With the rapid development of different types of photovoltaic power plants, the information sensing capability of the power system is insufficient, and existing regulatory technical means cannot achieve comprehensive observation, measurement, and control. The regulatory system management system is not sufficient to adapt to the new situation development requirements.Currently, the communication mode of solar inverters is characterized by high digitalization, intelligence, and networking, effectively supporting the collaborative operation of massive distributed objects and the accurate decision-making of complex system operating states under various market mechanisms, and promoting the efficient transformation and utilization of energy in the power-centered energy system.
As the core component of a power station, how should solar inverters choose and apply their communication methods in different application scenarios?
1. Communication mode and application scenario of solar inverter
1.1 4G communication
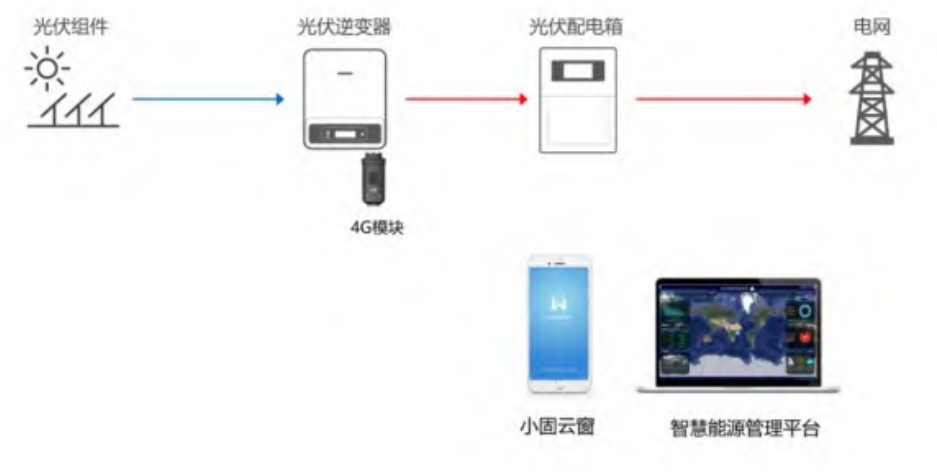
Introduction to communication mode: This mode is currently the most common communication mode. Solar inverters come with a 4G communication module (built-in SIM card) when shipped. Each solar inverter is configured independently, and data can be sent to the solar inverter platform through wireless networks and base stations for remote browsing.
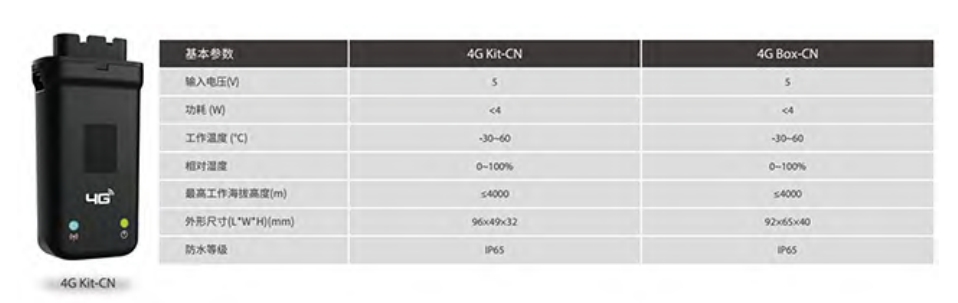
Main parameters: frequency band: 1800MHz, protocol used: modbus TCP
Applicable scenarios: areas where solar inverters are dispersed and wiring is inconvenient.
Advantages: Long communication distance;simple installation without wiring;support for encryption;support for resume from breakpoints;support for remote upgrades.
Disadvantages: There are traffic charges (the solar inverter comes with a 5-year free traffic allowance. On the Xiaoguyun window app, the traffic expiration time can be seen on the “Traffic Recharge” page on the homepage, and self-recharging is also available for 36 yuan per year);poor communication quality in areas with poor signal;unable to do real-time control.
