In recent years, China’s economy has developed rapidly, and people’s quality of life has greatly improved. Cars have basically become a convenient means of transportation for every family. At present, cars on the market are mainly divided into three categories. One is traditional cars, which use fuel or gas (combustible ice) as power; One type is new energy electric vehicles, which are powered by built-in lithium-ion battery modules; There is also a hybrid vehicle that is powered by fuel and an internal power battery module. In addition to new energy electric vehicles, both traditional and hybrid vehicles require their built-in lead-acid batteries as the starting power source. The battery used as the starting power supply generally uses a 12 V lead-acid battery (see Figure 1), which supports high current discharge and can reach a maximum instantaneous starting current of 600 A. However, this type of battery has a shorter lifespan, with a normal lifespan of 2-3 years and a maximum lifespan of no more than 6 years. Due to frequent starting, prolonged uninterrupted charging, or prolonged parking of the car, the battery may experience overcharging or over discharging, which can easily reduce the rated capacity and discharge performance of the battery and seriously affect its service life.

Lead acid batteries used for starting are prone to malfunctions due to their operating environment and poor user habits (such as prolonged parking without starting the car), resulting in the inability to start the car normally. When a car has been in use for a certain period of time, even with normal maintenance, the lead-acid battery used for starting may still fail to start the car due to long usage time, low battery output voltage, and insufficient remaining capacity. At this time, if a malfunction occurs in a remote mountainous area or sparsely populated area, calling for rescue cannot guarantee quick rescue and starting of the vehicle. As the owner, if the vehicle is equipped with a mobile power supply for emergency starting, self rescue can be achieved. Therefore, experienced car owners often prepare mobile power sources for emergency starting in case of emergencies. Mobile power supplies for emergency starting of vehicles generally have a 5V DC output port, USB charging port, battery indicator screen (light), lighting, and are equipped with a car start output connection cable, as shown in Figure 2. The mobile power supply for emergency starting of vehicles is easy to operate, compact, convenient, and supports high current discharge. It can start the vehicle when the lead-acid battery used for starting fails. It is also often used as a mobile power supply to power outdoor lighting, outdoor inflation, mobile phones, iPads, and other equipment. It is one of the essential products for outdoor travel and can cope with various emergency situations. Due to the above advantages and affordable prices, it is highly welcomed by car owners, and mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles have been widely used.
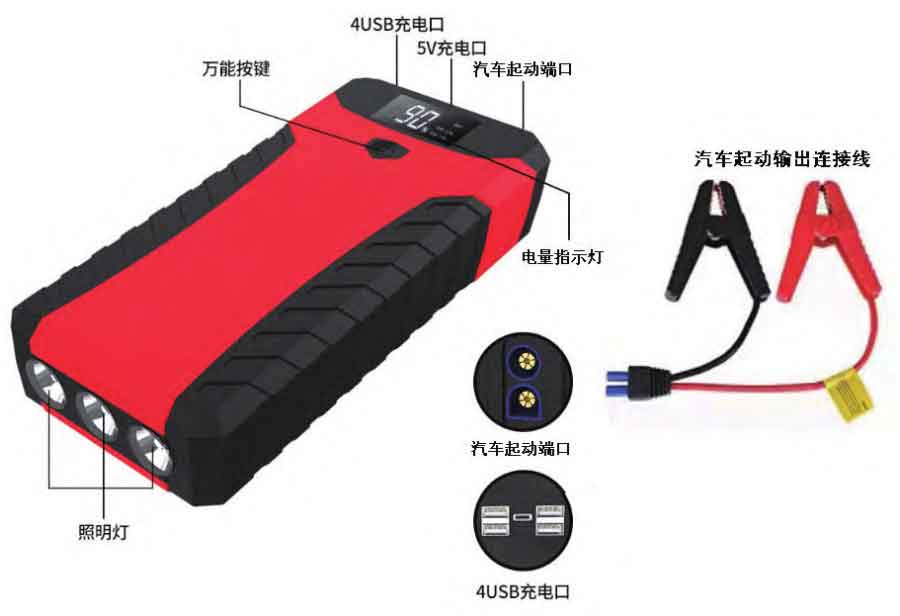
Below, we will elaborate on the significance of research, domestic research status, and testing methods of mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles.
