Based on the analysis, the LCOE results of different energy storage systems were calculated using deterministic models and fixed parameter values, as shown in Table. By comparing the LCOE results of different energy storage systems, it can be seen that under both IEA scenarios, the levelized electricity cost of the dual tank molten salt energy storage system is the highest. It is proposed that using concrete energy storage or phase change energy storage schemes can reduce the levelized electricity cost of the system. In the Roadmap scenario, the cumulative installed capacity of solar thermal power plants increases rapidly, therefore, under the same circumstances, the cost of energy storage system leveling electricity is lower than that in the Blue Map scenario.
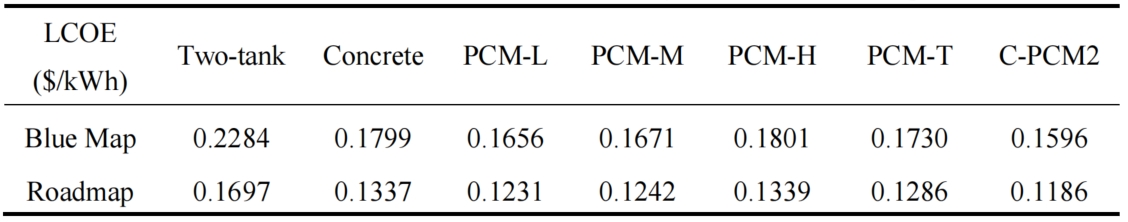
Among several energy storage systems, the levelized electricity cost of the sensible latent heat combined energy storage system is the lowest, with 0.1596 $/kWh and 0.1186 $/kWh respectively in the two scenarios. In a single phase change energy storage system, as the phase change temperature increases, the cost of system leveling increases. When using high-temperature energy storage systems, although the energy storage is relatively higher compared to medium and low temperature phase change energy storage, the cost of leveling the system is relatively high due to the high price of high-temperature phase change materials. When using a three-layer phase change energy storage system, the levelized electricity cost of the system is reduced, which is smaller than that of a high-temperature phase change energy storage system. In order to further reduce system costs, 50% volume of concrete was used to replace the phase change material in the middle section, resulting in the lowest cost of system leveling. Under two development scenarios, compared to the dual tank molten salt energy storage system, the levelized electricity cost of the sensible latent heat combination energy storage system decreased by 30.12% and 30.11%, respectively, while the levelized electricity cost of the concrete sensible heat energy storage system decreased by 21.23% and 21.21%, respectively.