Introduction to communication mode:
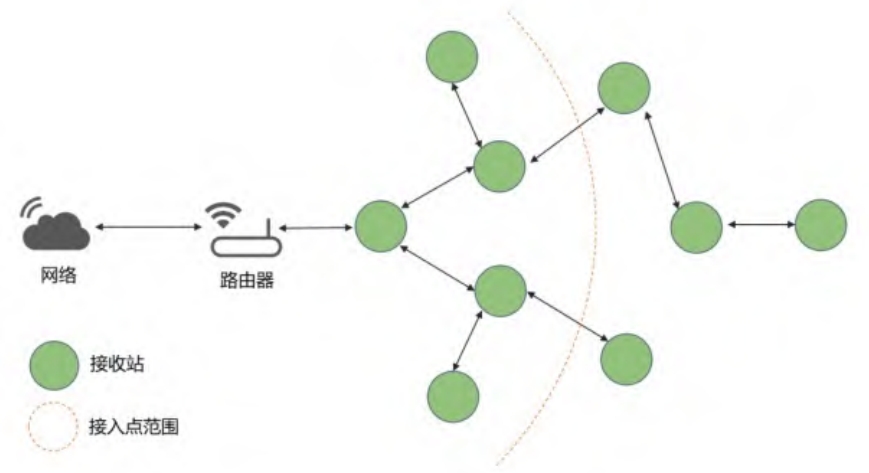
Method 1: Wireless communication can be achieved through a WiFi module matched with a solar inverter, using IEEE protocol to upload solar inverter data to a monitoring platform through a wireless network;
Method 2: Communication is conducted through the WiFi communication module that comes with the solar inverter itself, and can act as a relay for each other. The machine can act as both a transmitting source and a receiving station, and through the final root node, it can access the router to output communication signals at a transmission rate of approximately 20M/s. When the original path is disconnected, nearby nodes can be used for data transmission.
1.2 WiFi communication
WiFi module technical parameters
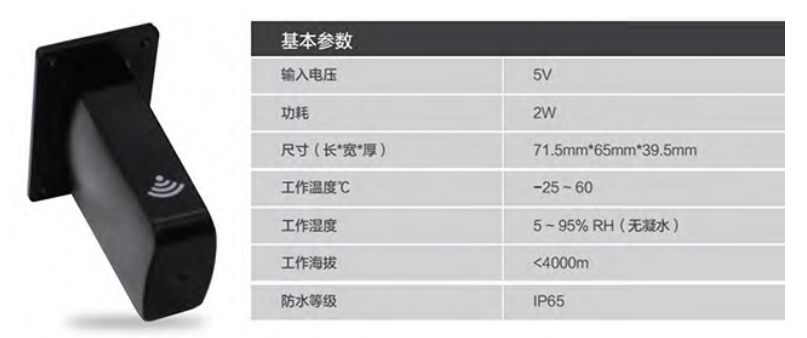
Main parameters: communication distance: 10m, frequency band: 2.412GHz-2.484GHz, protocol used: modbus TCP
Applicable scenarios: Areas with wireless network coverage;WiFi module + SolarGo APP can be used to debug solar inverters;suitable for micro-inverter scenarios.
Advantages: simple installation without wiring;no traffic charges;support for resume from a breakpoint;support for remote upgrades, flexible networking, and high reliability of communication.
Disadvantages: vulnerable to interference;subject to significant environmental constraints in the installation location.
1.3 Bluetooth communication
Introduction to communication mode: It can achieve short-range communication through a Bluetooth module matched with a solar inverter, using the LE protocol, mainly used for local debugging of solar inverters.
Main parameters: communication distance: 10m, protocol used: modbus RTU
Applicable scenarios: devices that require near-end debugging.
Advantages: easy connection;no traffic charges;fast communication speed;low power consumption.
Disadvantages: short communication distance;no access to the Internet.
1.4 LAN communication
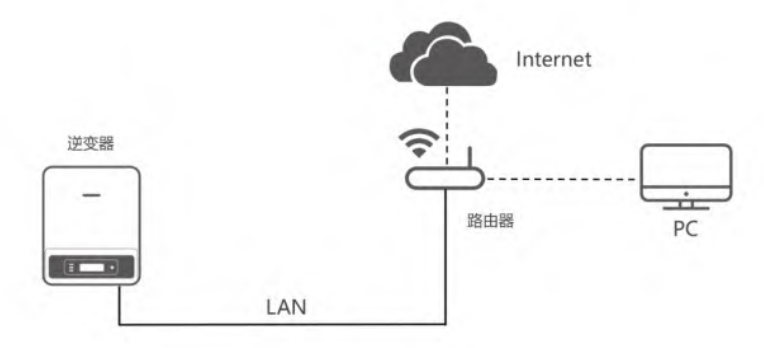
Introduction to communication mode: The solar inverter can be connected to the router through the LAN module built in the solar inverter, and finally upload the solar inverter data to the monitoring platform through wireless network.
Main parameters: communication distance: 100m;protocol used: modbus TCP
Applicable scenarios: mainly for foreign household scenarios and energy storage equipment.
Advantages: no traffic charges;easy wiring;stable communication.
Disadvantage: Solar inverters need to have a LAN interface.