1. The significance of research
With the stable growth of the number of cars in our country and the increasing demand for people’s travel, coupled with the advantages of powerful functions, convenient carrying, and affordable prices of mobile power sources for emergency starting of vehicles, the demand for mobile power sources for emergency starting of vehicles by consumers is also increasing significantly.
At present, most mobile power products for emergency starting in vehicles use lithium-ion batteries as energy storage devices because of their small size, large capacity, and support for high current discharge. However, due to the stability of its own materials, lithium-ion batteries have high requirements for effective protection under abnormal working conditions such as overcharging, over discharging, high-temperature environments, and internal and external short circuits. Manufacturers need to equip corresponding protective boards for mobile power supplies for emergency starting in vehicles. Only in this way can users avoid fire and explosion when using the mobile power supply for emergency starting in vehicles.
However, the quality of mobile power supply products for emergency starting in vehicles on the market varies, and general consumers cannot distinguish which mobile power supply products for emergency starting in vehicles are safe and reliable, and whether their emergency rescue performance is long-lasting. Many people believe that expensive or beautifully packaged mobile power supplies for emergency starting in vehicles are always safe and reliable. However, they are unaware that low-quality mobile power supplies for emergency starting may not be able to achieve their intended emergency rescue functions due to their inflated capacity. It is also possible that the use of low-quality lithium-ion batteries may cause danger such as leakage, fire, and explosion during rescue operations or storage in harsh environments, Furthermore, it poses immeasurable potential risks to consumers. Therefore, it is extremely important to study the testing methods of mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles.
2. Research status of domestic standards
Mobile power sources are popular among consumers as backup energy sources due to their portability and high cost-effectiveness. There has always been no corresponding national standard to guide the standardization of mobile power sources. Until December 29, 2017, the National Standards Committee officially released the industry’s first GB/T 35590-2017 “General Specification for Mobile Power Supplies for Portable Digital Devices in Information Technology” standard on mobile power supplies (power banks), which was officially implemented on July 1, 2018. However, so far, there are no corresponding testing standards for special products such as mobile power supplies for emergency starting of vehicles in China.
Due to the special application environment and functions of mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles, China’s GB/T 35590-2017 standard cannot meet the testing requirements of enterprises and consumers for this product. Therefore, it is urgent to conduct a systematic analysis of the working principle and function of mobile power supplies for emergency starting in vehicles, study testing methods, and develop corresponding testing standards to help enterprises improve the quality of their products, strengthen their competitiveness, and ensure the personal and property safety of consumers, thereby promoting their long-term healthy and stable development.
3. Testing methods and content
According to the usage environment and multifunctional use of mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles, they can be tested and assessed from three aspects: functionality, environment, and safety performance.
3.1 Function
The mobile power supply for emergency starting of vehicles is a portable mobile power supply that can not only serve as a temporary starting power source for cars (the car’s built-in battery generally uses a 12 V lead-acid battery), but also serve as a power supply for outdoor lighting, outdoor inflation, mobile phones, IPADs and other equipment (the general power supply voltage is 5 V). Therefore, it has the basic functions of conventional portable mobile power sources, such as DC 5 V input and output function.
(1) Capacity
The size of the capacity determines the length of its discharge time. The larger the capacity, the longer the battery life available for the device. Inadequate capacity can lead to a shorter time for supplying power to external devices, indirectly causing inconvenience to general consumers. For consumers engaged in hazardous operations, the operation time may be too short and the corresponding operations may be terminated, causing harm to personal safety. There are also many mobile power supplies for emergency starting vehicles circulating in the market with capacity falsely labeled products. There are two main cases of capacity falsely labeling: one is that the capacity labeled on the product nameplate is actually the capacity of the battery cell, just to deceive consumers; Another type is that the capacity is exaggerated, and the actual capacity cannot meet its nominal capacity at all. Both of these situations will shorten the charging time for external devices using mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles. For on-demand consumers, when using this product, the power supply may be interrupted in daily life, making it inconvenient for people to use; In other special industries such as healthcare, there will inevitably be incalculable losses.
