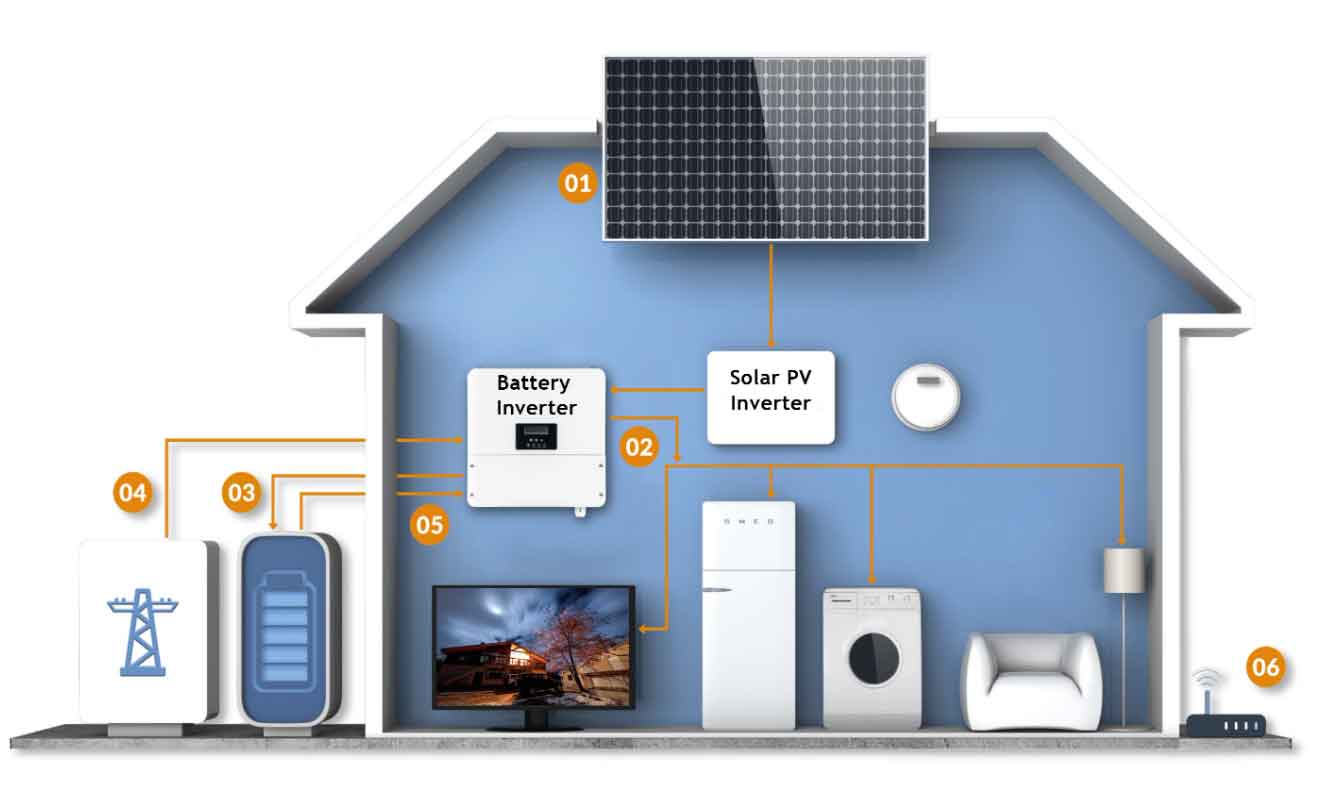
Introduction
In an era marked by increasing frequency and intensity of natural disasters, ensuring energy security has become a critical concern for governments, businesses, and households. Solar battery storage systems offer a promising solution for enhancing disaster resilience by providing a reliable and sustainable energy source during emergencies. This article explores strategies for leveraging solar battery storage to achieve energy security and improve disaster resilience, examining their benefits, implementation challenges, and future prospects.
The Role of Solar Battery Storage in Disaster Resilience
Solar battery storage systems store excess energy generated by solar panels, making it available for use when the grid is down or during periods of high demand. These systems can play a vital role in disaster resilience by ensuring a continuous power supply during emergencies, reducing reliance on centralized power grids, and promoting energy independence.
Benefits of Solar Battery Storage for Disaster Resilience
1. Continuous Power Supply
During natural disasters, power outages are common, disrupting essential services and daily activities. Solar battery storage systems can provide a continuous power supply by storing energy generated during sunny periods and using it during outages.
2. Grid Independence
Solar battery storage systems reduce dependence on centralized power grids, which are often vulnerable to damage during disasters. By decentralizing energy production and storage, these systems enhance grid resilience and reduce the impact of grid failures.