1.5 RS485 communication
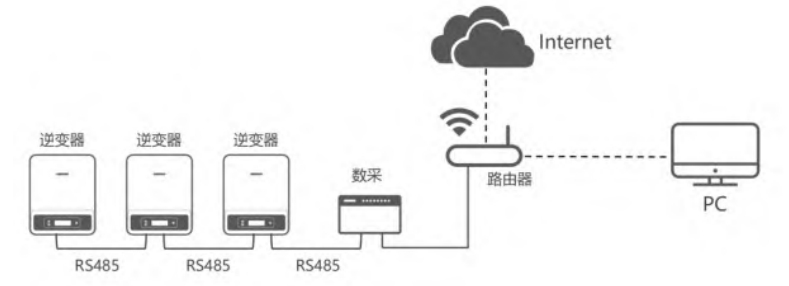
Communication method: RS485 communication uses wired connection. The solar inverters are connected in a hand-in-hand manner, and the last solar inverter is linked to the data collector. Then, the solar inverter data is transmitted to the monitoring platform through wireless network.

Main parameters: communication distance: 1200m;transmission rate: 9600bps/s;protocol used: modbus RTU
Application scenario: large project capacity, large number of solar inverters and centralized;special application scenarios requiring control, such as power control, anti-reverse flow, etc.
Advantages: stable communication, strong anti-interference ability;can achieve control functions;friendly communication with third parties.
Disadvantages: Requires the use of a data collector;requires cabling;communication distance of 1200m.
1.6 PLC Communication
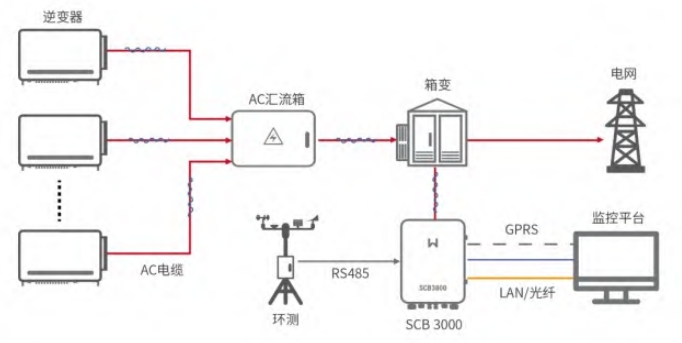
Introduction to communication mode: Power line carrier communication is used, using existing power lines as the transmission medium to achieve data transmission and information exchange.When sending data using power line communication, the transmitter first modulates the data onto a high-frequency carrier, and then couples it to the power line through a coupling circuit after power amplification. Finally, it is restored to identifiable data through modulation and demodulation.
Main parameters: communication distance: 1000m;transmission rate: 100kbps/s; frequency band: broadband 0.7-2.9MHz;protocol used: modbus RTU
Applicable scenarios: scenarios with large project capacity, large number of solar inverters, and use of boosting or low-voltage no-load conditions.
Advantages: No need for additional communication lines;stable communication.
Disadvantages: cannot be used with load;requires additional modulation and demodulation equipment;communication distance of 2000m.
2. Summary
Summary of communication characteristics of solar inverters:
| Mode | Application scenarios | Advantage | Disadvantages |
| 4G | In areas where inverters are scattered and wiring is inconvenient, they are mainly for household use and county wide promotion projects, or small-scale industrial and commercial projects | Long communication distance; Easy installation without wiring; Support encryption function; Support breakpoint continuation; Support remote upgrade | There is a traffic fee; Unable to use or ineffective when the operator’s signal is poor |
| WiFi | Areas with wireless network coverage; It can be debugged on-site using WiFi modules and apps, suitable for micro reverse scenarios | Easy installation without wiring; No traffic fee; Support breakpoint continuation; Support remote upgrades; Flexible networking and high communication reliability in micro inversion | Easy to be interfered with; Due to significant environmental limitations in the installation location |
| Bluetooth | Devices that require proximal debugging | Convenient connection without any traffic fees; Fast communication speed; Low power consumption | Short communication distance and inability to access the internet |
| LAN | Mainly for foreign household scenarios and energy storage equipment | No traffic fee; Convenient wiring and stable communication | The inverter needs to have a LAN interface |
| RS485 | The project has a large capacity, a large number and concentration of inverters; Special application scenarios that require participation in control, such as power control, anti backflow, etc | Stable communication and strong anti-interference ability; Can achieve control functions; Friendly communication with third parties | Require the use of a data collector; Need to increase wiring |
| PLC | Scenarios with large project capacity, a large number of inverters, and the use of boost voltage or situations with low voltage and no load | No need for additional communication cables; Stable communication | Cannot be used with load; Need to add modulation and demodulation equipment |
The above is a summary of various communication methods for solar inverters. The most suitable communication method can be selected according to different application scenarios and requirements. With multiple communication and control methods, an energy interconnection platform can be constructed to enhance the balance ability of the power system, support the rapid development and efficient utilization of new energy, support the collaborative control of power generation, grid, load, and storage, and facilitate the construction of a new power system.