The capacity testing of mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles is based on the parameters provided by the identification on their products. A reasonable and compliant nameplate usually uses simplified Chinese to reflect the product’s name, model, rated voltage (input and output) and rated capacity, starting current, peak current, rated energy, battery type, conversion efficiency, manufacturer or trademark, and warning signs. Incorrect labeling often leads to incorrect consumption guidance for general consumers. Easy to cause misoperation, inability to reasonably distinguish and select suitable models and specifications during purchase, and causing corresponding property and personal safety losses in the event of a fire or explosion in the mobile power supply, as well as inability to protect rights and trace compensation.
Therefore, the capacity of the mobile power supply for emergency starting in vehicles should meet the requirement of not being lower than its nominal rated capacity during testing at room temperature (23 ℃± 2 ℃); Under high temperature (45 ℃± 2 ℃) testing, it shall not be lower than its nominal rated capacity; Under low temperature (-10 ℃± 2 ℃) testing, it shall not be less than 60% of its nominal rated capacity.
(2) Output voltage
In general, after working for a period of time under rated load, the external output voltage of the mobile power supply for emergency starting in vehicles will gradually decrease. For lithium-ion batteries with good built-in quality and without virtual capacity, the decay rate of their output voltage is relatively small at rated load output. However, for products with virtual capacity, the attenuation rate of the output voltage is relatively large, which affects normal on load use.
The actual output voltage of a fully charged emergency starting mobile power supply for vehicles should not be lower than 90% of the rated voltage after 10 minutes of discharge at the rated current.
(3) Start testing
The rated capacity and corresponding configuration parameters required for the starting current of lead-acid batteries used in vehicles in China are shown in Table 1, which basically covers all existing vehicle models. The rated capacity of lead-acid batteries used for starting in general family cars is generally between 30-65 Ah, and the instantaneous starting current is between 240-500 A.
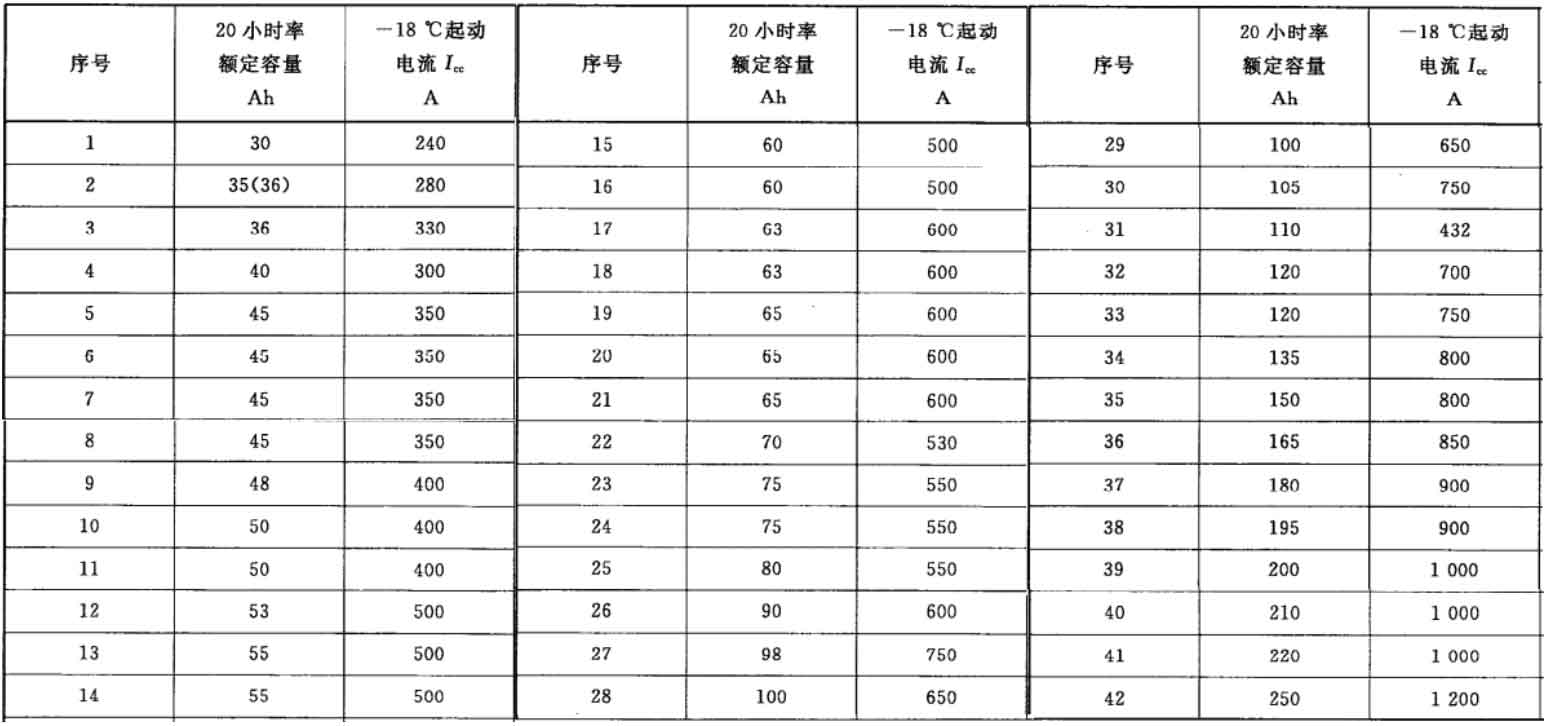
Startup testing is the most important assessment indicator for the function of mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles. All emergency starting mobile power sources for vehicles should have the function of assisting or independently starting the vehicle. This is a unique highlight of the product and an important reason for its popularity among consumers.
