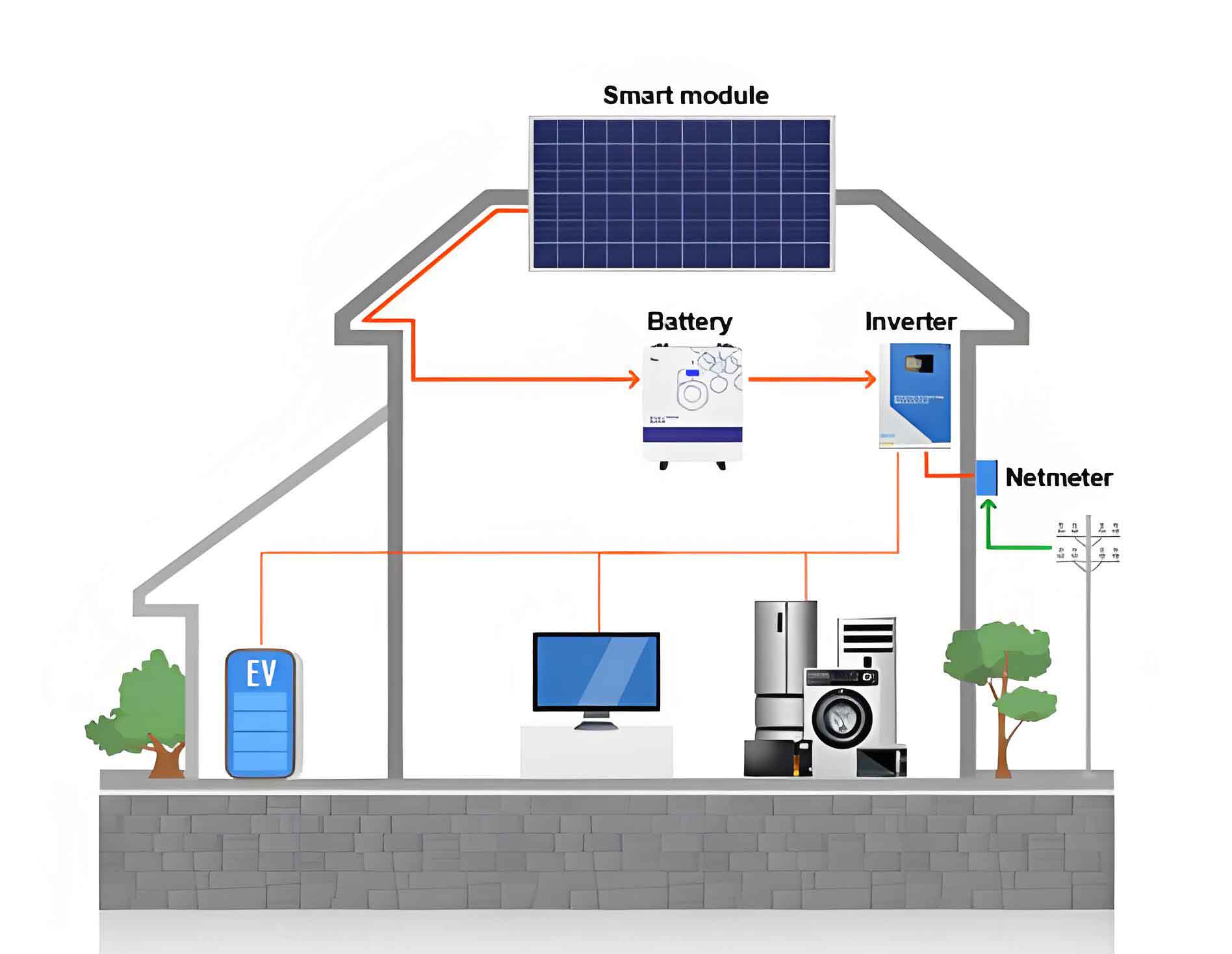
Introduction
Solar power inverter is essential components in solar energy systems, converting direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) for use in homes, businesses, and the power grid. However, like any complex electronic device, solar power inverter can experience failures that impact the efficiency and reliability of the entire solar energy system. Understanding common issues and implementing preventive measures can significantly enhance the long-term reliability of solar power inverter. This article explores common solar power inverter failures and provides strategies to prevent them, ensuring the sustained performance of solar energy systems.
Common Issues with Solar Power Inverter
Solar power inverter can encounter various issues that can disrupt their functionality and efficiency. Some of the most common issues include:
- Overheating: Overheating is a frequent problem in solar power inverter, caused by inadequate ventilation, high ambient temperatures, or excessive load. Prolonged overheating can damage internal components and reduce the inverter’s lifespan.
- DC/AC Conversion Failure: Failures in the DC to AC conversion process can occur due to faults in the inverter’s power electronics, such as transistors, capacitors, or transformers. These failures can lead to reduced power output or complete inverter shutdown.
