The journey of lithium-ion (Li-ion) battery innovations from laboratory breakthroughs to commercial success is a compelling narrative of scientific ingenuity, technological challenges, and strategic market positioning. This progression underscores the dynamic interplay between research and development (R&D), manufacturing advancements, and market demand that has propelled Li-ion batteries to the forefront of the energy storage and electric vehicle (EV) sectors. Let’s explore the key stages and milestones in the journey of Li-ion battery innovations to commercialization.
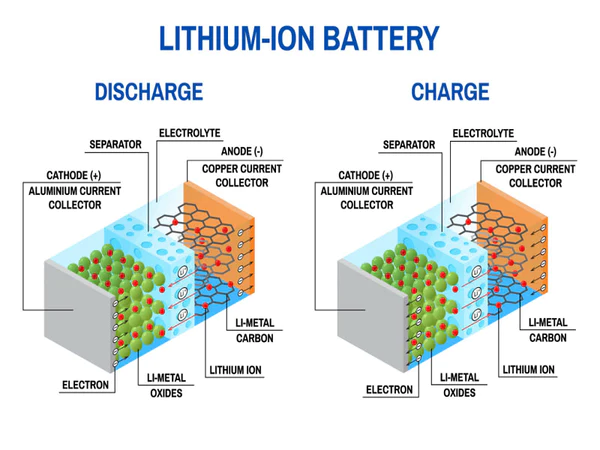
Initial Discovery and Development
The foundational work for lithium-ion batteries began in the 1970s with pioneering research by M. Stanley Whittingham, who explored lithium’s electrochemical properties for energy storage. This period was marked by experimental designs that leveraged lithium’s high energy density but also encountered significant safety challenges due to the reactive nature of lithium metal.
Breakthrough in Electrode Materials
The transition from laboratory curiosity to commercial potential took a significant leap forward in the 1980s with the introduction of lithium cobalt oxide (LiCoO2) as a cathode material by John Goodenough. Around the same time, Rachid Yazami demonstrated the viability of graphite anodes. These materials provided the basis for a rechargeable Li-ion battery with improved safety and energy density.
Commercialization and Market Entry
Sony Corporation commercialized the first Li-ion battery in 1991, marking the technology’s debut in consumer electronics. This initial application in portable devices, such as camcorders and cell phones, was driven by the battery’s high energy density, lightweight, and recharging capabilities. The success in consumer electronics established Li-ion batteries as the preferred choice for portable power, setting the stage for expansion into other markets.
Technological Improvements and Diversification
Following commercialization, continuous improvements in Li-ion technology have been crucial in expanding its applications. Innovations in electrode materials, electrolyte formulations, and battery management systems have enhanced safety, increased energy density, and extended life cycles. These advancements have facilitated the entry of Li-ion batteries into more demanding applications, including electric vehicles and renewable energy storage systems.
Scaling Up and Reducing Costs
The surge in demand for electric vehicles and renewable energy solutions in the 21st century has driven massive investments in Li-ion battery production capacity. Economies of scale achieved through the construction of gigafactories have been instrumental in reducing the cost per kilowatt-hour (kWh), making Li-ion batteries economically viable for a broader range of applications. This scale-up phase has been characterized by global competition, with major players in Asia, Europe, and the Americas vying for leadership in the battery market.
Challenges and Innovations
As Li-ion batteries have become more ubiquitous, challenges such as resource scarcity, environmental concerns, and end-of-life disposal have emerged. Addressing these challenges has spurred further innovations, including the development of alternative cathode materials that reduce reliance on cobalt, advances in battery recycling technologies, and research into next-generation battery chemistries such as solid-state batteries.
The Future of Lithium-Ion Batteries
The journey of Li-ion batteries is far from complete. The push for higher energy densities, faster charging times, improved safety, and sustainability continues to drive R&D efforts. Emerging trends, such as the integration of batteries with smart grids and the development of ultra-fast charging infrastructure for EVs, suggest that Li-ion batteries will remain at the heart of the energy transition for the foreseeable future.
Conclusion
The path from the initial discovery of lithium-ion battery principles to their widespread commercialization is a testament to the transformative power of sustained scientific and technological innovation. As the world increasingly turns to renewable energy sources and electric mobility, the evolution of Li-ion battery technology will continue to play a critical role in enabling these shifts, marking an ongoing journey of innovation, challenge, and opportunity.