According to the nameplate identification on the vehicle emergency starting mobile power supply product, under environmental temperature conditions (23 ℃± 2 ℃), the vehicle emergency starting mobile power supply should discharge the marked starting current for 3 seconds. After discharge, the voltage should not be less than 7.5 V, and the appearance should have no obvious deformation, liquid leakage, fire or explosion; Under ambient temperature conditions (60 ℃± 2 ℃), the mobile power supply for emergency starting of vehicles should be marked with a starting current discharge for 3 seconds. After discharge, its voltage should not be lower than 7.5 V, and its appearance should have no obvious deformation, liquid leakage, fire or explosion; Under ambient temperature conditions (-18 ℃± 2 ℃), the mobile power supply for emergency starting of vehicles should discharge for 3 seconds with a marked starting current of 0.6 times. After discharge, its voltage should not be lower than 7.5 V, and its appearance should have no obvious deformation, liquid leakage, fire or explosion.
3.2 Environment
(1) High temperature storage
Mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles are generally stored in the vehicle. With the arrival of summer, especially in the south, the temperature inside the car can reach up to 50-60 degrees Celsius under the scorching sun. In this environment, the use of mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles is a challenge. The special environment requires the mobile power supply for emergency starting of vehicles to be able to withstand sudden situations caused by high temperatures. Therefore, high-temperature storage is an important environmental factor that cannot be ignored.
Place the fully charged emergency starting mobile power supply for vehicles in a 55 ℃± 2 ℃ environment for 7 days, and its appearance should have no obvious deformation, liquid leakage, fire or explosion. The reduction in open circuit voltage should not exceed 0.5 V, and the starting current should be marked for 3 seconds of discharge. After discharge, the voltage should not be lower than 7.5 V, and the appearance should have no obvious deformation, liquid leakage, fire or explosion.
(2) Vibration
Because the mobile power supply for emergency starting in vehicles is stored in the vehicle. Vehicles on flat road surfaces such as scenic spots and highways have less bumps, and the vibration frequency and amplitude caused by the emergency power supply for vehicle use are relatively small; But driving on rugged mountain roads and bumpy mudslides can cause significant bumps, resulting in higher vibration frequencies and amplitudes for emergency starting mobile power sources used in vehicles. Therefore, the mobile power supply for emergency starting in vehicles can still function normally under various bumps and vibrations in various environments, regardless of the diversity of road conditions.
| Frequency | Displacement amplitude | Sweep frequency time | Sweep rate |
| 10 Hz~30 Hz | 2 mm | 30 min | 1oct/min |
| 30 Hz~55 Hz | 1 mm | 30 min | 1oct/min |
Secure the fully charged emergency start mobile power supply of the vehicle to the vibration test bench, and conduct horizontal and vertical vibration tests according to the parameters in Table 2 below. After the test, there should be no obvious deformation, liquid leakage, fire or explosion.
