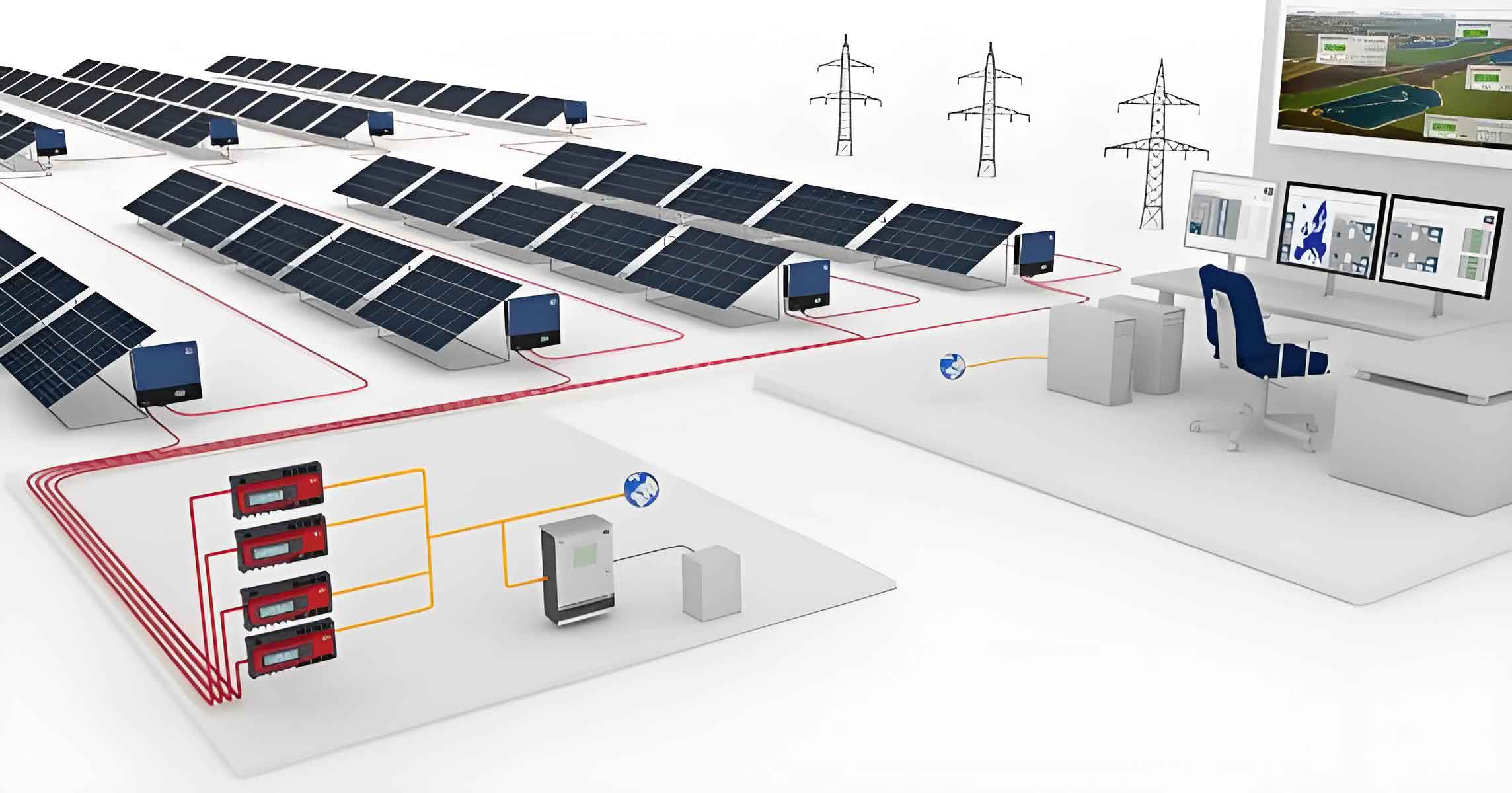
Large-Scale Solar Energy System projects are pivotal in the transition to renewable energy sources, offering not only environmental benefits but also significant economic impacts. These projects, characterized by extensive solar panel installations generating substantial amounts of electricity, influence various economic aspects, including job creation, energy costs, local economies, and overall economic growth. This article explores the multifaceted economic impacts of large-scale solar energy system.
