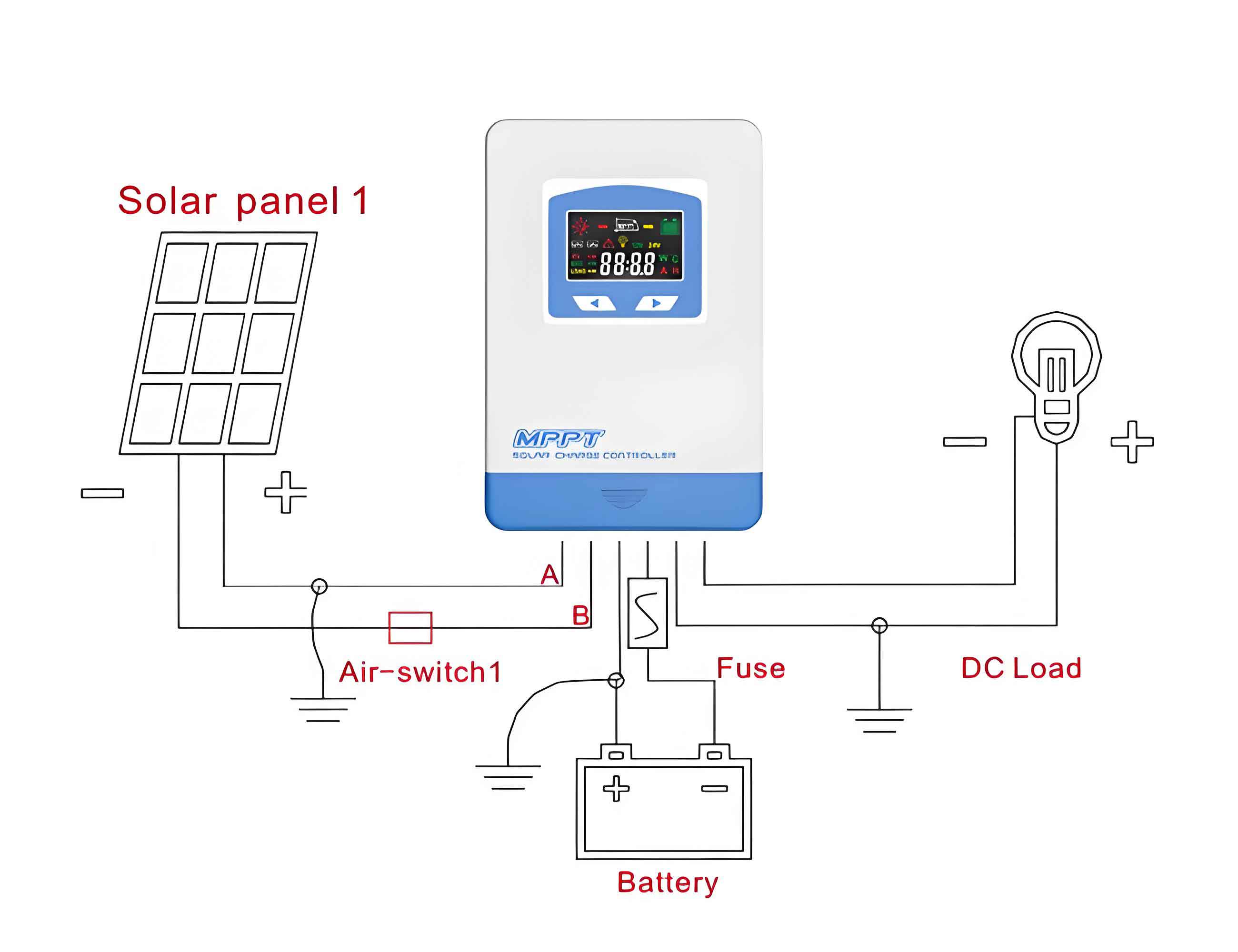
2. Environmental Adaptation
Environmental testing ensures performance under extreme conditions. The MPPT efficiency equation under temperature variations becomes:
$$η_{MPPT} = \frac{P_{actual}}{P_{max}} \times 100\%$$
where Pmax decreases exponentially with temperature rise:
$$P_{max}(T) = P_{25^{\circ}C} \times e^{-β(T-25)}$$
| Condition | UL 9540A | IEC 63056 |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Cycling | -40°C to +85°C | -20°C to +60°C |
| Humidity | 95% RH, 56 days | 93% RH, 48h |
3. Electrical Safety Protocols
MPPT controllers must comply with regional overcharge protection limits:
$$V_{OC\_max} = \frac{V_{MPPT\_max}}{1 – D_{safe}}$$
where Dsafe represents the safety derating factor mandated by different standards.
| Parameter | UL 1973 | GB/T 34131 |
|---|---|---|
| Overcharge Cut-off | 110% Vnom | 115% Vnom |
| Short Circuit Response | <50ms | <100ms |
4. Thermal Runaway Prevention
The thermal propagation model incorporating MPPT control can be expressed as:
$$\frac{dT}{dt} = \frac{P_{loss} – Q_{cooling}}{C_{th}}$$
where Ploss includes MPPT conversion losses:
$$P_{loss} = P_{in} \times (1 – η_{MPPT})$$
| Standard | Trigger Condition | Containment Time |
|---|---|---|
| UL 9540A | Single cell >150°C | 60min propagation limit |
| GB/T 36276 | Module >120°C | 30min containment |
5. MPPT Optimization Strategies
Advanced MPPT techniques improve safety compliance through:
$$\Delta D = k_p \frac{dP}{dV} + k_i \int \frac{dP}{dV} dt$$
where duty cycle (D) adjustment prevents operation in hazardous regions defined by safety standards.
| MPPT Method | UL Compatibility | IEC Certification |
|---|---|---|
| Perturb & Observe | Class III | Level B |
| Incremental Conductance | Class IV | Level A |
This comprehensive analysis demonstrates how MPPT integration enhances compliance with evolving global safety standards while maintaining energy harvesting efficiency. Regional differences in test rigor and methodology highlight the need for adaptive MPPT architectures in multinational energy storage deployments.