3. Reduced Peak Load on Grids
During disasters, energy demand often spikes, putting additional strain on already stressed power grids. Solar battery storage can alleviate this pressure by supplying stored energy during peak demand periods, preventing overloads and potential blackouts.
4. Sustainable Energy Source
Solar battery storage systems provide a clean and renewable energy source, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and lowering greenhouse gas emissions. This sustainability aspect is crucial in the long-term effort to combat climate change, which is a contributing factor to the increasing frequency of natural disasters.
Strategies for Implementing Solar Battery Storage for Disaster Resilience
1. Community Solar Programs
Community solar programs involve the collective investment in solar power systems and battery storage by a group of households or businesses. These programs can enhance disaster resilience by providing shared access to reliable energy sources during emergencies.
2. Microgrids
Microgrids are localized energy systems that can operate independently from the main grid. Integrating solar battery storage into microgrids can ensure that critical facilities, such as hospitals, emergency shelters, and communication centers, have a reliable power supply during disasters.
3. Residential Solar Battery Systems
Encouraging homeowners to install solar battery storage systems can enhance individual household resilience. These systems can provide backup power during outages, ensuring that essential appliances and devices remain operational.
4. Public-Private Partnerships
Collaborations between government agencies, private companies, and non-profit organizations can facilitate the deployment of solar battery storage systems. Public-private partnerships can leverage resources, expertise, and funding to implement large-scale projects aimed at improving disaster resilience.
5. Incentives and Regulations
Government incentives, such as tax credits, rebates, and grants, can encourage the adoption of solar battery storage systems. Additionally, regulations that mandate the inclusion of renewable energy and storage solutions in new construction projects can drive wider implementation.
Comparative Analysis of Implementation Strategies
The following table provides a comparative analysis of different strategies for implementing solar battery storage for disaster resilience:
| Strategy | Benefits | Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Community Solar Programs | Shared resources, cost-effective | Coordination among participants |
| Microgrids | Independent operation, critical facility support | High initial investment, technical complexity |
| Residential Systems | Individual resilience, direct benefits | Upfront costs, maintenance requirements |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Resource pooling, expertise sharing | Alignment of goals, managing partnerships |
| Incentives and Regulations | Increased adoption, market growth | Policy implementation, monitoring and enforcement |
Case Studies
1. Puerto Rico’s Post-Hurricane Maria Recovery
After Hurricane Maria devastated Puerto Rico’s power grid in 2017, the island has been actively investing in solar battery storage systems and microgrids to enhance energy resilience. Projects like the installation of Tesla’s Powerwall systems in homes and the development of community solar initiatives have significantly improved energy security.
2. California’s Wildfire Preparedness
California, prone to wildfires and power outages, has implemented policies to promote solar battery storage adoption. The state’s Self-Generation Incentive Program (SGIP) provides financial incentives for installing storage systems, helping homeowners and businesses maintain power during emergencies.
Challenges in Implementation
While the benefits of solar battery storage for disaster resilience are clear, several challenges must be addressed to ensure successful implementation:
1. High Initial Costs
The upfront cost of solar battery storage systems can be a barrier to widespread adoption. Financial incentives and innovative financing solutions are needed to make these systems more accessible.
2. Technical and Maintenance Issues
The installation and maintenance of solar battery storage systems require technical expertise. Ensuring that there is a skilled workforce to support these systems is essential for their reliability and longevity.
3. Regulatory and Policy Hurdles
Navigating the regulatory landscape can be complex, with varying policies and standards across regions. Streamlined regulations and supportive policies are necessary to facilitate the deployment of solar battery storage systems.
Future Prospects
The future of solar battery storage in enhancing disaster resilience looks promising, with several trends and advancements on the horizon:
1. Advancements in Battery Technology
Ongoing research and development are leading to more efficient, durable, and cost-effective battery technologies. Innovations such as solid-state batteries and green hydrogen storage offer potential improvements in energy storage capabilities.
2. Integration with Smart Grids
The integration of solar battery storage with smart grids can enhance energy management and disaster response capabilities. Smart grids can optimize the use of stored energy, improving overall grid resilience.
3. Increased Government and Private Sector Support
As the importance of disaster resilience becomes more apparent, increased support from governments and the private sector is expected. Investments in infrastructure, research, and incentives will drive the adoption of solar battery storage systems.
Conclusion
Solar battery storage systems offer a powerful solution for enhancing energy security and disaster resilience. By providing a reliable and sustainable energy source during emergencies, these systems can mitigate the impact of natural disasters and improve the stability of power grids. Implementing effective strategies, such as community solar programs, microgrids, and public-private partnerships, can maximize the benefits of solar battery storage.
Addressing challenges related to costs, technical expertise, and regulatory frameworks is crucial for successful deployment. With continued advancements in technology and increased support from stakeholders, solar battery storage systems will play a vital role in creating resilient and sustainable energy systems for the future.