- Grid Connection Issues: Problems with connecting to the power grid, such as synchronization errors, voltage fluctuations, or frequency mismatches, can prevent the solar power inverter from efficiently feeding electricity into the grid.
- Firmware and Software Bugs: Firmware and software issues can affect the performance and functionality of modern solar power inverter. Bugs or glitches in the control software can lead to erroneous readings, inefficient power conversion, or system instability.
- Component Degradation: Over time, components within the solar power inverter, such as capacitors, cooling fans, and semiconductors, can degrade due to wear and tear, leading to reduced performance or failures.
- Environmental Factors: Exposure to harsh environmental conditions, such as moisture, dust, and extreme temperatures, can cause corrosion, short circuits, or other damage to the solar power inverter.
Preventive Measures for Long-Term Reliability
Preventing solar power inverter failures involves a combination of proper installation, regular maintenance, and advanced technological solutions. Here are some strategies to ensure long-term reliability:
- Proper Installation:
- Adequate Ventilation: Ensure that the solar power inverter is installed in a well-ventilated area to prevent overheating. Avoid direct sunlight and ensure there is enough space around the inverter for air circulation.
- Environmental Protection: Install the inverter in a location protected from harsh environmental conditions, such as rain, dust, and extreme temperatures. Use enclosures or shelters if necessary.
- Regular Maintenance:
- Periodic Inspections: Conduct regular inspections of the solar power inverter to identify and address any signs of wear, damage, or component degradation. Check for loose connections, signs of overheating, and accumulation of dust or debris.
- Firmware Updates: Keep the inverter’s firmware and software up to date to ensure optimal performance and address any known bugs or vulnerabilities. Manufacturers often release updates that improve efficiency and reliability.
- Advanced Monitoring and Diagnostics:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Utilize advanced monitoring systems that provide real-time data on the inverter’s performance, energy production, and potential issues. This data can help detect problems early and prevent costly failures.
- Predictive Maintenance: Implement predictive maintenance strategies using data analytics and machine learning to anticipate potential failures and perform maintenance before issues escalate.
- Quality Components:
- High-Quality Materials: Use solar power inverter that incorporate high-quality materials and components designed for durability and reliability. Investing in a reputable brand with a proven track record can reduce the likelihood of failures.
- Thermal Management: Ensure the inverter has effective thermal management systems, such as cooling fans or heat sinks, to dissipate heat and maintain optimal operating temperatures.
- Grid Compatibility:
- Compliance with Grid Codes: Ensure that the solar power inverter complies with local grid codes and standards for voltage, frequency, and synchronization. Compliance reduces the risk of grid connection issues and enhances overall system reliability.
Common Solar Power Inverter Failures and Prevention Strategies
| Common Issue | Description | Prevention Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Overheating | Inadequate ventilation or excessive load | Proper installation, adequate ventilation, cooling systems |
| DC/AC Conversion Failure | Faults in power electronics (transistors, capacitors) | Regular maintenance, use of high-quality components |
| Grid Connection Issues | Synchronization errors, voltage fluctuations | Compliance with grid codes, real-time monitoring |
| Firmware and Software Bugs | Software glitches affecting performance | Regular firmware updates, advanced diagnostics |
| Component Degradation | Wear and tear of internal components | Periodic inspections, predictive maintenance |
| Environmental Factors | Exposure to moisture, dust, extreme temperatures | Environmental protection, proper installation |
Case Study: Enhancing Inverter Reliability
Consider a residential solar energy system with a 5 kW solar power inverter installed in a region with high ambient temperatures and frequent voltage fluctuations. The homeowner experienced multiple inverter shutdowns due to overheating and grid connection issues. By implementing the following preventive measures, the homeowner significantly improved the system’s reliability:
- Proper Installation: The solar power inverter was relocated to a shaded, well-ventilated area with sufficient space for air circulation. An additional cooling fan was installed to enhance thermal management.
- Regular Maintenance: Monthly inspections were conducted to check for dust accumulation, loose connections, and signs of wear. The solar power inverter’s firmware was updated regularly to ensure optimal performance.
- Advanced Monitoring: A real-time monitoring system was installed, providing data on energy production, temperature, and grid connection status. Alerts were set up to notify the homeowner of any potential issues.
- Grid Compatibility: The solar power inverter was configured to comply with local grid codes, reducing the risk of synchronization errors and voltage fluctuations.
Conclusion
Solar power inverters are crucial for the efficient and reliable operation of solar energy systems. Understanding common issues and implementing preventive measures can significantly enhance the long-term reliability of solar power inverter. Proper installation, regular maintenance, advanced monitoring, and the use of high-quality components are essential strategies to prevent failures and ensure sustained performance. By addressing these challenges proactively, homeowners and businesses can maximize the benefits of their solar energy systems and contribute to a more sustainable future.
