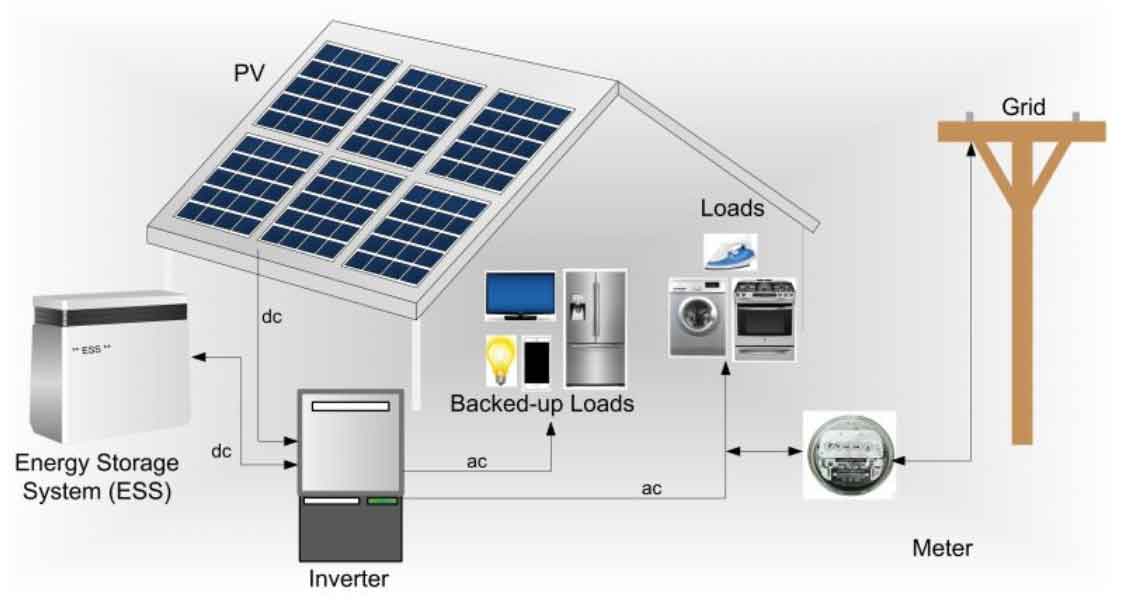
Choosing a residential energy storage system (ESS) for your house involves several key considerations to ensure that it meets your energy needs, budget, and future goals. Here are the steps and factors to consider when selecting an energy storage system for your home:
1. Assess Your Energy Needs
- Energy Usage: Start by reviewing your household’s energy usage, which you can find on your electricity bills. Understand your peak energy demands and total energy consumption over different seasons.
- Purpose of Storage: Determine whether the energy storage system is primarily for backup during power outages, for energy cost savings (e.g., time-of-use shifting), for maximizing the use of solar energy, or a combination of these.
2. Evaluate Solar PV Integration
- Existing Solar System: If you have or plan to install solar panels, consider how the energy storage system will integrate with them. The size and output of your solar system will influence the capacity and type of energy storage system you need.
- Grid-tied or Off-grid: Decide if your system will be grid-tied with backup capabilities or fully off-grid. Grid-tied systems can sell excess power back to the grid and draw from it when needed, while off-grid systems must be entirely self-sufficient.
3. Choose the Right Technology
- Battery Types: Common types include lithium-ion, lead-acid, and saltwater batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are popular due to their longer lifespan, higher efficiency, and compact size but are generally more expensive. Lead-acid batteries are cheaper but have a shorter lifespan and lower efficiency.
- Voltage Levels: Consider whether a low voltage (up to 48 volts) or high voltage (above 48 volts) system is more suitable based on your home’s energy demands, safety requirements, and installation complexity.
4. Size the System Appropriately
- Capacity and Power: Calculate the system’s required capacity (kilowatt-hours, kWh) and power rating (kilowatts, kW) based on your peak energy requirements and how long you need the system to provide power during an outage or for daily use.
- Scalability: Consider whether you might want to expand the system in the future. Some systems are more easily scalable than others.
5. Consider Regulatory and Safety Issues
- Local Regulations: Check local codes and regulations regarding battery storage systems, including required permits and inspections.
- Safety Standards: Ensure that the system meets national and international safety standards. Look for certifications and testing proof to ensure safety and reliability.
6. Analyze Economic Factors
- Costs: Consider the upfront cost of the energy storage system and installation, along with ongoing maintenance costs. Calculate potential savings on energy bills to understand the payback period and return on investment.
- Incentives and Rebates: Research available government incentives, rebates, or tax credits that can reduce the overall cost of the energy storage system.
7. Select a Reputable Brand and Installer
- Manufacturer Reputation: Choose a well-known and reliable manufacturer with good reviews and a proven track record in the industry.
- Certified Installer: Use certified and experienced installers who provide good warranty terms and after-sales support.
8. Review Warranty and Maintenance
- Warranty Period: Look for long warranty periods that cover battery capacity and defects. A longer warranty can be indicative of a more reliable system.
- Maintenance Requirements: Understand the maintenance needs of energy storage system. Some systems require more regular maintenance than others.
By thoroughly assessing these factors, you can choose a residential energy storage system that is well-suited to your home’s needs, enhances your energy independence, and provides economic benefits over time.