(3) Flame retardant
The materials used for the packaging of mobile power supplies for emergency starting in vehicles should be able to limit the spread of flames in the event of an accident that causes the protection function to fail and triggers a fire or explosion. The use of a flame-retardant shell can ensure that flames do not spread and automatically extinguish inside. Even if a fire occurs, it will not endanger the life and property safety of vehicles and users.
The fire resistance of the shell of the mobile power supply for emergency starting in vehicles should comply with the provisions of 4.7.3.2 in GB 4943.1-2011 standard, and its flame retardant level should meet the requirements of V-1.
3.3 Safety performance
(1) Overcharge protection
Mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles generally support charging with on-board chargers or matching power adapters. However, there are a wide variety of car charger products and power adapters, and the quality of the products also varies. When using low-quality power adapters or power adapters with mismatched input voltage for charging, there is a risk of overvoltage charging. Excessive charging voltage can easily cause hazards such as fire, explosion, and leakage of mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles, thereby endangering the personal and property safety of users.
Therefore, the protection system of the mobile power supply for emergency starting in vehicles should have overcharging protection, and the overcharging protection voltage should be ± 0.05 V of the charging cut-off voltage of the corresponding lithium battery material system. When the mobile power supply for emergency starting of vehicles experiences overcharging, its protection system should be able to cut off the charging circuit and achieve self-protection.
(2) Overdischarge protection
When the mobile power supply for emergency starting in vehicles is not used for a long time or is not charged in a timely manner after being used for a period of time, its capacity consumption is significant. When used again, it is possible to cause over discharge of the emergency starting mobile power supply for vehicles. If used to start the vehicle, the generated starting current can easily cause the built-in lithium-ion battery to lose control, rapidly increase the battery temperature, and thus cause fire and explosion hazards.
The protection system of the mobile power supply for emergency starting of vehicles should have over discharge protection, and the over discharge protection voltage is ± 0.05 V of the discharge cut-off voltage of the corresponding lithium battery material system. In addition, there should be corresponding indicator lights to display or indicate the remaining capacity of the device, and whether it can continue to independently or assist in starting the vehicle.
(3) Anti reverse connection protection
Mobile power supplies for emergency starting of vehicles are generally connected to the powered equipment through external connecting wires, and it cannot be completely ruled out that users will not reverse the positive and negative poles of the output lines. Reverse connection can cause high current discharge, directly causing the battery temperature to lose control, thereby posing a risk of fire and explosion.
The protection system of the mobile power supply for emergency starting of vehicles should have anti reverse connection protection. When the positive and negative poles of the mobile power supply for emergency starting of vehicles are reversed due to misoperation, the protection system should immediately activate the protection, stop external output, and should not damage the vehicle and the mobile power supply for emergency starting of vehicles, so as not to cause harm to personnel.
(4) Short circuit protection
Mobile power supplies for emergency starting in vehicles may experience a decrease in the creepage distance and electrical clearance of the power output line due to the failure of their insulation materials, or high temperatures may cause deformation of the insulation shell material, resulting in exposed components and short circuits. This can instantly generate significant current shocks, damage their own protective systems, and cause hazards such as fire, explosion, and liquid leakage.
The protection system of the mobile power supply for emergency starting in vehicles should have anti short circuit protection. In the event of a direct short circuit between the positive and negative poles caused by misoperation or internal component failure of the mobile power supply for emergency starting in vehicles, the protection system should immediately activate protection, stop external output, and should not damage the vehicle and the mobile power supply for emergency starting in vehicles, so as not to cause harm to personnel.
4. Conclusion
With the increasing number of vehicles in China’s automotive market, the demand for mobile power sources for emergency starting in vehicles by consumers is also gradually increasing. This article focuses on the prominent characteristics of fire and explosion risks in mobile power supplies for emergency starting vehicles, as well as their unique functions and special environments. It deeply analyzes the reasons and mechanisms for their easy operation of fire and explosion, and summarizes corresponding testing methods. The study of this testing method is beneficial for enterprises to improve the quality of their products, strengthen their competitiveness, and ensure the personal and property safety of consumers. It provides reference opinions for the future development of testing work for such products and the improvement of relevant standards.