1. Job Creation and Employment Opportunities
One of the most immediate economic impacts of large-scale solar energy system projects is the creation of jobs. These projects require a substantial workforce for various stages, including planning, construction, operation, and maintenance.
Job Categories in Solar Energy System Projects:
- Construction and Installation: Workers are needed to build and install solar panels and related infrastructure.
- Operation and Maintenance: Technicians and engineers are required to ensure the ongoing functionality and efficiency of the solar energy system.
- Manufacturing: Producing solar panels and other components generates jobs in the manufacturing sector.
- Research and Development: Continuous improvement and innovation in solar technology necessitate a skilled workforce in R&D.
| Job Category | Roles | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Construction and Installation | Builders, electricians, engineers | High initial employment, skill development |
| Operation and Maintenance | Technicians, supervisors | Long-term stable jobs, local employment |
| Manufacturing | Assembly line workers, quality control | Boosts local manufacturing industry |
| Research and Development | Scientists, engineers, analysts | Drives innovation, high-skill jobs |
2. Reduction in Energy Costs
Large-scale solar energy system projects contribute to a reduction in energy costs over time. Once installed, solar energy system has low operational costs compared to fossil fuel-based power plants. The initial investment in solar infrastructure is offset by the long-term savings in fuel and maintenance.
Benefits of Reduced Energy Costs:
- Lower Electricity Bills: Consumers and businesses benefit from reduced electricity costs, increasing disposable income and lowering operating expenses.
- Stabilized Energy Prices: Solar energy provides a hedge against volatile fossil fuel prices, contributing to more stable and predictable energy pricing.
| Aspect | Benefit | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Lower Electricity Bills | Reduced costs for consumers/businesses | Increased disposable income, reduced business costs |
| Stabilized Energy Prices | Less price volatility | Economic stability, predictable planning |
3. Stimulating Local Economies
Large-scale solar energy system projects can significantly boost local economies by generating new economic activities and investments.
Economic Stimuli from Solar Projects:
- Local Procurement: Sourcing materials and services locally stimulates the regional economy.
- Infrastructure Development: Improved infrastructure, such as roads and grid connections, benefits the broader community.
- Increased Tax Revenue: Solar energy projects contribute to local tax revenues, funding public services and community projects.
| Stimulus | Description | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Local Procurement | Using local materials/services | Supports local businesses, creates jobs |
| Infrastructure Development | Enhancing roads, grid connections | Long-term community benefits, improved local services |
| Increased Tax Revenue | Taxes from solar projects | Funds public services, community improvements |
4. Economic Diversification
Large-scale solar energy system projects contribute to economic diversification, particularly in regions heavily reliant on traditional industries such as mining or agriculture. Diversification can lead to a more resilient economy capable of withstanding market fluctuations.
Advantages of Economic Diversification:
- Reduced Economic Risk: Diversifying energy sources reduces dependence on a single industry, mitigating risks associated with market volatility.
- New Business Opportunities: Solar energy projects can spur the development of new businesses and industries, fostering innovation and entrepreneurship.
| Aspect | Benefit | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Economic Risk | Less dependence on single industry | Economic stability, resilience |
| New Business Opportunities | Fostering innovation and entrepreneurship | Economic growth, job creation |
5. Environmental and Social Benefits
The economic impacts of large-scale solar energy system projects extend beyond direct financial benefits to include significant environmental and social advantages.
Environmental and Social Impacts:
- Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Solar energy system contribute to reducing carbon emissions, mitigating climate change and its associated economic costs.
- Improved Public Health: Reduced air pollution leads to better health outcomes, lowering healthcare costs and increasing productivity.
- Energy Access: Large-scale solar projects can improve energy access in remote or underserved areas, fostering economic development and improving quality of life.
| Benefit | Description | Economic Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions | Mitigates climate change impacts | Lower economic costs of climate adaptation |
| Improved Public Health | Better health outcomes from reduced pollution | Lower healthcare costs, increased productivity |
| Energy Access | Improved access in remote areas | Economic development, quality of life improvement |
Conclusion
The economic impacts of large-scale solar energy system projects are profound and multifaceted. From job creation and reduced energy costs to stimulating local economies and fostering economic diversification, these projects contribute significantly to economic growth and stability. Moreover, the environmental and social benefits of solar energy further enhance its economic value, making large-scale solar energy system cornerstone of sustainable development. As the world continues to transition towards renewable energy, the economic advantages of large-scale solar energy system will play a critical role in shaping a prosperous and sustainable future.
